Telmisartan
Telmisartan dosages: 80 mg, 40 mg, 20 mg
Telmisartan packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Discount telmisartan online amex
Reversibility of chronic rejection is limited; in patients with therapy-resistant chronic rejection blood pressure yahoo answers cheap telmisartan master card, retransplantation has yielded encouraging results. For those whose level of decompensation mandates continuous in-hospital care prior to transplantation, the 1-year survival rate is ~70%, whereas for those who are so decompensated that they require life support in an intensive care unit, the 1-year survival rate is ~50%. Thus, irrespective of allocation scheme, high disease severity before transplantation corresponds to diminished posttransplantation survival. In contrast, among patients in high-risk categories-cancer, fulminant hepatitis, age >65, concurrent renal failure, respirator dependence, portal vein thrombosis, and history of a portacaval shunt or multiple right upper quadrant operations-survival statistics fall into the range of 60% at 1 year and 35% at 5 years. Failures within the first 3 months result primarily from technical complications, postoperative infections, and hemorrhage. Whether autoimmune hepatitis and sclerosing cholangitis recur after liver transplantation is controversial; data supporting recurrent autoimmune hepatitis (in up to one-third of patients in some series) are more convincing than those supporting recurrent sclerosing cholangitis. Similarly, reports of recurrent primary biliary cirrhosis after liver transplantation have appeared; however, the histologic features of primary biliary cirrhosis and chronic rejection are virtually indistinguishable and occur as frequently in patients with 2074 primary biliary cirrhosis as in patients undergoing transplantation for other reasons. Hepatic vein thrombosis (Budd-Chiari syndrome) may recur; this can be minimized by treating underlying myeloproliferative disorders and by anticoagulation. Hepatitis A can recur after transplantation for fulminant hepatitis A, but such acute reinfection has no serious clinical sequelae. In fulminant hepatitis B, recurrence is not the rule; however, in the absence of any prophylactic measures, hepatitis B usually recurs after transplantation for end-stage chronic hepatitis B. Also recognized in the era before availability of antiviral regimens was fibrosing cholestatic hepatitis, rapidly progressive liver injury associated with marked hyperbilirubinemia, substantial prolongation of the prothrombin time (both out of proportion to relatively modest elevations of aminotransferase activity), and rapidly progressive liver failure. Patients who undergo liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B plus D are less likely to experience recurrent liver injury than patients undergoing liver transplantation for hepatitis B alone; still, such co-infected patients would also be offered standard posttransplantation prophylactic therapy for hepatitis B. Nonetheless, despite the relative clinical benignity of recurrent hepatitis C in the early years after liver transplantation, and despite the negligible impact on patient survival during these early years, histologic studies have documented the presence of moderate to severe chronic hepatitis in more than onehalf of all patients and cirrhosis in ~20% at 5 years. Allograft cirrhosis is even more common, occurring in up to two-thirds of patients at 5 years, if moderate hepatitis is detected in a 1-year liver biopsy. Not surprisingly, then, for patients undergoing liver transplantation for hepatitis C, allograft and patient survival are diminished substantially between 5 and 10 years after transplantation. Sustained virologic responses are the exception, and reduced tolerability is often dose-limiting. Patients who undergo liver transplantation for end-stage alcoholic cirrhosis are at risk of resorting to drinking again after transplantation, a potential source of recurrent alcoholic liver injury. Recidivism is more likely in patients whose sobriety prior to transplantation was <6 months. Psychosocial maladjustment interferes with medical compliance in a small number of patients, but most manage to adhere to immunosuppressive regimens, which must be continued indefinitely. In fact, some women have conceived and carried pregnancies to term after transplantation without demonstrable injury to their infants.
Telmisartan 40 mg order visa
Binder Disorders of absorption constitute a broad spectrum of conditions with multiple etiologies and varied clinical manifestations arrhythmia breathing order 20 mg telmisartan with visa. Almost all of these clinical problems are associated with diminished intestinal absorption of one or more dietary nutrients and are often referred to as the malabsorption syndrome. This term is not ideal as it represents a pathophysiologic state, does not provide an etiologic explanation for the underlying problem, and should not be considered an adequate final diagnosis. Most malabsorption syndromes are associated with steatorrhea, an increase in stool fat excretion to >6% of dietary fat intake. Some malabsorption disorders are not associated with steatorrhea: primary lactase deficiency, a congenital absence of the small-intestinal brush border disaccharidase enzyme lactase, is associated with lactose "malabsorption," and pernicious anemia is associated with a marked decrease in intestinal absorption of cobalamin (vitamin B12) due to an absence of gastric parietal-cell intrinsic factor, which is required for cobalamin absorption. Disorders of absorption must be included in the differential diagnosis of diarrhea (Chap. First, diarrhea is frequently associated with and/or is a consequence of the diminished absorption of one or more dietary nutrients. The diarrhea may be secondary either to the intestinal process that is responsible for the steatorrhea or to steatorrhea per se. Thus, celiac disease (see below) is associated with both extensive morphologic changes in the small-intestinal mucosa and reduced absorption of several dietary nutrients; in contrast, the diarrhea of steatorrhea is the result of the effect of nonabsorbed dietary fatty acids on intestinal (usually colonic) ion transport. In addition, diarrhea per se may result in mild steatorrhea (<11 g of fat excretion while on a 100-g fat diet). Some 10% of patients referred to gastroenterologists for further evaluation of unexplained diarrhea do not have an increase in stool water when this variable is determined quantitatively. Such patients may have small, frequent, somewhat loose bowel movements with stool urgency that is indicative of proctitis but do not have an increase in stool weight or volume. Unfortunately, both secretory and osmotic elements can be present simultaneously in the same disorder; thus, this distinction is not always precise. Nonetheless, two studies-determination of stool electrolytes and observation of the effect of a fast on stool output-can help make this distinction. In contrast, diarrhea secondary to lactose malabsorption in primary lactase deficiency would undoubtedly cease during a prolonged fast. Thus, a substantial decrease in stool output by a fasting patient during quantitative stool collection lasting at least 24 h is presumptive evidence that the diarrhea is related to malabsorption of a dietary nutrient. The persistence of stool output during fasting indicates that the diarrhea is likely secretory and that its cause is not a dietary nutrient. The observed effects of fasting can be compared and correlated with stool electrolyte and osmolality determinations. Measurement of stool electrolytes and osmolality requires comparison of Na+ and K+ concentrations in liquid stool with the osmolality of the stool in order to determine the presence or absence of a so-called stool osmotic gap.
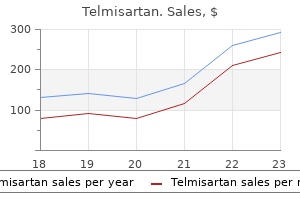
Order telmisartan no prescription
They are often used to facilitate mechanical ventilation or other critical care procedures blood pressure reader buy telmisartan 40 mg free shipping, but with prolonged use persistent neuromuscular blockade may result in weakness even after discontinuation of these agents hours or days earlier. Risk factors for this prolonged action of neuromuscular blocking agents include female sex, metabolic acidosis, and renal failure. Once the offending medications are discontinued, full strength is restored, although this may take days. Critical illness myopathy is an overall term that describes several different discrete muscle disorders that may occur in critically ill patients. Panfascicular muscle fiber necrosis may also occur in the setting of profound sepsis. This less common acute necrotizing intensive care myopathy is characterized clinically by weakness progressing to a profound level over just a few days. Acute rhabdomyolysis can occur from alcohol ingestion or from compartment syndromes. Clinically this syndrome is most often recognized when a patient fails to wean from mechanical ventilation despite resolution of the primary pulmonary process. If patients survive their underlying critical illness, the myopathy invariably improves and most patients return to normal. However, because this syndrome is a result of true muscle damage, not just prolonged blockade at the neuromuscular junction, this process may take weeks or months, and tracheotomy with prolonged ventilatory support may be necessary. Some patients do have residual long-term weakness, with atrophy and fatigue limiting ambulation. Monitoring with a peripheral nerve stimulator can help to avoid the overuse of these agents. However, this is more likely to prevent the complication of prolonged neuromuscular junction blockade than it is to prevent this myopathy. Other causes include bleeding from a vascular malformation (arteriovenous malformation or dural arteriovenous fistula) and extension into the subarachnoid space from a primary intracerebral hemorrhage. For patients who arrive alive at hospital, the mortality rate over the next month is about 45%. Of those who survive, more than half are left with major neurologic deficits as a result of the initial hemorrhage, cerebral vasospasm with infarction, or hydrocephalus. If the patient survives but the aneurysm is not obliterated, the rate of rebleeding is about 20% in the first 2 weeks, 30% in the first month, and about 3% per year afterward. Unruptured, asymptomatic aneurysms are much less dangerous than a recently ruptured aneurysm. Because of the longer length of exposure to risk of rupture, younger patients with aneurysms >10 mm in size may benefit from prophylactic treatment. As with the treatment of asymptomatic carotid stenosis, this risk-benefit ratio strongly depends on the complication rate of treatment.
Telmisartan 20 mg order on line
Because many families burn biomass fuels in open stoves arteria poplitea cheap telmisartan 80 mg with mastercard, which are highly inefficient, and inside homes with poor ventilation, women and young children are exposed on a daily basis to high levels of smoke. For example, sulfur dioxide and particulate matter emissions from a coal-fired power plant may react in air to produce acid sulfates and aerosols, which can be transported long distances in the atmosphere. Oxides of nitrogen and volatile organic compounds from automobile exhaust react with sunlight to produce ozone. Although originally thought to be confined to Los Angeles, photochemically derived pollution ("smog") is now known to be a problem throughout the United States and in many other countries. Both acute and chronic effects of these exposures have been documented in large population studies. The symptoms and diseases associated with air pollution are the same as conditions commonly associated with cigarette smoking. In addition, decreased growth of lung function and asthma have been associated with chronic exposure to only modestly elevated levels of traffic-related gases and respirable particles. Multiple populationbased time-series studies within cities have demonstrated excess health care utilization for asthma and other cardiopulmonary conditions as well as increased mortality rates. Anthracitic pigment is seen accumulating along alveolar septae (arrowheads) and within a pigmented dust macule (single arrow). A high-power photomicrograph contains a mixture of fibroblasts and carbon-laden macrophages. In addition to the common occupational exposure to biomass smoke of women in developing countries, men from such countries may be occupationally exposed. Because of increased migration to the United States from developing countries, clinicians need to be aware of the chronic respiratory effects of exposure to biomass smoke, which can include interstitial lung disease. Baron, Miriam Baron Barshak Bronchiectasis refers to an irreversible airway dilation that involves the lung in either a focal or a diffuse manner and that classically has been categorized as cylindrical or tubular (the most common form), varicose, or cystic. Clues to the underlying etiology are often provided by the pattern of lung involvement. Focal bronchiectasis refers to bronchiectatic changes in a localized area of the lung and can be a consequence of obstruction of the airway-either extrinsic. Diffuse bronchiectasis is characterized by widespread bronchiectatic changes throughout the lung and often arises from an underlying systemic or infectious disease process. Bronchiectasis with predominant involvement of the lower lung fields usually has its source in chronic recurrent aspiration. Consider workup for bowel disease); immuneallergic bronchopulmonary mediated disease (allergic aspergillosis, especially in bronchopulmonary patients with refractory aspergillosis) asthma. Congenital causes of bronchiectasis with predominant midlung field involvement include the dyskinetic/ immotile cilia syndrome.
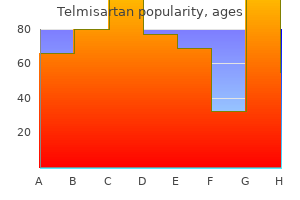
Diseases
- Hypertelorism and tetralogy of Fallot
- Distal arthrogryposis Moore Weaver type
- Blepharitis
- Cinchonism
- Thrush
- Tangier disease
- Mastocytosis
- Mohr Tranebirg syndrome
- Lymphocytic colitis
- Spastic dysphonia
Telmisartan 20 mg purchase with amex
Rarely blood pressure drops after exercise safe 80 mg telmisartan, video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery to obtain a larger sample of lung tissue may be required to determine the specific diagnosis of environmentally induced lung disease (hypersensitivity pneumonitis or giant cell interstitial pneumonitis due to cobalt exposure). Watersoluble gases such as ammonia and sulfur dioxide are absorbed in the lining fluid of the upper and proximal airways and thus tend to produce irritative and bronchoconstrictive responses. In contrast, nitrogen dioxide and phosgene, which are less soluble, may penetrate to the bronchioles and alveoli in sufficient quantities to produce acute chemical pneumonitis. These particles are divided into three size fractions on the basis of their size characteristics and sources. Although the total mass of an ambient sample is dominated by these larger respirable particles, the number of particles, and therefore the surface area on which potential toxic agents can deposit and be carried to the lower airways, is dominated by particles <2. These fine particles are created primarily by the burning of fossil fuels or high-temperature industrial processes resulting in condensation products from gases, fumes, or vapors. If they do deposit, however, particles of this size range may penetrate into the circulation and be carried to extrapulmonary sites. New technologies create particles of this size ("nanoparticles") for use in many commercial applications. Besides the size characteristics of particles and the solubility of gases, the actual chemical composition, mechanical properties, and immunogenicity or infectivity of inhaled material determine in large part the nature of the diseases found among exposed persons. In addition to workers involved in the production of asbestos products (mining, milling, and manufacturing), many workers in the shipbuilding and construction trades, including pipe fitters and boilermakers, were occupationally exposed because asbestos was widely used during the twentieth century for its thermal and electrical insulation properties. Asbestos also was used in the manufacture of fire-resistant textiles, in cement and floor tiles, and in friction materials such as brake and clutch linings. Cases of asbestos-related diseases have been encountered in individuals with only bystander exposure, such as painters and electricians who worked alongside insulation workers in a shipyard. Community exposure resulted from the use of asbestos-containing mine and mill tailings as landfill, road surface, and playground material. Asbestos has largely been replaced in the developed world with synthetic mineral fibers such as fiberglass and refractory ceramic fibers, but it continues to be used in the developing world. The major health effects from exposure to asbestos are pleural and pulmonary fibrosis, cancers of the respiratory tract, and pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma. Asbestosis is a diffuse interstitial fibrosing disease of the lung that is directly related to the intensity and duration of exposure. Usually, exposure has taken place for at least 10 years before the disease becomes manifest. The mechanisms by which asbestos fibers induce lung fibrosis are not completely understood but are known to involve oxidative injury due to the generation of reactive oxygen species by the transition metals on the surface of the fibers as well as from cells engaged in phagocytosis.
Telmisartan 40 mg purchase online
Proper training of observers arrhythmia recognition course trusted telmisartan 40 mg, positioning of the patient, and selection of cuff size are essential. Most patients with hypertension have no specific symptoms referable to their blood pressure elevation. Other nonspecific symptoms that may be related to elevated blood pressure include 1622 should equal at least 40% of the arm circumference; the length of the cuff bladder should encircle at least 80% of the arm circumference. It is important to pay attention to cuff placement, stethoscope placement, and the rate of deflation of the cuff (2 mmHg/s). In current practice, a diagnosis of hypertension generally is based on seated, office measurements. However, ambulatory monitoring is not used routinely in clinical practice and generally is reserved for patients in whom white coat hypertension is suspected. Examination of the heart may reveal a loud second heart sound due to closure of the aortic valve and an S4 gallop attributed to atrial contraction against a noncompliant left ventricle. Left ventricular hypertrophy may be detected by an enlarged, sustained, and laterally displaced apical impulse. An abdominal bruit, particularly a bruit that lateralizes and extends throughout systole into diastole, raises the possibility of renovascular hypertension. Kidneys of patients with polycystic kidney disease may be palpable in the abdomen. More extensive laboratory testing is appropriate for patients with apparent drugresistant hypertension or when the clinical evaluation suggests a secondary form of hypertension. Although the impact of lifestyle interventions on blood pressure is more pronounced in persons with hypertension, in short-term trials, weight loss and reduction of dietary NaCl have been shown to prevent the development of hypertension. In hypertensive individuals, even if these interventions do not produce a sufficient reduction in blood pressure to avoid drug therapy, the number of medications or doses required for blood pressure control may be reduced. Dietary modifications that effectively lower blood pressure are weight loss, reduced NaCl intake, increased potassium intake, moderation of alcohol consumption, and an overall healthy dietary pattern (Table 298-7). Based on results of meta-analyses, lowering of blood pressure by limiting daily NaCl intake to 4. Several long-term, prospective, randomized clinical trials have reported that a reduced salt intake results in a decreased incidence of cardiovascular events. Potassium and calcium supplementation have inconsistent, modest antihypertensive effects, and, independent of blood pressure, potassium supplementation may be associated with reduced stroke mortality. Reduction of daily NaCl intake to <6 g (100 meq) augmented the effect of this diet on blood pressure. Fruits and vegetables are enriched sources of potassium, magnesium, and fiber, and dairy products are an important source of calcium. The degree of benefit derived from antihypertensive agents is related to the magnitude of the blood pressure reduction. Hypertension control is the single most effective intervention for slowing the rate of progression of hypertension-related kidney disease.
Generic 40 mg telmisartan
This inconsistency argues that the results of a clinical trial may not apply to individual patients blood pressure 50 over 20 buy 80 mg telmisartan amex, even within a carefully selected patient population. It also suggests that, at a minimum, a sepsis intervention should show a significant survival benefit in more than one placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial before it is accepted as routine clinical practice. In one attempt to reduce patient heterogeneity in clinical trials, experts have called for changes that would restrict these trials to patients who have similar underlying diseases. Agents in ongoing or planned clinical trials include intravenous immunoglobulin, a polymyxin B hemofiltration column, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, which has been reported to restore monocyte immunocompetence in patients with sepsis-associated immunosuppression. It is possible that neutralizing one of many different mediators may help patients who are very sick, whereas disrupting the mediator balance may be harmful to patients whose adaptive defense mechanisms are working well. In theory, such a strategy would improve care by mandating measures that seem to bring maximal benefit, such as the rapid administration of appropriate antimicrobial therapy, fluids, and blood pressure support. Caution may be engendered by the fact that three of the key elements of the initial algorithm were eventually withdrawn for lack of evidence; moreover, the benefit of the current sepsis bundles has not been established in randomized controlled clinical trials. Death is significantly more likely in severely septic patients with preexisting illness. The most commonly identified etiologic agents in patients who die are Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis. Individuals with preexisting comorbidities are at greater risk of dying of severe sepsis at any age. Cognitive impairment may be significant in survivors, particularly those who are elderly. In developed countries, most episodes of severe sepsis and septic shock are complications of nosocomial infections. These cases might be prevented by reducing the number of invasive procedures undertaken, by limiting the use (and duration of use) of indwelling vascular and bladder catheters, by reducing the incidence and duration of profound neutropenia (<500 neutrophils/ L), and by more aggressively treating localized nosocomial infections. Indiscriminate use of antimicrobial agents and glucocorticoids should be avoided, and optimal infection-control measures (Chap. Research is needed to identify patients at increased risk and to develop adjunctive agents that can modulate the septic response before organ dysfunction or hypotension occurs. Ingbar Cardiogenic shock and pulmonary edema are life-threatening conditions that should be treated as medical emergencies. Systolic and diastolic myocardial dysfunction results in a reduction in cardiac output and often pulmonary congestion. A systemic inflammatory response syndrome may accompany large infarctions and shock.
Discount telmisartan 40 mg free shipping
Such secondary injury blood pressure medication hair loss telmisartan 40 mg purchase fast delivery, in turn, may lead to necrosis of hepatocytes; injure bile ducts, producing cholestasis; or block pathways of lipid movement, inhibit protein synthesis, or impair mitochondrial oxidation of fatty acids, resulting in lactic acidosis and intracellular triglyceride accumulation (expressed histologically as microvesicular steatosis). Immune mechanisms may include cytotoxic lymphocytes or antibody-mediated cellular cytotoxicity. As shown in Table 361-1, direct toxic hepatitis occurs with predictable regularity in individuals exposed to the offending agent and is dose-dependent. For example, carbon tetrachloride and trichloroethylene characteristically produce a centrilobular zonal necrosis, whereas yellow phosphorus poisoning typically results in periportal injury. The hepatotoxic octapeptides of Amanita phalloides usually produce massive hepatic necrosis; the lethal dose of the toxin is ~10 mg, the amount found in a single deathcap mushroom. Liver injury, which is often only one facet of the toxicity produced by the direct hepatotoxins, may go unrecognized until jaundice appears. That said, recent data suggest that most agents causing idiosyncratic toxicity are given at a daily dose exceeding 100 mg, suggesting a role for dose-drugs with low potency must be given in higher doses that engender greater chances for "off-target" effects. Adding to the difficulty of predicting or identifying idiosyncratic drug hepatotoxicity is the occurrence of mild, transient, nonprogressive serum aminotransferase elevations that resolve with continued drug use. Extrahepatic manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as rash, arthralgias, fever, leukocytosis, and eosinophilia, occur in about onequarter of patients with idiosyncratic hepatotoxic drug reactions but are characteristic for certain drugs and not others. Both primary immunologic injury and direct hepatotoxicity related to idiosyncratic differences in generation of toxic metabolites have been invoked to explain idiosyncratic drug reactions. The most current data appear to implicate the adaptive immune system responding to the formation of immune stimulatory compounds resulting from phase I metabolic activation of the offending drug. Depending on the agent involved, idiosyncratic hepatitis may result in a clinical and morphologic picture indistinguishable from that of viral hepatitis. So-called hepatocellular injury is the most common form, featuring spotty necrosis in the liver lobule with a predominantly lymphocytic infiltrate resembling that observed in acute hepatitis A, B, or C. Cholestasis may result from binding of drugs to canalicular membrane transporters, accumulation of toxic bile acids resulting from canalicular pump failure, or genetic defects in canalicular transporter proteins. Nodular regenerative hyperplasia, a subtle form of portal hypertension, may also result from vascular injury to portal venous endothelium following systemic chemotherapy, such as with oxaliplatin, as part of adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. Not all adverse hepatic drug reactions can be classified as either toxic or idiosyncratic.
Kor-Shach, 64 years: Dyspnea, weakness, fatigue, oliguBegin hemodialysis ria, and purpura are also common initial symptoms and findings. Portal vein obstruction may be idiopathic or can occur in association with cirrhosis or with infection, pancreatitis, or abdominal trauma.
Ressel, 53 years: Treatment strategies should include physical conditioning, with encouragement to begin at low levels of aerobic exercise and to proceed with slow but consistent advancement. Nontyphoidal Salmonella species, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and E.
Brant, 22 years: The patients subsequently may develop a patchy alveolar infiltrate and air bronchograms, which may progress to acute respiratory failure that is sometimes fatal. An important exception is small-bowel obstruction due to surgical adhesions, which is generally not diagnosed or treated endoscopically.
Yasmin, 57 years: These latter patients produce kappa light chains that do not have the biochemical features necessary to form amyloid fibrils. Hypoxemia and acidosis must be corrected; most patients require ventilatory support (see "Pulmonary Edema," below).
Ines, 65 years: Lesions can be disfiguring, particularly on the face and mation,bloodpressure,hyperlipidemia,andhyperglycemia. Fever, exercise, obesity, sleep apnea, emotional stress, and congestive heart failure can explain transient proteinuria.
Sanuyem, 59 years: However,ithasnotbeen shown that smoking cessation, while having many health benefits, improvesdiseaseactivity. High doses may be given by nebulizer in treating acute severe asthma but should only be given following 2-agonists, because they have a slower onset of bronchodilatation.
Harek, 34 years: Other diagnostic considerations would include celiac disease and ischemic liver disease, which would be readily distinguishable by clinical and laboratory features from autoimmune hepatitis. Although the impact of lifestyle interventions on blood pressure is more pronounced in persons with hypertension, in short-term trials, weight loss and reduction of dietary NaCl have been shown to prevent the development of hypertension.
Ilja, 50 years: However, tracheostomy carries the risk of complications, which occur in 540% of these procedures and include bleeding, cardiopulmonary arrest, hypoxia, structural damage, pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, and wound infection. The upper and lower esophageal sphincters appear as zones of high pressure that relax on swallowing, while the intersphincteric esophagus exhibits peristaltic contractions.
Saturas, 58 years: The goal of the transabdominal approach is to restore normal anatomy by removing redundant bowel and reattaching the supportive tissue of the rectum to the presacral fascia. In the early phase of acute pancreatitis, which lasts 12 weeks, severity is defined by clinical parameters rather than morphologic findings.
Yokian, 35 years: Complications requiring cholecystectomy are much more common in gallstone patients who have developed symptoms of biliary pain. Not all adverse hepatic drug reactions can be classified as either toxic or idiosyncratic.
Sanford, 48 years: Effusions occurring within the first weeks are typically left-sided and bloody, with large numbers of eosinophils, and respond to one or two therapeutic thoracenteses. Diagnosis Clinical clues to the diagnosis include anemia, bone pain, hypercalcemia, and an abnormally narrow anion gap due to hypoalbuminemia and hypergammaglobulinemia.
Mazin, 62 years: Anaerobic coverage by a drug such as metronidazole should be added if gangrenous or emphysematous cholecystitis is suspected. For unexplained reasons, the frequency of lymphoma in patients with celiac disease is higher in Ireland and the United Kingdom than in the United States.
Moff, 36 years: In some instances, radiologic approaches offer advantages over endoscopy for gastroenterostomy placement. Pain is often exacerbated by eating or emotional stress and improved by passage of flatus or stools.
Ingvar, 54 years: A reduction in systemic vascular resistance accompanying an increase in cardiac output indicates that compensatory vasoconstriction is reversing due to improved tissue perfusion. Most patients receiving risperidone have elevated prolactin levels, sometimes exceeding 200 g/L.
Myxir, 37 years: Glomerulonephritis and vasculitis associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and systemic lupus erythematosus have been described in patients with scleroderma. Once chronic hyperventilation is established, a sustained 10% increase in alveolar ventilation is enough to perpetuate hypocapnia.
Falk, 42 years: Other causes of coma and disorientation should be excluded, mainly electrolyte imbalances, sedative use, and renal or respiratory failure. However, typical signs and symptoms of lung infection, such as fever and new infiltrates, may not be present.
Tarok, 40 years: A Whipple procedure, total pancreatectomy, and autologous islet cell transplantation have been used in selected patients with chronic pancreatitis and abdominal pain refractory to conventional therapy. The chemical irritation caused by stomach acid and activated pancreatic enzymes is extreme and secondary bacterial infection may occur.
Kan, 63 years: However, the presence of abnormal brainstem signs does not always indicate that the primary lesion is in the brainstem because hemispheral masses can cause secondary brainstem damage by the earlier described transtentorial herniations. The most common pattern is constipation alternating with diarrhea, usually with one of these symptoms predominating.
Ronar, 52 years: Treatment with inhibitors of the reninangiotensin system decreases the proteinuria. Unfortunately, this treatment has little effect on established arthritis, which, along with chondrocalcinosis, may progress.
10 of 10 - Review by L. Kulak
Votes: 119 votes
Total customer reviews: 119