Snafi
Snafi dosages: 20 mg
Snafi packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills

Order snafi with mastercard
Second-order neurones arising from the nucleus solitarius cross the midline erectile dysfunction medication south africa buy generic snafi 20 mg on-line, and many ascend through the brain stem in the dorsomedial part of the medial lemniscus. They terminate in the medial part of the ventral posteromedial nucleus of the thalamus. From the ventral posteromedial nucleus, third-order neurones project through the internal capsule to the anteroinferior part of the sensory cortex and to the limen insulae. Other ascending projections to the hypothalamus have been described that may represent the pathway by which gustatory information reaches the limbic system. The axons constitute the auditory component of the vestibulocochlear nerve, which enters the brain stem at the cerebellopontine angle. Afferent fibres bifurcate and terminate in the dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei. The dorsal cochlear nucleus projects via the dorsal acoustic stria to the contralateral inferior colliculus. The ventral cochlear nucleus projects via the trapezoid body or the intermediate acoustic stria to relay centres in the superior olivary complex, the nuclei of the lateral lemniscus or the inferior colliculus. The superior olivary complex is dominated by the medial superior olivary nucleus, which receives direct input from the ventral cochlear nucleus on both sides, and is involved in localization of sound by measuring the time difference between afferent impulses arriving from the two ears. The dorsal cortex lies dorsomedially, and the external cortex lies ventromedially. They converge in the central nucleus, which projects to the ventral division of the medial geniculate body of the thalamus. It projects to the medial division of the medial geniculate body and, together with the central nucleus, also projects to olivocochlear cells in the superior olivary complex and to cells in the cochlear nuclei. The dorsal cortex receives an input from the auditory cortex and projects to the dorsal division of the medial geniculate body. Connections also run from the nucleus of the lateral lemniscus to the deep part of the superior colliculus, to coordinate auditory and visual responses. The ascending auditory pathway crosses the midline at several points both below and at the level of the inferior colliculus. However, the input to the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus and higher centres has a clear contralateral dominance. The medial geniculate body is connected reciprocally to the primary auditory cortex, which is located in the superior temporal gyrus, buried in the lateral fissure. They also establish important connections for reflex movements governing the equilibrium of the body and the fixity of gaze. Functionally, the vestibular apparatus is customarily divided into two components: the kinetic labyrinth, which provides information about acceleration and deceleration of the head, and the static labyrinth, which detects the orientation of the head in relation to the pull of gravity. In terms of structure, the kinetic labyrinth consists of the semicircular canals and their ampullary cristae, and the static labyrinth consists of the maculae of the utricle and saccule. However, the saccular macula also responds to head movements, and both maculae can be stimulated by low-frequency sound and may therefore have minor auditory functions.
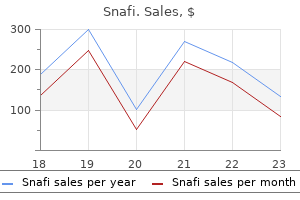
Order line snafi
Renal function: a freshly spun urine sample will often show red cell casts but is rarely assessed these days erectile dysfunction massage buy snafi 20 mg mastercard. Colour Doppler examination is a very sensitive means of detecting new valvular regurgitation, which may be an important sign of endocarditis. Transoesophageal echocardiography allows better definition of valvular involvement and is more likely to detect vegetations. Perhaps more importantly, it is much more likely to detect such complications as valve abscesses. The names of the viridans streptococci are subject to frequent revision, but current important types for endocarditis include S. Look for signs of a prosthetic valve and for scars that may be present from previous valvotomy or repair operations. Nevertheless, a mobile mass attached to a valve in a patient with positive blood cultures makes the diagnosis of endocarditis almost certain. It also enables detection of left ventricular enlargement, which suggests haemodynamic compromise. Serial echocardiograms allow assessment of the treatment of endocarditis and help with the decision about the timing of possible surgery. More detailed analysis of the heart is possible with transoesophageal echocardiography, which is now routine in cases of endocarditis. It enables smaller vegetations to be identified, as well as complications, such as valve ring abscesses. Evidence of endocardial involvement: echocardiogram showing a mobile intracardiac mass on a valve or in the path of a regurgitant jet, or an abscess or new valvular regurgitation. Single positive blood culture for Coxiella burnettii or anti-phase IgG antibody > 1: 800. Two major criteria, one major and three minor, or five minor criteria secure the diagnosis. Early infection is acquired at operation; late infection occurs from another source. Currently, more than 70% of patients with endogenous infection survive, as do 50% of those with a prosthetic valve infection. Prophylaxis Confusion between rheumatic fever and endocarditis prophylaxis is common. Rheumatic fever prophylaxis consists of long-term, low-dose antibiotic administration.
Syndromes
- Knee x-ray
- Side effects of chemotherapy
- Idiopathic aplastic anemia
- Sweating
- Does the breath smell like ammonia or urine?
- Progesterone level
Proven 20 mg snafi
Enquire about symptoms of thyroid excess or thyroid hormone replacement (thyroxine) impotence hernia cheap snafi 20 mg buy line. Note that X-rays are insensitive for bone loss, because a substantial reduction of bone mass must occur before changes will be visible on the X-rays. Medications that cause osteoporosis include steroids, alcohol, heparin, thyroxine over-replacement, anticonvulsants (by affecting vitamin D metabolism), and cyclosporin. Phosphate unavailability caused by phosphate-binding antacids, hereditary hypophosphataemia, tumour-induced osteomalacia. Consider this in all patients with reduced bone density and especially in those with bone pain or muscle weakness. Risk factors include lack of exposure to sunlight (nursing home residents), fear of sunburn, dark skin and modest dress. Enquire about a poor diet (a low-fat diet often limits calcium intake) or inadequate sunlight exposure if the patient is a nursing home resident, or has a history of renal disease or phenytoin use (all risk factors for osteomalacia) (Tables 10. This is the number of standard deviations by which the measured bone density falls below the average for a young normal person of the same sex. The vertebral trabeculae become more prominent with the loss of horizontal trabeculae. Other characteristic abnormalities may include a triangular (trefoil) pelvis and biconcave collapsed vertebrae. If there is secondary hyperparathyroidism present with osteomalacia, then bone cysts, erosion of the distal ends of the clavicles and subperiosteal resorption in the phalanges may be seen. In difficult cases, an iliac crest bone biopsy with double tetracycline labelling can help to distinguish osteoporosis from osteomalacia. Consider undertaking tests for secondary causes of osteoporosis if the clinical picture suggests this may be helpful. Generally recommend ceasing smoking, avoiding excess alcohol consumption: institute fall prevention measures and prescribe regular weight-bearing exercise. Bisphosphonates (risendronate and alendronate): these drugs increase bone mineral density in postmenopausal women and have been shown to reduce the risk of fracture for postmenopausal women with osteoporosis by 50%. Intravenous treatment should be avoided in people with moderate or severe chronic kidney disease.
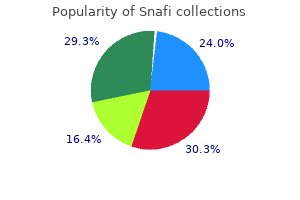
Order generic snafi pills
Layer 4: Outer Nuclear Layer - this consists of several tiers of rod and cone cell bodies and their nuclei impotence and smoking order online snafi, the cone nuclei lying outermost. Mingled with these are the outer and inner fibres from the same cell bodies, directed outward to the bases of inner segments and inward toward the outer plexiform layer. Layer 5: Outer Plexiform Layer - this is a region of complex synaptic arrangements between the processes of cells whose cell bodies lie in the adjacent layers. The outer plexiform layer contains the synaptic processes of rod and cone cells, bipolar cells, horizontal cells and some interplexiform cells (which, in this account, are grouped with the amacrines). Horizontal cell nuclei form the outermost zone; then, in sequence inward, are the nuclei and cell bodies of bipolar cells, radial glial cells and the outer set of amacrine cells, including the interplexiform cells whose dendrites cross this layer. Layer 7: Inner Plexiform Layer - this is divisible into three layers, depending on the types of contact that occur. Its inner regions consist of the cell bodies, nuclei and initial segments of retinal ganglion cells of various classes. Layer 9: Nerve Fibre Layer - this contains the unmyelinated axons of retinal ganglion cells. It forms a zone of variable thickness over the inner retinal surface and is the only component of the retina at the point where the fibres pass into the nerve at the optic disc. The inner aspect of this layer contains the nuclei and processes of astrocytes, which, together with radial glial cells, ensheathe the nerve fibres. Between the nerve fibre layer and the ganglion cells is another narrow innermost plexiform layer, where neuronal processes make synaptic contact with axon hillocks and initial segments of ganglion cells. Layer 10: Internal Limiting Membrane - this is a glial boundary between the retina and the vitreous body. It is formed by the end-feet of radial glial cells and astrocytes and is separated from the vitreous body by a basal lamina. Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells - the retinal pigment epithelial cells are low cuboidal cells that form a single continuous layer, extending from the periphery of the optic disc to the ora serrata and continue from there into the ciliary epithelium. Apically (toward the rods and cones), the cells bear long (5 to 7 mm) microvilli that contact or project between the outer ends of rod and cone processes. The tips of rod outer segments are deeply inserted into invaginations in the apical membrane. The attachments are unsupported by junctional complexes and are broken in the clinical condition of retinal detachment arising from trauma or disease processes. Pigment epithelial cells play a major role in the turnover of rod and cone photoreceptive components. Their cytoplasm contains the phagocytosed ends of rods and cones undergoing lysosomal destruction.
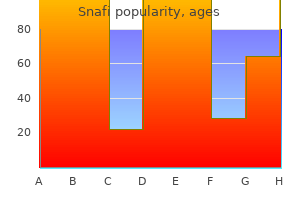
Buy cheap snafi line
His gait is shuffling impotence and age order 20 mg snafi mastercard, with a decidedly propulsive and festinating quality (marche a petit pas). Section through the midbrain demonstrating depigmentation in the substantia nigra due to loss of melanin (arrow). Anatomical changes may in fact be much more widespread, involving a variety of brain stem nuclei as well as the cerebral cortex. Although these drugs usually provide good symptomatic relief for many years, levodopa and, to a lesser extent, dopamine agonists eventually lead to the development of motor complications, including dyskinesias. This leads to physiological inhibition of the subthalamic nucleus by overactive pallidosubthalamic neurones. Underactivity of the subthalamic nucleus removes the excitatory drive from medial pallidal neurones, which are known to be underactive in dyskinesias. Although it is true that underactivity of the medial globus pallidus is associated with dyskinesias, it is also known that lesions of the globus pallidus alleviate them. This suggests that the dynamic aspects of pallidal and nigral efferent activity are important factors in the generation of dyskinesia. Another manifestation of basal ganglia dysfunction is dystonia, which is characterized by increased muscle tone and abnormal postures. Like dyskinesia, it is probably caused by underactivity of basal ganglia output, so deep brain stimulation of the globus pallidus may be beneficial. There is evidence that dysfunction of the basal ganglia is involved in other complex, less well-understood behavioural disorders. In animal experiments, lesions of the basal ganglia, especially of the caudate nucleus, induce uncontrollable hyperactivity. In this respect, it may be significant that the basal ganglia, besides receiving connections from the frontal lobe and limbic cortices, also have an ascending influence on the prefrontal and cingulate cortices through the substantia nigra pars reticulata and dorsomedial and ventromedial thalamus. The globus pallidus and thalamus were favoured targets for chemical or thermal lesions. Pallidotomy and thalamotomy often improved rigidity and tremor, but they produced little consistent beneficial effect on akinesia. This finding raised the possibility that the subthalamic nucleus could be used as a clinical target. Indeed, lesions of the subthalamic nucleus in humans exert a powerful effect in alleviating tremor, rigidity and bradykinesia; however, the likelihood of side effects is not trivial (the subthalamic nucleus is a small structure wrapped by fibres of passage and close to the hypothalamus and internal capsule). The patient has played the piano 6 to 8 hours a day, often 7 days a week, since late childhood. He had a successful career as a performer and master-level teacher in a school for performing artists. Three years before assessment, he began complaining of difficulty controlling the movement of his left arm, but only when playing the piano; this was characterized by involuntary pronation of the left forearm and posturing of the hand.
Purchase 20 mg snafi with mastercard
The preliminary testing of hearing and balance is possible only if the patient is conscious and responsive to verbal commands erectile dysfunction workup cheap snafi 20 mg online. Olfactory testing to exclude anosmia often cannot be performed in the acute stage but should be done at a later time. For medicolegal reasons, it should always precede surgical treatment (see Olfactometry, p. With an isolated central midfacial fracture that does not involve the anterior skull base, surgical treatment of the maxilla should be provided by a maxillofacial surgeon to ensure the restoration of normal occlusion. The urgency of surgical intervention for a frontobasal fracture is shown in Table 3. The choice depends on the individual situation and is made in consultation with the other involved specialties. The coronal scans show air in the cranial cavity (c) and a fracture of the ethmoid roof (d) (arrow). Although rhinitis and sinusitis are on a continuum owing to the special anatomical and physiological relationships of the nose and paranasal sinuses (see 1. The various forms of rhinitis are discussed according to their etiology, noting that the great majority of cases seen in clinical practice are mixed forms that have more than one cause. Inflammatory diseases of the nasal skin usually have a bacterial cause and may be manifested on the exposed skin and the dermal appendages. Although these diseases fall primarily within the scope of dermatology, the otolaryngologist is frequently faced with inflammations of this type that can lead to lifethreatening complications unless adequately treated. Inflammation of the nasal cavity (rhinitis) predominantly involves the nasal mucosa. While it can have a variety of causes, it always exhibits a more or less Purulent Inflammations of the Hair Follicles Pyodermas of the hair follicles are common purulent inflammations that can occur at almost any age. If the infection spreads to deeper tissues and forms a central core of purulent liquefaction, it is called a furuncle. Symptoms: Nasal furuncles present as painful, tender, erythematous swellings about the nasal tip and nares. Also, the upper lip should be moved as little as possible, and so the patient should be placed on a liquid or semisolid diet and speak as little as possible. An essential goal of these measures is to prevent the potentially lethal complication of intracranial spread. Complications: Inadequate treatment or manipulations of the nasal furuncle itself can result in hematogenous spread to intracranial structures, since the veins of the nose and upper lip drain via the angular and ophthalmic veins into the cavernous sinus. If facial erysipelas spreads lateral to the nose and about the eyelids, there is a risk of intracranial involvement by hematogenous spread of the causative organisms, as with a nasal furuncle. Treatment: the treatment of choice is the parenteral administration of penicillin.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Epa (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)). Snafi.
- Pregnancy-related high blood pressure (eclampsia).
- Psoriasis.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Epa (eicosapentaenoic Acid) work?
- What is Epa (eicosapentaenoic Acid)?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What other names is Epa (eicosapentaenoic Acid) known by?
- For wound healing, when used with RNA and L-arginine following surgery.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96955
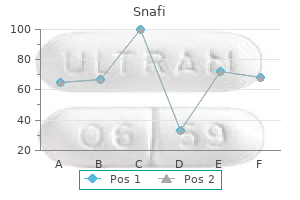
Snafi 20 mg sale
The lumbar plexus lies deep within psoas major erectile dysfunction 37 years old 20 mg snafi buy otc, anterior to the transverse processes of the first three lumbar vertebrae. The sacral plexus lies in the pelvis on the anterior surface of piriformis, deep to the pelvic fascia, which separates it from the inferior gluteal and pudendal vessels. The lumbosacral trunk (L4 and L5) emerges medial to psoas major and lies on the ala of the sacrum before crossing the pelvic brim to join the anterior primary ramus of S1. In the leg it is the nerve of the posterior compartment and descends with the posterior tibial vessels to lie between the heel and the medial malleolus. It ends beneath the flexor retinaculum by dividing into the medial and lateral plantar nerves. Its cutaneous area of supply, including its terminal branches, includes the back of the calf, the whole of the sole, the lateral border of the foot and the medial and lateral sides of the heel. It arises from the posterior divisions of the second to fourth lumbar ventral rami, descends through psoas major and emerges on its lateral border to pass between psoas and iliacus and enter the thigh behind the inguinal ligament and lateral to the femoral sheath. Its terminal branches form in the femoral triangle approximately 2 cm distal to the inguinal ligament. In the abdomen the nerve supplies small branches to iliacus and a branch to the proximal part of the femoral artery. It subsequently supplies a large cutaneous area on the anterior and medial thigh and medial leg and foot and gives articular branches to the hip and knee. It arises from the anterior divisions of the second to fourth lumbar ventral rami, descends through psoas major and emerges from its medial border at the pelvic brim. It crosses the sacroiliac joint behind the common iliac artery and lateral to the internal iliac vessels, runs along the lateral pelvic wall on obturator internus and enters the thigh through the upper part of the obturator foramen. Near the foramen it divides into anterior and posterior branches, separated at first by part of obturator externus and more distally by adductor brevis. It gives articular branches to the hip and knee and may supply skin on the medial thigh and leg. The sciatic nerve is the nerve of the posterior compartment of the thigh and, via its major branches, of all the compartments of the lower leg and foot. Formed in the pelvis from the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar to third sacral spinal nerves, it is 2 cm wide at its origin and is the thickest nerve in the body. It enters the lower limb via the greater sciatic foramen below piriformis and descends between the greater trochanter and the ischial tuberosity. The nerve passes along the back of the thigh, where it is crossed by the long head of biceps femoris, and divides into the tibial and common peroneal (fibular) nerves proximal to the knee. The actual level of division is very variable because the tibial and common peroneal nerves are structurally separate and only loosely connected throughout their proximal course.
Snafi 20 mg amex
Routine admission to hospital three or four times a year for intensive physiotherapy and intravenous antibiotics and bronchodilators (a tuneup) can be advantageous erectile dysfunction test video generic snafi 20 mg on line. Ask whether the patient knows about or belongs to the local cystic fibrosis association and whether he or she has been in touch with other affected patients. Try to find out tactfully whether the patient understands the inheritance of the disease; male patients may know that azoospermia is usually present owing to destruc tion of the vas deferens by abnormal secretions (95%). Eighty per cent of women are fertile, and pregnancy and breastfeeding are often successful. Find out in some detail how a young adult copes with this debilitating and lifeshortening disease. By the age of 10 years, Pseudomonas is the main pathogen in most patients, but usually it does not cause systemic infection. A full blood count should be asked for to look for anaemia, which may be caused by malabsorption or chronic disease; the white cell count may indicate acute infec tion. Mucous plugs may be seen in onethird and atelectasis occurs in just over 10% of patients. Look also for pneumothorax and pleural changes at the site of previous pneumothoraces or pleurodesis. Estimate forced expiratory time and examine the chest, listening particularly for crackles, wheezes and reduced breath sounds. Examine the abdomen for signs of faecal loading, especially in the right iliac fossa, organomegaly, such as hepatomegaly, or hard liver edge, as in cirrhosis, splenomegaly and other signs of portal hypertension as well as sites of insulin injections in the abdominal wall, also scars of previous surgery including those for meconium ileus at birth. Intravenous antibiotics may be indicated for acute exacerbations of pulmonary disease if these are severe or fail to respond to oral antibiotic treatment. Malabsorption may require aggressive treatment with pancreatic enzyme supple ments, including lipase, and frequent small meals as well as vitamin supplements. Doublelung transplantation is now an accepted, although still uncommon, treat ment in patients with advanced disease. The patient may remember having to give early morning sputum specimens on a number of occasions or having had a bronchocospy with washings, if sputum was not being produced. Bronchoscopy may have been per formed to exclude other causes of an abnormal chest Xray, such as carcinoma of the lung. A tuberculin (Mantoux) skin test may have been performed as a screening test or to support the diagnosis where cultures have been negative.
Purchase snafi 20 mg online
Both nasal cavities should always be packed in order to produce adequate counterpressure zocor impotence buy 20 mg snafi with amex. Balloon catheters should be progressively deflated starting on the second day; otherwise they may cause irreversible tissue necrosis. The left middle turbinate and right inferior turbinate are visible in the background. The ligation or angiographic embolization of a larger arterial trunk may be considered as a last recourse. When this is done, the source of the bleeding must be accurately identified since the nasal lining is supplied by various arteries. Prevention of recurrent bleeding: Besides the conservative treatments noted above, some causes of epistaxis require surgical treatment since nasal packing alone is of only temporary, symptomatic benefit (3. In diseases that are associated with vascular changes, such as Osler disease, telangiectatic areas on the septal mucosa can be treated with a surgical laser. The figure shows numerous punctate telangiectasias in the left nasal cavity in Osler disease. In a Saunders dermoplasty, for example, the telangiectatic septal mucosa is resected and replaced with a free skin graft. This deals with necessary diagnostic measures and also reviews the most important techniques of facial plastic surgery. Facial soft-tissue injuries are still a common occurrence in recreational and traffic accidents. Poor cosmetic results are particularly Diagnosis Before a traumatic facial wound is treated, possible coexisting fractures should be excluded by clinical examination and, if necessary, by imaging studies such as biplane skull films, standard sinus projections. Especially with bite wounds, a smear should be taken for microbiologic examination. In the interest of maximum tissue preservation, only tissues that are definitely necrotic should be debrided from facial wounds. Wound margins should never be reapproximated under tension, as this would result in aesthetic and functional deficits such as incomplete eyelid closure. In most soft-tissue injuries to the nose, adequate treatment consists of primary reapproximation and suturing of the wound margins. The techniques described below are also useful for revising a functionally and/or aesthetically objectionable result, such as lengthening a heavily contracted scar. The wound area should be broadly undermined to eliminate tension on the reapproximated wound margins.
Snafi 20 mg order visa
In contrast to the sympathetic system erectile dysfunction san antonio cheap 20 mg snafi mastercard, postganglionic parasympathetic neurones are cholinergic. Postganglionic fibres, which are thinly myelinated, travel in the short ciliary nerves that pierce the sclera to run forward in the perichoroidal space to the 371 Chapter 21 Transverse process, C. It has been suggested that the lesion involves preganglionic fibres originating at T2 and T3. Occasionally, segmental autonomic dysfunction is observed in an upper extremity as well. A relationship to Ross syndrome (segmental anhidrosis, tonic pupils and hyporeflexia) has also been suggested. A 55-year-old woman presents with a 3-month history of exercise-induced anhidrosis and lack of flushing on the left side of the face, with normal autonomic responses on the right. Provocative manoeuvres such as controlled exercise confirm loss of flushing on the left side of the face, as described historically, along with hemifacial anhidrosis. Discussion: Asymmetric facial flushing and sweating suggest a diagnosis of harlequin syndrome, with asymmetric involvement of vasomotor and sudomotor fibres. Their activation mediates accommodation of the eye to near objects and pupillary constriction. The facial nerve contains preganglionic parasympathetic axons of neurones with their somata in the superior salivatory nucleus (see Ch. The fibres emerge from the brain stem in the nervus intermedius, leave the main facial nerve trunk above the stylomastoid foramen and travel in the chorda tympani, which subsequently joins the lingual nerve (see Ch. In this way, preganglionic fibres are conveyed to the submandibular ganglion, where they synapse on ganglionic neurones. Postganglionic fibres innervate the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands and are said to travel in the lingual nerve. Some preganglionic fibres may synapse around cells in the hilum of the submandibular gland. Stimulation of the chorda tympani dilates the arterioles in both glands, in addition to having a direct secretomotor effect. The facial nerve also contains efferent parasympathetic lacrimal secretomotor axons, which travel in its greater petrosal branch and then via the nerve of the pterygoid canal, to relay in the pterygopalatine ganglion. Postganglionic axons are thought to travel by the zygomatic nerve to the lacrimal gland and by ganglionic branches to the nasal and palatal glands. The glossopharyngeal nerve contains preganglionic parasympathetic secretomotor fibres for the parotid gland. These originate in the inferior salivatory nucleus and travel in the glossopharyngeal nerve and its tympanic branch. On examination, he is found to have bilateral disc oedema (papilloedema), with paresis of up-gaze. Magnetic resonance imaging reveals a tumour involving the dorsal midbrain (collicular plate) that is also responsible for obstructive hydrocephalus.
Killian, 33 years: The patient was clinically doing well, and this was thought to represent benign pneumatosis.
Iomar, 46 years: Articulation is slurred (cerebellar dysarthria) because of faulty coordination of the groups of muscles that move the lips, tongue and soft palate and act on the temporomandibular joint.
Navaras, 54 years: Changes in these regions may include firm infiltrates in the nasal mucosa that resemble a nasal furuncle.
Trano, 47 years: The 1st needle remains in place so that additional contrast can be injected if needed.
Grubuz, 63 years: Its effect on cholesterol levels is substantial, although not as great as that of the statins.
9 of 10 - Review by V. Varek
Votes: 60 votes
Total customer reviews: 60