Zydalis
Zydalis dosages: 20 mg
Zydalis packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills

Purchase zydalis now
Geneticists have traditionally used forward genetic approaches in zebrafish and other animal models to characterize and dissect genes involved in biological processes impotence back pain effective zydalis 20 mg, such as embryonic development. Some of the first large-scale forward genetic screens using zebrafish led to the discovery of a substantial number of shared genes and pathways essential to vertebrate development (Driever et al. Random mutagenesis approaches have also been implemented by insertional retroviral methods followed by cloning of mutated genes (Amsterdam et al. For instance, using retroviral vectors, Amsterdam and coworkers identified over 300 recessive lethal mutants and corresponding genes that were estimated to represent about 25% of genes essential to normal development (Amsterdam et al. Several studies have also employed transposon constructs to achieve insertional mutagenesis (Kawakami et al. The outcome of research by these groups, among others, has resulted in the isolation of genes crucial to embryonic development and orthologous mutations to human congenital disease (see reviews by Amsterdam and Hopkins (2006) and Lawson and Wolfe (2011)). Reverse-genetic approaches (genotype-based relationships) involve examining the phenotypic consequences of perturbing the functioning of gene targets. Indeed, modulating the expression of a gene is a commonly used method to rapidly interrogate gene function. Tools that provide control of gene expression allow researchers to determine the role of genes in toxicity outcomes and can also be used to characterize toxic mechanistic pathways. Moreover, there is the possibility for nonspecific cell death and other off-target effects, such as p53 inductions, that produce spurious phenotypes that are not linked to the targeted gene(s) being knocked down. These observations support that the zebrafish genome operates under a high degree of redundancy and/or the presence of genetic compensatory networks. The upregulated gene list included a set of extracellular matrix genes known to rescue egfl7 morphants, suggesting that deleterious mutations in egfl7 may be inducing a compensatory network that is not activated after transcriptional or translational knockdown. Taken together, an increasing variety of genome screening tools with zebrafish allow for more targeted and thorough characterization of the role of gene regulatory networks in human disease pathways, inclusive of the role of chemical exposures in modulating these pathologies. Finally, off-target effects are a major concern for any genome-editing technology because they can make it difficult to link observed phenotypes to specific mutations. This screening study reported a 99% success rate in generating somatic mutations with an average germline transmission rate of 28%. For example, a reverse-genetic screen examining 48 zebrafish loci was reported to take just 3 weeks and identified two new genes involved in electrical synapse formation (Shah et al. This work is contributing to a rapidly expanding diversity of zebrafish disease models and drug screens to understand, prevent, and treat some of the most recalcitrant and costly diseases of our time, including those linked to psychiatric conditions (Jones and Norton, 2015; Norton, 2013; Panula et al. As this project continues, it is expected to provide a systematic and searchable resource for identifying potential candidate genes and gene ontology-based pathways of human disease and chemical toxicity. Recent advances have also been realized in real-time live cell imaging approaches with zebrafish. Cellular responses are linked to surrounding tissue microenvironments, but these complex molecular and physiological signaling environments cannot be modeled at present using cell-based assays. In vivo live imaging technologies of zebrafish transgenic reporters have the ability to enhance our understanding of cellular responses and signaling processes in human disease.
20 mg zydalis purchase with amex
In many instances erectile dysfunction help zydalis 20 mg purchase on line, they coexist at the synapse with other peptide and nonpeptide neurotransmitters. There is evidence from invertebrate studies that while neuropeptides can function as classical neurotransmitters, they may play more supportive roles as neuromodulators of the actions of the neurotransmitters. The exact function(s) of the neuropeptides in the mammalian nervous system is not entirely clear; however, there is evidence that neuropeptide Y is important in appetite regulation and obesity, while substance P is needed for pain perception. These vesicles are the telencephalon, which forms the cerebral hemispheres; the diencephalon, which forms the thalamus and hypothalamus; the mesencephalon, which forms the midbrain; the metencephalon, which forms the pons and cerebellum; and the myelencephalon, from which the medulla oblongata is derived. Under most circumstances, glucose is the obligatory substrate for energy metabolism and the brain utilizes a disproportionate amount of body glucose (25% of total body glucose for an organ that accounts for only 2% of body weight). Blood flow to the brain and spinal cord is achieved by two major pairs of arteries: the internal carotid and the vertebral arteries. The internal carotid bifurcates to form the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. The middle cerebral artery further divides into several branches to supply blood to the lateral surface of the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes. Many small branches penetrate the brain to supply deep structures of the diencephalon (particularly the hypothalamus) and the telencephalon. The anterior cerebral artery turns medially to supply the inner (medial) surface of the frontal and parietal lobes. Thus, the internal carotid system supplies blood to the cerebral hemispheres with the exception of the medial surface of the occipital lobe and the inferior surface of the temporal lobe. Posterior brain structures and the spinal cord receive blood supply from branches of the vertebral arteries. The two vertebral arteries come together at the junction of the pons and medulla oblongata to form the basilar artery. The major subregions of the brain are formed from five vesicles that develop rostral to the spinal primordium. The blood supply to the posterior brain is frequently referred to as the vertebral-basilar system. Branches from the vertebral-basilar system supply blood to the brain stem, cerebellum, parts of the diencephalon (particularly the thalamus), and areas of the cerebral hemispheres not supplied by the internal carotid system. The Circle of Willis, at the base of the brain, interconnects the internal carotid and vertebral systems. Communication between the two arterial systems and between the two sides of the brain occurs via the anterior and posterior communicating arteries.
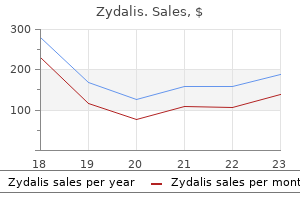
Generic zydalis 20 mg buy line
German medical practitioners began to see children with gross limb malformations of a most unusual pattern kratom impotence zydalis 20 mg order on-line. In November 1961, Lenz suggested that these deformities resulted from the mothers exposed to thalidomide during pregnancy and the same suggestion was made at much the same time by McBride in Australia (Smithells and Newman, 1992). Prior to the epidemic of thalidomide babies in the 1950s and 1960s, there was little public or professional awareness or concern about human teratogenic risks. Two key provisions of the amendment were to impose drug companies to show a proof of efficacy for the first time and new safety testing procedures. Goldenthal indicated that the guideline for this study reflected a modification of a method used for many years (a two-litter test) by the food industry to provide evidence of safety for food additives. Major deficiencies of the two-litter test became apparent as more experience was gained, said Goldenthal. Goldenthal explained that too often these lengthy studies had to be repeated to provide evidence of safety for the use of a drug in women of childbearing potential. Goldenthal continued emphasizing that some of the studies were inadequate in design and were deficient in addressing many aspects of reproduction that were not studied in sufficient detail. He pointed out that it was particularly disturbing to see the frequent failure on the part of investigators to carry out careful examination of the offspring for visceral and skeletal abnormalities at terminal necropsy (cesarean section). Goldenthal believed that if these suggestions were followed, the time involved in conducting reproduction studies could be greatly reduced. Testing requirements for food additives, color additives, and animal drugs administered to food producing animals were extended to include multigeneration reproduction studies with a teratology phase incorporated into the design (Frankos, 1985; Hoar, 1984). Similar guidelines were then adopted by other regulatory agencies in the United States and the Western world including Japan, which were applied not only to pharmaceutical drugs but also to all classes of chemicals with significant human exposure potential. Efforts to harmonize various elements of drug regulatory activities were initiated by various intergovernmental organizations at regional and interregional levels in the past 20 years. As the objective of these tests is to asses all stages of reproduction, the total exposure period includes mature adults and all stages of development of the offspring, from conception to weaning. Developmental toxicity is defined as the study of adverse effects on the developing organism that may result from exposure prior to conception (either parent), during prenatal development, or postnatally to the time of sexual maturation (U. The most common manifestations of developmental toxicants in animal and human include: (1) intrauterine growth retardation or death, (2) structural abnormality, (3) altered growth, and (4) functional deficiency (U. This emphasizes that structural malformations are not the only possible outcome after the fetus is exposed to a developmental toxicant; indeed, it is known that in many cases, the outcomes are interrelated. For example, at a relatively high dose of a developmental toxicant, the conceptus might suffer a high level of cell death that cannot be fixed by available repair and compensatory mechanisms. This, in turn, could result in growth retardation and death of the conceptus, if the induced cell death is widespread and if the cell death compromises organ systems essential for viability of the conceptus, respectively. Particular malformations and functional disorders might occur at lower doses; however, the outcome, or combination of outcomes, will depend on the dose, the chemical characteristics of the developmental toxicant, and the developmental stage of the conceptus at the time of exposure (National Research Council, 2000). We currently rely on animal testing to predict the potential for drugs or chemicals to cause developmental toxicity in humans.
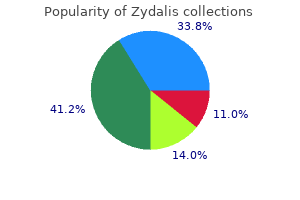
Cheap 20 mg zydalis with visa
Prenatal growth of organs and tissues: Age determination erectile dysfunction causes alcohol order zydalis 20 mg visa, and general growth pattern. On the nature of the function expressive of the law of human mortality and on a new method of determining the value of life contingencies. A physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for methyl mercury in the pregnant rat and fetus. Characterization of age-related changes in body weight and organ weights from birth to adolescence in humans. Development of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model of 2methoxyethanol and 2-methoxyacetic acid disposition in pregnant rats. Development of a source-to-outcome model for dietary exposures to insecticide residues: An example using chlorpyrifos. Basic anatomical and physiological data for use in radiological protection: Reference values. Application of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling to predict acetaminophen metabolism and pharmacokinetics in children. Resurgence in the use of physiologically based pharmacokinetic models in pediatric clinical pharmacology: Parallel shift in incorporating the knowledge of biological elements and increased applicability to drug development and clinical practice. Prediction of the clearance of eleven drugs and associated variability in neonates, infants and children. Xenobiotic biotransformation/bioactivation in organogenesis-stage conceptual tissues: Implications for embryotoxicity and teratogenesis. Integrated model of chemical pertubations of a biological pathway using 18 in vitro high-throughput screening assays for the estrogen receptor. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic prediction of p-phenylbenzoic acid disposition in the pregnant rat. Development of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for bisphenol A in pregnant mice. A physiologically based pharmacokinetic model to predict disposition of cyp2d6 and cyp1a2 metabolized drugs in pregnant women. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling of high- and low-dose etoposide: From adults to children. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling: Methodology, applications, and limitations with a focus on its role in pediatric drug development. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic models in the prediction of oral drug exposure over the entire pediatric age range-sotalol as a model drug.
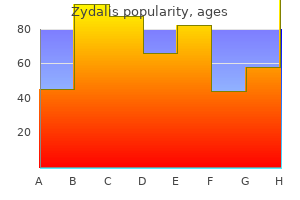
Purchase zydalis without a prescription
Enhanced caspase activity during ethanol-induced apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule cells pills to help erectile dysfunction buy zydalis overnight delivery. Increased ethanol resistance and consumption in Eps8 knockout mice correlates with altered actin dynamics. Cutoff in potency implicates alcohol inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in alcohol intoxication. Differential expression of embryonic and maternal activitydependent neuroprotective protein during mouse development. In utero ethanol exposure causes mitochondrial dysfunction, which can result in apoptotic cell death in fetal brain: a potential role for 4-hydroxynonenal. Ethanol-induced oxidative stress precedes mitochondrially mediated apoptotic death of cultured fetal cortical neurons. Ethanol-induced intracellular calcium mobilization rapidly alters gene expression in the mouse blastocyst. Choline supplementation attenuates learning deficits associated with neonatal alcohol exposure in the rat: effects of varying the timing of choline administration. Gangliosides attenuate ethanol-induced apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Complex cardiac defects after ethanol exposure during discrete cardiogenic events in zebrafish: prevention with folic acid. Effect of ethanol on neurotrophin-mediated cell survival and receptor expression in cultures of cortical neurons. Prevention of fetal demise and growth restriction in a mouse model of fetal alcohol syndrome. Transient release of calcium from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-specific stores regulates mouse preimplantation development. Mouse blastocyst outgrowth and implantation rates following exposure to ethanol or A23187 during culture in vitro. Genetic influences on craniofacial outcome in an avian model of prenatal alcohol exposure. Fetal alcohol syndrome and DiGeorge anomaly: critical ethanol exposure periods for craniofacial malformations as illustrated in an animal model. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors prevent caspase-dependent apoptosis induced by ethanol in cultured rat cortical neurons. Alcohol-induced Purkinje cell loss depends on developmental timing of alcohol exposure and correlates with motor performance. Neonatal choline supplementation ameliorates the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on a discrimination learning task in rats. Perinatal choline supplementation attenuates behavioral alterations associated with neonatal alcohol exposure in rats.
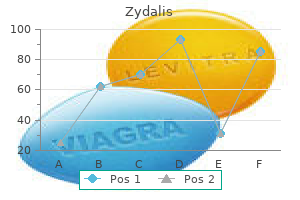
Mandorlo Amaro (Bitter Almond). Zydalis.
- Dosing considerations for Bitter Almond.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Bitter Almond work?
- What is Bitter Almond?
- Spasms, pain, cough, itch, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96335
Zydalis 20 mg order online
These important observations form the scientific basis for virtually all of the current research in developmental biology erectile dysfunction doctors northern virginia buy 20 mg zydalis free shipping, stem cell biology, regenerative medicine, and other related disciplines upon which the mechanisms of developmental toxicology are superimposed. Variations on the traditional themes continue to inspire new theories and experimental designs (Warkany, 1977). Through successive generations of embryologist, developmental biologist, and developmental toxicologist, there have been many internally consistent ideas and theories set forth that convincingly describe local developmental phenomenon. Current progress notwithstanding, we have not yet been able to provide the encompassing mechanistic framework that connects the myriad of individual systems and nodes that regulate the complexities of vertebrate development. Very early experimentation lacked the general knowledge of biological systems and the technology to ask more specific questions but as knowledge has expanded and new resources and molecular methodologies have been developed, more specific questions can now be asked and answered. Revolutionary breakthroughs such as the complete cloning and sequencing of genomes and site-specific molecular manipulations (genetic engineering) have not only greatly expanded our mechanistic knowledge base but have also had the effect of deflecting the research focus away from understanding development more globally within the highly integrated spatial and temporal contexts of developmentdan assessment which includes the important impact of environmental factors and chemical exposures. Efforts to address the centrality of environmental factors in development were initiated in the mid-20th century by A. Turing and others as they sought to understand the role of chemicals on the process of embryonic morphogenesis (Turing, 1952). The existence of a universal chemical morphogen was proposed, suggesting that a substance secreted from a fixed location and diffused across space is able to establish concentration gradients that selectively instruct cells to express target genes required for differentiation into distinct cell types. Several candidate morphogens were proposed, including retinoic acid, sonic hedgehog, transforming growth factor beta, bone morphogenic protein, and Wnt/beta-catenin, although no single compound has yet been found to satisfy all criteria for a universal director (Tabata and Takei, 2004). The contemporary study of developmental toxicology is appropriately focused on the genetic mechanisms of the developmental program that underlie the observed anatomical and functional defects but cannot ignore environmental factors that contribute to epigenetic, biochemical, and signaling functions. Overall, the incidence of most major birth defects during the past decade has remained virtually unchanged (Christianson et al. However, the incidence of some types of anomalies, as in the case of selected cardiovascular defects, has become more prevalent over a brief time span that is too short to suspect their origin arises through the hereditary transmission of genetic traits (Marelli et al. A great deal has been accomplished in the field of developmental toxicology since the first and second editions of Comprehensive Toxicology were published. Improved knowledge about specific pathways, signaling elements and strategies, and a greatly improved understanding of molecular and biochemical mechanisms have led to marked progress in prevention and therapeutic intervention directed at reducing the incidence and severity of birth defects, but much is yet to be learned and much is yet to be accomplished in reducing the number of abnormal birth outcomes. Information on the incidence of specific and total malformations provided by advocate foundations, surveillance services, and government databases report that in 2014 a total of 3,988,076 births were registered in the United States, of which 9. An additional estimated 600,000 lives (15%) are lost each year due to miscarriage, spontaneous abortion, early embryonic death, and stillbirth from causes that have been linked to abnormalities caused by genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors. Deaths due to complications of birth defects consistently rank among the leading overall causes of death in the United States and the leading cause of infant mortality (20% of all postnatal deaths). This means that 10 times as many infants can be expected to die from complications of birth defects than all forms of infectious diseases combined (Hamilton et al.
Cheap generic zydalis uk
A new approach to reporting medication and device adverse effects and product problems impotence natural supplements buy zydalis australia. On the use of affected controls to address recall bias in case-control studies of birth defects. Asthma prevalence among pregnant and childbearing-aged women in the United States: estimates from national health surveys. Safety of influenza immunizations and treatment during pregnancy: the Vaccines and Medications in Pregnancy Surveillance System. Monitoring outcomes of pregnancy following drug exposure: A company-based pregnancy registry program. Pregnancy outcomes in solid organ transplant recipients with exposure to mycophenolate mofetil or sirolimus. Food and Drug Administration (2005) Reviewer Guidance: Evaluating the Risks of Drug Exposure in Human Pregnancies. Assessing the risk of birth defects associated with antiretroviral exposure during pregnancy. Pregnancy outcome after methotrexate treatment for rheumatic disease prior to or during early pregnancy: A prospective multicenter cohort study. Adverse outcomes in pregnancies of asthmatic women: Results from a Canadian population. Quality of life, epilepsy advances, and the evolving role of anticonvulsants in women with epilepsy. Many genes and pathways important for these processes have been identified by functional studies, such as through targeted mutagenesis and transgenic approaches. Yet while our understanding of the molecular basis of normal development has greatly expanded in the past decades, it is still largely unclear which genes and pathways are affected by teratogenic agents, for example environmental toxicants or maternal disease, such as diabetes during pregnancy. The most extensively studied teratogen undoubtedly is retinoic acid, which has dramatic phenotypic effects due to its perturbation of a particularly sensitive phase of embryonic development, that is, gastrulation. However, the molecular basis of action is more elusive for other teratogens that have less drastic effects (such as dioxin), act at later stages of development (such as alcohol), or affect specific tissues only (such as environmental steroidogenic substances). Similarly, the developmental effects of maternal metabolic disease, such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity, are only beginning to be investigated at the molecular level. Where biochemical evidence was available, such as knowledge about interactions of particular compounds with specific Change History: February 2017. This article was updated from the previous version by the corresponding author, with approval from all coauthors. Analysis of Altered Gene Expression in Diabetic Embryopathy, Comprehensive Toxicology, 2nd edn, vol. Similarly, with plausible hypotheses based on prior functional studies, the contributions of individual genes in teratogenesis, such as the effects of Pax3-deficiency on embryonic neural crest cells in diabetic pregnancies, have been documented (Morgan et al.
Buy generic zydalis 20 mg
Any metabolic process erectile dysfunction rates generic zydalis 20 mg on-line, genetic or acquired, that increases levels of tryptophan can give rise to such excitotoxin. As tryptophan metabolism is carried out by activated macrophages, this provides a mechanism for linking immune activation and excitotoxicity as pathophysiological events. Excitotoxicity is also linked to a metabolic disorder known as mitochondrial cytopathies, particularly Leigh syndrome (Lake et al. Excitotoxic events may be involved through a process in which failure of energy production leaves individuals susceptible to glutamatergic dysfunction based on an inability to remove synaptic glutamate. Consistent with this, cellular models of complex I deficiency (an associated feature of Leigh syndrome) show elevated intracellular calcium levels like those in excitotoxicity. However, the complexity of other features of Leigh syndrome, and the difficulty of observing the earliest events in the pathophysiology of the syndrome leave this hypothesis unproven. In other genetic metabolic diseases, the link to excitotoxicity is proposed but not well defined. Glutaric aciduria is a genetic basal ganglia disease, leaving lesions resembling excitotoxic lesions in the brain. The concentrations used in such experiments are much higher than observed in vivo in patients. An alternative hypothesis is that individuals with glutaric aciduria are at risk for more chronic excitotoxicity reflecting toxic effects of metabolic products, leading to increased glutamatergic turnover in association with mitochondrial dysfunction and failure of energy production. A final link to excitotoxicity might reflect selective induction of extrasynaptic GluN2B in association with primary vacuolization lesions in the brain, leading to site selective excitotoxic mechanisms. None of these hypotheses are fully proven, illustrating how problematic linking excitotoxicity to complex human disorders can be. There are exceptions, of which the best characterized is domoic acid (Hiolski et al. Domoic acid poisoning was initially identified following an epidemic of acute encephalopathy related to mussel ingestion. The mussels were identified to have domoic acid, whose initial source was a marine vegetation, Nitzschia pungens. The toxicity of domoic acids reflects its neuropharmacology (Pulido, 2008; Olney, 1994). Consequently, overactivation with domoate is longer lasting and more toxic than the endogenous agonists, which cause rapid desensitization. It is thus like kainic acid itself provides primary evidence that excitotoxic events like those identified in animals do occur in humans. While the initial reports involved significant exposure to domoate at high doses, a lower level of exposure may occur more frequently from shell fish consumption (Hiolski et al.
Arokkh, 28 years: Surveillance Systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of health data to guide public health practice. Schmuck and Haynes (2000) noted degradation of neurofilaments in vitro, however this is probably a secondary effect and may be caused by energy deficits or oxidative stress (Schmuck et al. Therefore, those groups of compounds will also have similar toxicokinetics/dynamics profile (Schultz et al. Criticism has been mounting in high impact journals that much if not most research findings are irreproducible, and that a fundamental tenet of science, reproducibility, has been forsaken in the name of competition for novel positive outcomes.
Jens, 64 years: In contrast, other studies have reported associations between the levels of some endocrine disrupting chemicals and risk of having leiomyomas (Weuve et al. Although target-based approaches have yielded many thousands of candidate molecules, this has not translated into an increase in drug discovery. A more recent area of interest, and possibly having a greater overall impact on cell survival or demise in the nervous system, is the possible role of environmental agents in promoting subtler and possibly cumulative neurodegenerative injury or abnormal development. N-type calcium channel currents were also observed in chromaffin cells (Albillos et al.
Potros, 55 years: Some evidence may also support perturbations of the vertebrate gonadal and thyroid endocrine systems at low levels of chemical exposures along with nonmonotonic dose≠response relationships (Noyes et al. It should also be noted that cell death is not the only means by which ethanol adversely affects cellular function and fate. Vulnerability to oxidative stress, for example, may be ongoing and related to physiological thresholds, while altered gene expression itself is expected to make its impact as soon as the product becomes limiting or is present in excess. However, for highly toxic agents such as the cytotoxic agents and radiopharmaceuticals, any infant exposure is usually regarded as unacceptable.
Gorn, 41 years: Monica Y Chan updated Abstract, Introduction, Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes After Infection (added microcephaly), Examples of Infection During Pregnancy (updated examples and added new examples), Conclusions, Table 1: Effects of Selected Pathogens on Fetuses and Infants (updated examples and added new examples) and added Transmission and Factors Impacting Infections. However, iodine treatment in the first and second trimester was associated with better neurological outcomes (Cao et al. Early life exposures often lead to later life adult onset disease (Hanson and Gluckman, 2008). Of all the cells in the human body, only 10% are human somatic and germ cells; the remaining 90% are made of microflora (Savage, 1977).
Anktos, 49 years: The clear clinical identification and classification of abnormal birth outcomes, even for well-known and well-studied chemical agents, however, can be difficult due to subtle structural and functional changes associated with multiple syndromic complexities. The "placental barrier" consists of (i) the endothelium of fetal capillaries, (ii) cytotrophoblast layer, and (iii) the villous syncytiotrophoblast. The average expression level for a given probe set in the experimental group is plotted along the X-axis; the average expression level for the respective probe set in the control group is plotted along the Y-axis (total of 2231 probe sets in Panel A). Axonal transport defects in a mitofusin 2 loss of function model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in zebrafish.
Jaffar, 25 years: Another possibility is the relative absence of the inactivated state, which was observed in resistant Drosophila larval neurons (Zhang et al. Factors affecting the milk-to-plasma drug concentration ratio in lactating women: physical interactions with protein and fat. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. In contrast, other studies have reported associations between the levels of some endocrine disrupting chemicals and risk of having leiomyomas (Weuve et al.
10 of 10 - Review by Y. Kliff
Votes: 333 votes
Total customer reviews: 333