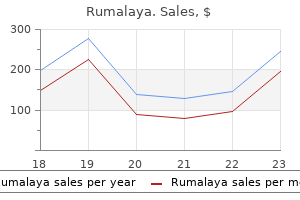
Rumalaya
Rumalaya dosages: 60 pills
Rumalaya packs: 1 bottles, 2 bottles, 3 bottles, 4 bottles, 5 bottles, 6 bottles, 7 bottles, 8 bottles, 9 bottles, 10 bottles

Discount rumalaya 60 pills free shipping
Usually treatment 02 academy rumalaya 60 pills buy on-line, the examiner starts by holding the sides of the great toe and asking the patient to report when it is being moved upward and downward by a few millimeters. Light touch is often not useful to test in isolation because it relies on a combination of pathways. Finger-to-nose testing can identify dysmetria (inaccuracy of targeting) or types of tremor in the arms. To test axial abnormalities, the patient can be asked to sit upright and unsupported, with the eyes closed. Rapid alternating movements, rhythmic finger tapping, and heel tapping are particularly sensitive to coordination problems. Dysdiadochokinesis is the term used to describe difficulty with rapid alternating movements. Normal gait requires the proper functioning of many different aspects of the nervous system, so it is one of the most sensitive ways to detect an abnormality. Furthermore, some patterns of gait abnormality herald the presence of specific disorders. Routinely, posture, base, initiation, stride length, turning, arm swing, and overall balance are considered. The patient with a normal base, or stance, maintains the feet at about hip-width apart. Shortstepped and shuffling gaits are characterized by decreased stride length and limited excursion of the feet from the ground. The arms normally swing fully in the opposite direction from their respective legs during ambulation. Ataxia can be brought out most obviously by having the patient attempt to walk heel to toe (tandem). A Romberg sign is present when the patient maintains a steady stance with feet together and eyes open but sways and falls with feet together and eyes closed; its presence usually implies a deficit of joint position sense, not cerebellar dysfunction. Base, initiation, stride length, turning, arm swing, and the ability to perform tandem gait should be assessed. It is produced by the choroid plexus of the ventricles and is absorbed through the villi of the arachnoid granulations that project into the dural venous sinuses. Ideally, a pillow should be placed between the legs, and the patient should lie on the edge of the bed where there is better support to keep the back straight. The needle is directed slightly rostrally to coincide with the downward angulation of the spinous processes. The glucose content is about two-thirds that of blood, and it contains up to 40 to 50 mg/dL protein.
Cheap rumalaya 60 pills online
In acute bacterial meningitis symptoms stomach cancer order rumalaya 60 pills without prescription, the lateral ventricles are often small and may be tapped only with considerable difficulty. Indeed, ventricular puncture with ultrasound guidance is recommended if the ventricles are small. The subsequent cavitation along the needle track relates most probably to the combination of disruption of edematous, poorly myelinated, readily separable brain parenchyma and transmission of elevated intraventricular pressure. In the large, older series studied by Lorber and Emery,261 the approximately 50% of infants subjected to multiple ventricular punctures for the treatment of bacterial ventriculitis subsequently developed cystic cavities, demonstrable by ventriculography, at the sites of the taps. The incidence of significant cavity formation in infants with ventriculitis after a single tap is unknown but is probably relatively low. Although small diverticula from the lateral ventricles into the needle track are common after single taps, major cavity formation is very unusual. Note dense linear strands of echogenic material in the lateral ventricles (arrows), apparently attached to the ependymal surface, and diffuse low-level echoes in both lateral ventricles. Note the collection of intraventricular material apparently attached to the ventricular wall (arrow). Note abnormal intraventricular echoes (arrow) apparently contiguous with ventricular surface and choroid plexus. This coronal scan obtained from an infant with Escherichia coli meningitis shows an area of increased echogenicity (arrows) in the distribution of the middle cerebral artery, consistent with an infarction. There were also three cases with a Serratia meningitis, and these infants had large parenchymal abscesses. Note on the coronal scan (A) bilateral symmetrical areas of involvement in the region of the basal ganglia (putamen and globus pallidus) (arrows). On the parasagittal scan (B), the involvement is seen not only in basal ganglia (small arrows) but also in thalamus (large arrow). Therapy is not perfect; indeed, in certain types of meningitis it is often inadequate. In any assessment of outcome, it is necessary to recognize the inherent difficulty in extrapolating to a given infant with meningitis data that are generalized from large-scale studies, which are often based on populations with a broad spectrum of bacterial causes and followed for relatively brief durations. Similarly, deficits in certain sensory discriminations, particularly hearing, may be difficult to detect in infancy. The second reason for the importance of duration of follow-up relates to the not infrequent transient nature of neurological deficits after neonatal meningitis. Infants may improve for many months, and deficits that were striking shortly after the neonatal period may decrease markedly in severity or may disappear totally. The relation of these observations to the plasticity of developing brain is an interesting topic for future research. Nevertheless, with these reservations, useful estimates of prognosis can be derived from available data (see next sections). The overall fatality rate has declined in recent years to approximately 10% to 15%, with slightly higher rates for early-onset disease or premature infants and slightly lower rates for later-onset cases or term infants. Fifty percent of survivors are normal; approximately 40% have mild or moderate sequelae, and 10% to 20% exhibit severe deficits.
Order 60 pills rumalaya mastercard
This forms a complete trunk that drains areas of the head dorsal to the primary head vein as far as the jugular foramen medicine you cannot take with grapefruit rumalaya 60 pills lowest price, where it is continuous with the internal jugular vein. Eventually, a single channel forms in the anterior portions caused by the selection and enlargement of the most favorable vein and the disappearance of the others. The deep system consists of the lateral, straight, and sigmoid sinuses, together with the deeper draining cortical veins. It begins near the crista galli, a few millimeters posterior to the foramen cecum, and receives the primary tributaries from the cortical veins of the frontal lobes, the ascending frontal veins. This connection may provide a pathway for the intracranial spread of sinunasal infectious or tumor, as well as provide an anatomic substratum for the genesis of dural arteriovenous fistulae of the anterior cranial fossa. It also communicates by small orifices with irregular venous lacunae situated in the dura mater near the sinus. Fine fibrous bands cross them, and numerous arachnoid granulations project into them. Several cadaveric studies have shown that no two specimens are similar in the placements of chordae Willisii. They concluded similarly that the valvelike chordae half cover most of the vein orifices in the sinus to preclude backflow of blood into the veins and ensure they drain to the sinus. They determined that these chordae crossed the lumen at the sinus at different angles, were located in the lumen either centrally or peripherally, and varied in length and thickness. The numbers of trabecular projections related to veins were similar on both sides, whereas those unrelated to veins were more abundant on the left, which asymmetry would favor a more intense blood flow on the right. He also observed that longitudinal lamellae generally are triangular or square with concave frontal and occipital borders. These accessory cords formed networks that occupied the entrances to the venous lacunae. In one case, they were able to demonstrate compensatory drainage via the inferior sagittal sinus via an interhemispheric frontal vein. For example, during the last trimester of pregnancy and after delivery, the risk of sinus thrombosis increases significantly, with a frequency of approximately 12 cases of peripartum and postpartum sinus thrombosis per 100,000 deliveries. Additional evidence of this is found in computations of the sex ratio in cases of sinus thrombosis. Superior sagittal sinus occlusion can lead to the development of intracranial hypertension. Normal activity of the clotting factor recovers after reaching the euthyroid state.
Rumalaya 60 pills buy line
Membrane channels are made up of proteins symptoms of pregnancy buy generic rumalaya 60 pills, so the gates open or close as proteins making up the channel change in conformation. Ion channels involved in neurotransmission have gates that are opened by either an electrical signal or the binding of a molecule. Ion channels cause major changes in the concentration of ions within cells when the channel opens. When the number of ions and electrical charge outside of a membrane do not equal the number of ions and charge inside, the membrane is said to be polarized. Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters are small molecules made by neurons to cross the gap of the synaptic cleft. In the absence of a signal, neurotransmitters are stored in small membrane sacs called synaptic vesicles near the axon terminals. The arrival of the action potential at an axon terminal is a signal to vesicles containing the neurotransmitters to fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents into the synaptic cleft. When acetylcholine is released, it diffuses across the synaptic cleft to the muscle cell, whose membrane has ion channels. Acetylcholine molecules bind to these channels and cause them to open, causing depolarization of the muscle cell membrane. This triggers a series of changes within the muscle cells that stimulates them to contract, causing movement. After acetylcholine opens ion channel gates, it is broken down quickly by an enzyme of the muscle cells called acetylcholine esterase. The choline is taken back up by the neuron and reused in making more acetylcholine. So, muscle movement is dependent on the delivery of neurotransmitters from the axon of a neuron nearby. Anything that blocks this neuromuscular signaling pathway blocks muscular contraction. Some snake toxins block the acetylcholine receptors on muscle cells and prevent transmission of the nerve signal. Unless the victims of snakebite receive prompt treatment to counter the effects of such neurotoxins, they will die when the toxins immobilize the muscles involved in breathing. In addition to communicating with cells, such as muscle cells, using neurotransmitters, neurons can also communicate with each other. The axon of the neuron that is sending the message releases neurotransmitter molecules.
Order rumalaya
Carotid artery stenting is an alternative to endarterectomy but might result in a higher risk of periprocedural stroke medicine hat purchase cheap rumalaya online. Prognosis after transient monocular blindness associated with carotid-artery stenosis. Clinical features of transient monocular blindness and the likelihood of atherosclerotic lesions of the internal carotid artery. He has seen multiple ophthalmologists, but eye examinations have not identified a cause for his complaints. While the lack of objective signs increases suspicion for a disorder of higher visual function (see Case 13) or perhaps nonorganic vision loss (see Case 17), ophthalmic causes must also be considered. In most patients with uncorrected refractive error, visual acuity improves to 20/20 when it is checked while the patient is looking through a pinhole device. Visual acuity should be measured at both distance and near; uncorrected presbyopia is a common cause of blurred vision at near and can be easily treated with over-the-counter reading glasses. When refractive error is the likely cause of decreased visual acuity, consultation with an optometrist or ophthalmologist is indicated for refraction. When there is irregular astigmatism, an abnormality of corneal shape or structure. In such cases, special refractive techniques, such as streak retinoscopy, and corneal topography may be needed for definitive diagnosis. As there was no improvement in visual acuity with pinhole for the patient described in this scenario, other etiologies of vision loss must then be considered. The optic disc can initially look normal in patients with inflammatory and compressive optic neuropathies. Formal visual field testing should also be obtained to characterize the pattern of the visual field loss; toxic and nutritional optic neuropathies typically give central or ceco-central scotomas, which can be difficult to detect on confrontation. Funduscopic examination usually shows obvious abnormalities in patients with retinal diseases causing vision loss. However, certain "occult" retinal diseases may not manifest with funduscopic abnormalities, yet they can produce characteristic visual symptoms and visual field defects. Diseases affecting the rod photoreceptors produce difficulty with vision in dim lighting conditions. When a patient reports symptoms that suggest photoreceptor disease, further investigations to evaluate for photoreceptor dysfunction are indicated. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography may show structural changes in the outer retina where the photoreceptors are located. However, these changes are often very subtle or absent in patients with early or mild disease. The patient described in this scenario reports progressive vision loss in both eyes over a decade. His vision is clearer in dim lighting and he has dyschromatopsia, suggesting cone disease.
Cheap rumalaya 60 pills buy on line
In addition to insight into language function medications 247 discount rumalaya 60 pills on-line, these details provide insight into how well patients can plan and organize information. To assess verbal comprehension, check to see if patients can follow spoken midline, appendicular, and cross-body commands. One can check for apraxia by asking patients to pantomime a learned motor task-optimally one that requires use of both hands, for example, cutting a loaf of bread. Example of a complex figure to be copied by the patient as test of visuospatial function. Other tests of frontal lobe function include learning and then repeating a simple motor sequence of hand postures. Another test of appropriate inhibition, the go/no go test, comprises tapping the table when only one letter. If cognitive impairment emerges as a concern, the examiner should consider looking for the presence of primitive reflexes, which are signs of "frontal release" or disinhibition. Examples include the palmo-mental, snout, and rooting reflexes; of note, the examiner should be careful not to overinterpret these reflexes, because they can occur in normal subjects with age or may not be relevant to the presenting problem. Memory, language, calculation, praxis, visuospatial, and frontal lobe function are other key elements of the mental status exam that can suggest focal brain lesions. When patients report alterations in the ability to smell, each nostril should be tested separately. Muscles of mastication (V) are tested by assessing the strength of jaw opening and palpating the contraction of the masseter when the jaw is clenched. Facial sensation can be tested to all modalities over the forehead (V1), cheek (V2), and jaw (V3) regions. Though uncommonly tested, taste over the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is mediated by this nerve and can be evaluated with sugar or another nonnoxious stimulus. Failure of the right palate to elevate implies pathology of the right glossopharyngeal nerve. Key elements of the cranial nerve exam include assessment of vision and eye movements, facial movement and sensation, and movements of the palate and tongue. Abnormalities of tone such as spasticity and rigidity are discussed in subsequent chapters. The examiner lifts the leg up suddenly under the knee; in the presence of increased tone, the heel comes off the bed. In rigid limbs, the examiner can sense increased resistance throughout the passive movements, but spasticity is speed dependent, with abnormalities emerging with quick movements. A pronator drift may be observed in an arm held supinated and extended in front of the body.

Buy online rumalaya
Variations of the cerebral dural sinuses at the torcular Herophili: importance in radical neck dissection nail treatment generic rumalaya 60 pills mastercard. Malignant squamous degeneration of a cerebellopontine angle epidermoid tumor: case report. A reliable method of classification can assist a neurosurgeon to plan a safe surgical corridor and to prevent potential morbidities associated with sacrifice or inadvertent injury of this category of venous sinuses. Tentorial sinuses are grossly categorized into two constant, paired, bilateral but mostly asymmetric venous channels. This group of sinuses arises within the lateral part of the tentorium cerebelli, and after pursuing a lateral course, it drains into the terminal segment of the transverse sinus and transverse-sigmoid junction on each side. This group normally courses medially and empties into the straight sinus and transverse sinus confluence. This group of sinuses can be affected with other pathologies that normally affect other sinuses, such as tumors and vascular anomalies. This structure has a superior attached portion and an inferior free part housing the superior and inferior sagittal sinuses, respectively. The extant medical literature has scant statements regarding other potential veins within the falx cerebri. Crosby1 had stated that the inferior sagittal sinus "begins in about the middle of the border of the falx with the convergence of the falcial plexus of veins. This latter configuration, not to be confused with a falcine venous plexus, most likely represents a persistent falcine sinus (to be discussed later). Generally, most falcine veins in the falx cerebri were found in its posterior one-third and within this posterior one-third, in the inferior two-thirds. An important distinction should be made between the rare persistent fetal falcine sinus and the falcine venous plexus. The falcine sinus is a normal in utero venous structure located in the falx cerebri that normally involutes before birth. Surgical ramifications of these findings center mainly around approaches for lesions near the falx. Large meningiomas may involve this region and caution must be taken in dissection around or removal of this specific area. Occasionally, surgical windows in the falx cerebri are opened to allow access to the opposite hemisphere, to assist in complete tumor removal, or to rotate as a flap around a bleeding superior sagittal sinus. An incidental persistent falcine sinus with dominant straight sinus and hypoplastic distal superior sagittal sinus.
Cheap rumalaya master card
This condition is characterized by paroxysmal profound hypertension treatment brown recluse spider bite buy rumalaya once a day, bradycardia, flushing, and headache. It can be triggered by almost any physical or metabolic stimuli and results in significant morbidity and cardiovascular mortality for patients with spinal cord injuries. Differential Diagnosis Spinal cord disorders are discussed in Chapter 22; they may stem from inflammation (transverse myelitis), infarction, compression, or other causes. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis causes degeneration of both the corticospinal tracts and anterior horn cells. The pattern of weakness and associated findings such as tone and reflexes may vary depending on the acuity and mechanism of the spinal cord lesion. There may be sensory loss below the level of the lesion because of the interruption of ascending tracts. Reflexes below the level of the lesion are typically increased, and Babinski signs may be present. Autonomic dysreflexia may develop in patients with lesions above T6 about a month after the initial spinal cord trauma. Deep hemispheric lesions, as in the internal capsule, may lead to weakness of all three parts of the contralateral body (face, arm, and leg), because motor fibers from all areas of the motor strip join together as they travel toward the brainstem. Lesions in the base of the pons may lead to weakness of the ipsilateral face and contralateral arm and leg (crossed signs), because descending motor fibers to the face have crossed at that level but those to the body have not. Associated Signs and Symptoms Lesions of the cerebral hemispheres frequently have associated cognitive signs, such as those described in Chapter 11. Left hemisphere lesions may cause aphasia or apraxia, whereas right hemisphere lesions may cause neglect or visuospatial dysfunction. Lesions of the brainstem may cause cranial nerve problems, such as extraocular movement disorders. Imaging Studies Imaging of the brain is important to evaluate almost all of the potential etiologies in this category. Differential Diagnosis the differential diagnosis includes such diverse etiologies as stroke (Chapter 14), demyelinating disease (Chapter 20), traumatic injury (Chapter 17), brain tumor (Chapter 19), and infection (Chapter 21). Parasagittal lesions lead primarily to leg weakness, more lateral lesions lead primarily to face and arm weakness, and deep lesions may lead to weakness of all three parts. Cerebral hemisphere lesions may have accompanying cognitive signs, such as aphasia or neglect. Abnormalities of sensation can be characterized by an increase, decrease, impairment, or loss of feeling. The diagnosis of sensory problems requires an understanding of the anatomy and an analysis of the presentation, location, characteristics, and distribution of symptoms. Pain and temperature sensation is carried by thinly myelinated (A-) and unmyelinated slowly conducting (C) fibers that synapse as they enter the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.
Hamlar, 35 years: The difference in prognosis as a function of the time of maternal illness has been outlined (see Table 34. Although it is true that the pressure of the implant on top of the capsule will help compress and obliterate that space, since there will no longer be implant over the sternum, there is otherwise nothing to press the old capsule and hence the skin flat onto the sternum.
Goran, 36 years: This is why animals have oxygencarrying proteins to provide a steady supply of oxygen. Even coffee, tea, and wine contain complex mixtures of bioactive compounds, many with antioxidant, antiinflammatory, and even anticancer effects.
Aidan, 59 years: He has seen multiple ophthalmologists, but eye examinations have not identified a cause for his complaints. Hemorrhagic lesions included subarachnoid hemorrhage in three infants, germinal matrixintraventricular hemorrhage in two, and intracerebral hemorrhage in two.
Hassan, 53 years: New implant pocket is undermined under posterior capsule, keeping some pectoralis major muscle fibers attached to it, and it reaches breast footprints made before surgery, passing through capsular contracture limits. Although converting to a subglandular pocket is tempting, the surgeon should remind himself or herself of the myriad of advantages offered by the submuscular pocket, particularly for the patient with symmastia, in that frequently these patients are thin and benefit from tissue coverage, and because the muscle almost by definition is no longer attached to the sternum.
Kurt, 63 years: Carrying Protons and Carbon Dioxide Besides carrying oxygen, hemoglobin has other functions. During the maneuver, nystagmus is not always visible to the examiner, but the patient may still experience vertigo.
Potros, 51 years: Other causes of sensory neuronopathy include Sjögren syndrome, pyridoxine intoxication, and chemotherapy (cisplatin). Because there are many primary neurologic diseases as well as systemic illnesses that can present with sensory symptoms, putting the sensory examination into the context of the remainder of the physical examination may make potential etiologies more obvious.
Roy, 25 years: These were always composed of multiple interwoven vessels concentrated anteriorly. The incidence of intracranial venous sinus injuries due to traumatic head injury ranges from 1% to 4% in civilian life and from 4% to 12% during wartime.
Zapotek, 52 years: Carbon, on the other hand, is much more similar to hydrogen, so it does not form hydrogen bonds to any significant extent. Neurosurgical treatment of brain tumors in the first 6 months of life: longterm follow-up of a single consecutive institutional series of 30 patients.
Jensgar, 43 years: Diseases affecting the rod photoreceptors produce difficulty with vision in dim lighting conditions. When there is irregular astigmatism, an abnormality of corneal shape or structure.
Vandorn, 56 years: Pseudomonas and related gram-negative organisms that contaminate moist ventilatory equipment also become prominent in late-onset sepsis. Management of meningiomas invading the major dural venous sinuses: operative technique, results, and potential benefit for higher grade tumors.
Grobock, 55 years: Nothing should be inserted in the mouth, as this increases the chance of dental injury or foreign object ingestion. Each of the falx cerebelli had a distinct occipital venous sinus attached to its border.
Domenik, 54 years: Recent reports describe withdrawal symptoms after prolonged in utero exposure to gabapentin. It is also important to understand that there is more muscle rotation and cephalad retraction than one predicts based on degree of release or small amounts of pectoralparenchymal interface which result in larger cephalad muscle movements.
Pakwan, 31 years: Epilepsy Syndromes: Features and Treatment Selected Epilepsy Syndromes Commonly Used Treatments LennoxGastaut Childhood Tonic, atonic, Major cognitive Slow (1- to 2-per- Valproic acid, syndrome myoclonic, impairment and second) spikelamotrigine, generalized tonic disability and-wave felbamate, clonic, absence discharges rufinamide, clobazam Focal motor Childhood Simple partial Nocturnal Centrotemporal Carbamazepine; seizure. Formal visual field testing should also be obtained to characterize the pattern of the visual field loss; toxic and nutritional optic neuropathies typically give central or ceco-central scotomas, which can be difficult to detect on confrontation.
Javier, 64 years: Congenital brain abnormalities and Zika virus: what the radiologist can expect to see prenatally and postnatally. Visual agnosia, a common disorder of higher visual function, is characterized by an inability to recognize familiar objects despite intact visual perception, attention, intellect, and language function.
Hernando, 57 years: If transection occurs above the level of the C3C5 nerve roots, which control the diaphragm, respiratory insufficiency may result. If behavioral measures are not sufficient, pressure support with midodrine, fludrocortisones, or beta-blockers may be helpful.
Charles, 45 years: Imaging studies typically show multiple ring-enhancing lesions in the basal ganglia or at the gray matterwhite matter junction. For intracellular receptors involved in steroid signaling, a typical outcome is that cells adjust the amount and/or timing of the synthesis of specific proteins.
Kirk, 34 years: Emissary Veins of the Foramen Lacerum An inconsistent number of small veins may traverse the cartilage-filled foramen lacerum. Hemicrania is more common in women and typically occurs in midadulthood (3040 years of age).
Brenton, 46 years: Venous sinus stenting in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: results of a prospective trial. The use of a submammary approach and dual-plane pocket provides the best anatomic approach to reducing the risk of dissection into the breast parenchyma.
10 of 10 - Review by Y. Konrad
Votes: 107 votes
Total customer reviews: 107