Prometrium
Prometrium dosages: 200 mg, 100 mg
Prometrium packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills
Order 200 mg prometrium with mastercard
The npt gene (neomycin phosphotransferase) is the most widely used and provides resistance to both kanamycin and the closely related neomycin symptoms 5dp5dt fet 200 mg prometrium order with amex. Aminoglycosides are made by bacteria of the Streptomyces group, which are mostly found in soil. Probably, therefore, the aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes came originally from the same Streptomyces strains that make these antibiotics. Amikacin is a more recent derivative of kanamycin A in which the amino group on the middle ring that gets acetylated is blocked with a hydroxybutyrate group. This made amikacin resistant to all modifying enzymes except one obscure N-acetyl transferase. However, evolution moves on and an enzyme that phosphorylates amikacin has already appeared in some bacterial strains! However, the mechanism of resistance is quite different from aminoglycosides Family of antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis by binding to the small subunit of the ribosome; includes streptomycin, kanamycin, neomycin, tobramycin, gentamycin, and many others kanamycin Antibiotic of the aminoglycoside family that inhibits protein synthesis neomycin Antibiotic of the aminoglycoside family that inhibits protein synthesis npt gene Gene for neomycin phosphotransferase. One member, kanamycin B, can be modified by a variety of covalent modifications, such as phosphorylation, acetylation, or adenylation. A variety of bacterial enzymes make these modifications to prevent kanamycin B from attaching to the small ribosomal subunit. Rather than inactivating tetracycline by modification, R-plasmids produce proteins that pump the antibiotic out of the bacteria. Bacteria are more sensitive than animal cells because tetracyclines are actively taken up by bacterial cells, but not by eukaryotic cells. In tetracycline-resistant bacteria, the antibiotic is actively taken into the cell, but then pumped out again. As there is no similarity between tetracycline and any known transportable nutrients, the purpose of the bacterial transport system that takes up tetracycline and its mechanism of operation are still baffling. However, the Tet-resistance protein is part of a large family of sugar transporter proteins, and may have evolved from recognizing sugar to recognizing tetracycline. Both resistance levels are due to production of proteins that are found in the cytoplasmic membrane and actively expel tetracycline from the cell. Tetracycline enters the cell as the protonated form by an active transport system. The Tet-resistance protein uses energy to expel the Tet-Mg2 complex by proton antiport.
Discount prometrium on line
Since the phage cannot integrate treatment using drugs is called prometrium 200 mg order online, pbio must enter the lytic phase and are thus obligate plaque formers (hence, the "p" in pbio). If wildtype helper phage is added, the int function is restored, and the phage forms lysogens. Cloning vectors derived from lambda are widely used in genetic engineering (see Ch. Transfer of Plasmids between Bacteria Transferability is the ability of certain plasmids to move from one bacterial cell to another. Many medium-sized plasmids, such as the F-type and P-type plasmids, are able to move and are referred to as Tra (transfer-positive). The donor cell manufactures a sex pilus that binds to a suitable recipient and draws the two cells together. In real life, mating bacteria actually tend to cluster together in groups of five to ten. Since plasmid transfer requires over 30 genes, only medium or large plasmids possess this ability. Donor cells are sometimes known as F or "male" and recipient cells as F or "female" and conjugation is sometimes referred to as bacterial mating. Thus, bacterial mating is not at all equivalent to sexual reproduction among higher organisms. This is used as a template for the synthesis of a new second strand to replace the one that just left. When the sex pilus is assembled, its protein subunits travel through the channel in the basal structure (also known as the transfer apparatus). After donor and recipient have made contact, the pilus is retracted and the pilus subunits return through the same channel. This brings the two cells into contact and leaves the basal structure bridging the inner and outer membranes of the donor and in contact with Transferable plasmids move from one cell to another via the conjugation bridge. First, the cell containing a Tra plasmid manufactures a rod-like extension on the surface of the outer membrane called a sex pilus. The sex pilus binds to a nearby cell and pulls the two cells together by retracting. Once the cells are in contact, the basal structure of the pilus makes a connection between the two cells known as the conjugation bridge. This connects the cytoplasm of the two cells, so the plasmid can transfer a copy of itself to the recipient cell. The two strands start to separate and synthesis of a new strand starts at the origin (green strand). Once the complete plasmid has been transferred, it is re-ligated to form a circle once again. The details of individual components vary somewhat between organisms, depending on the specific role of the system. Although ColE and other small plasmids are not self-transferable, they are often mobilizable (Mob).
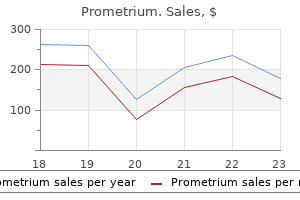
Discount prometrium 100 mg buy on line
Often treatment warts purchase prometrium australia, the inverted repeats at the ends of insertion sequences are not quite exact repeats. Insertion sequences only encode a single enzyme, the transposase, the enzyme needed for movement. Between the inverted repeats is a region that actually contains two open reading frames, orfA and orfB. The transposase itself is derived from both open reading frames by a frameshift that occurs during translation. Since the frameshift is a rare event, transposase is produced in very low amounts, which ensures that the transposons do not move very often. When no frameshift occurs during translation, only the first open reading frame, orfA, is converted into a protein. This gene product is a transcriptional regulator that controls the production of transposase and of itself. Two open reading frames within the insertion sequence encode the transposase gene. When a frameshift occurs during translation, transposase is produced and the insertion sequence "jumps" to a new location. This protein regulates transposition by turning off transcription of orfA and orfB at the promoter. This, in turn, allows transfer of chromosomal genes by the F-plasmid as explained in Chapter 25. Originally their presence was recognized because movement of the insertion sequence inactivated genes with a noticeable phenotype. Such insertion mutations usually abolish gene function completely and are often polar to downstream genes of the operon. Second, the whole structure between the two outermost inverted repeats may move as a unit, that is as a composite transposon. Many of the well-known bacterial transposons that carry genes for antibiotic resistance or other useful properties are composite transposons. Three of the best known are Tn5 (kanamycin resistance), Tn9 (chloramphenicol resistance), and Tn10 (tetracycline resistance). Usually the pair of insertion sequences at the ends of the transposon is inverted relative to each other, as in Tn5 and Tn10. Once a useful composite transposon has assembled by chance, natural selection will act to keep the parts together. Mutations accumulate that inactivate the innermost pair of inverted repeats, which prevents the insertion sequences from jumping independently. The result is that the two ends and the middle are now permanently associated and always move as a unit.
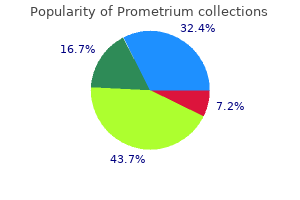
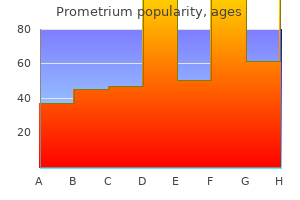
200 mg prometrium purchase amex
Although histones evolve very slowly medical treatment 80ddb order 100 mg prometrium fast delivery, only eukaryotic cells possess them; they are missing from bacteria. Furthermore, since protein synthesis is so vital, ribosomal components are highly constrained and evolve slowly. Higher organisms traditionally consist of three main groups-plants, animals, and fungi. Despite traditionally being studied by botanists, fungi are actually more closely related to animals than plants. Varieties of single-celled organisms sprout off the eukaryotic tree near the bottom and do not fall into any of the three major kingdoms. Most eukaryotic cells contain mitochondria and, in addition, plant cells contain chloroplasts. These organelles are derived from symbiotic bacteria and contain their own ribosomes (see below). Sequence analysis indicates that fungi are closer to being immobile animals than nonphotosynthetic plants. Chloroplasts Eukaryotic Nucleus Archaea Mitochondria Various groups of eubacteria Eubacteria Life consists of three domains- the Eubacteria, the Archaea, and the eukaryotes. There is as much difference between the two genetically-distinct types of prokaryote as between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Several new groups of Eubacteria and Archaea have been discovered by this method, despite never being cultured. The Archaea versus the Eubacteria Genetically, the Archaea are somewhat closer to the eukaryotes than to the Eubacteria. They both have single circular chromosomes and divide in two by simple binary fission. Of the two groups of prokaryotes, the Archaea are more closely-related genetically to eukaryotes. In addition, the details of protein synthesis and the translation factors of Archaea resemble those of eukaryotes, rather than Eubacteria. Such similarities suggest that the primeval eukaryote evolved from an archaeal-type ancestor. Archaea have no peptidoglycan and their cytoplasmic membrane contains unusual lipids, which are made up from C5 isoprenoid units rather than C2 units as with normal fatty acids. Moreover, the isoprenoid chains are attached to glycerol by ether linkages instead of esters.
Discount 200 mg prometrium otc
The Purkinje fibers (green) are specialized cardiac muscle fibers located within this matrix that are responsible for electrical impulse propagation from the atrioventricular node to the ventricular myocardium 9 treatment issues specific to prisons cheap prometrium 100 mg. Cardiac myocytes are organized in myofibers and are electromechanically coupled by intercalated discs. Small blood vessels and capillaries are located adjacent to myofibers to provide nutrients, deliver oxygenated blood, and remove metabolic by-products. Cardiac fibroblasts become enmeshed in this network, which allows them to contract the endomysial collagen, exerting mechanical force on the myocytes. In the adult myocardium, this network includes the epimysium that surrounds large groups of muscle fibers, the perimysium arising from the epimysium that surrounds smaller groups of muscle fibers and the endomysium, which tethers individual fibers to each other and the adjacent vasculature. In addition to acting as scaffolding for cells and vessels, the collagen network also coordinates the transmission of force generated by myocytes, serving as a viscoelastic medium facilitating compression and recoil properties of the tissue (12). Cardiac fibroblasts are regulated by mechanical and molecular signals during cardiac development. Basement Membrane A specialized area of the matrix termed the basement membrane or basal lamina surrounds all cells in the myocardium except cardiac fibroblasts. An intact basement membrane is necessary for normal cardiac growth and maturation and plays an important role in postnatal cardiac myocyte sarcomerogenesis via activation of integrin-mediated signaling (14). Cardiac Myocytes Cardiac myocytes are derived from two waves of anterior splanchnic mesoderm known as the primary heart field, which forms the primary heart tube. Cardiac myocytes have two major mechanistic functions: Force generation by myofibrils in response to E-C coupling and force transmission across cell bundles mediated by the integration of electromechanical signals at the intercalated disc. Plasma Membrane the plasma membrane (or sarcolemma) is the region of the cell that contains ion pumps, channels, and exchangers that contribute to action potential propagation, as well as maintenance of proper ionic and chemical gradients. In the rodent heart, the low digitalis affinity 1 isoform predominates through all phases of development, while there is a postnatal transition from the neonatal 3 isoform to the adult 2 isoform that occurs within the second week of postnatal life (19). B: the interstitial connective tissue consisting of perimysial and endomysial components presents a honeycomb shape. C: the endomysium (arrow) supports and connects individual cardiomyocyte fascicles. This exchanger is bidirectional and capable of moving Ca2+ in either direction across the sarcolemma.
Buy prometrium american express
The carotenoid pigments provide the red medications in canada buy prometrium toronto, yellow, and green colors typical of these insects. Red and green versions of the aphids are found that are recognized and eaten by different predators. The green variants have a defect in carotenoid desaturase and consequently lack the red version of the pigment. The chemical theory of the origin of life was put forward by the Russian biochemist Alexander Oparin in the 1920s. Polymerization of monomers into biological macromolecules requires the removal of water. The autotrophic theory of origins argues that the earliest life forms used energy released by the reaction of iron and sulfur compounds. New genes may also be created by mixing and shuffling segments of pre-existing genes. Although the Archaea share prokaryotic cell structure with the Bacteria, they are more closely related to Eukaryotes genetically. The mitochondria and chloroplasts of eukaryotic cells are derived from symbiotic bacteria that gradually lost their independence. Several protozoan lineages have arisen by engulfing other single-celled algae and thus have chloroplasts acquired by what is known as secondary endosymbiosis. Horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer occurs when genetic information is passed "sideways" to a relatively unrelated organism (as opposed to a direct descendent). The extent of horizontal gene transfer is difficult to measure accurately and has often been over-estimated. What alternatives may have allowed polymerization of amino acids on the early Earth Describe an example of how gene duplication can lead to the formation of a gene family. Describe a process by which many new genes can evolve that occurs mostly in plants. What could you infer about a protein that evolves very quickly and whose sequence is highly divergent among various species What molecules are most appropriate to determine evolutionary relatedness between two closely-related species Explain how it is possible to sequence a gene without actually isolating or culturing the organism. Do scientists believe horizontal gene transfer is less common, as common, or more common than was thought previously Name three different regions of a nuclear genome that accumulate mutations faster. There are rooted trees where the base represents the basic sequence on which the other organisms are compared, and there are unrooted trees that only show the relationship between the sequences or organisms. Each branch of the tree represents one of the sequences or organisms, and the bifurcation point represents a common ancestor between the two branches. The first step to making a phylogenetic tree is to align the sequences to make comparisons, determine how similar the sequences are in a pairwise manner (comparing two at a time), and group the sequences based on similarity. Based on the sequence information, place each sequence on the rooted tree drawn below. Understanding molecular evolution is actually very complex, and the use of computers is necessary to analyze large numbers of sequence homologies. The primary atmosphere of Earth likely consisted mostly of very light gases, such as hydrogen and helium.
Cheap prometrium 100 mg without a prescription
Here brazilian keratin treatment prometrium 100 mg lowest price, they will just be introduced to give some idea of the range of gene creatures that share the biosphere with the more traditional life forms. At the bottom, a variety of gene creatures are shown whose relationships are still mostly uncertain. They range from those causing major diseases of cellular organisms to those whose existence is scarcely noticeable without sophisticated molecular analysis. Viroids and plasmids are self-replicating molecules of nucleic acid that lack the protein coat characteristic of a virus. Like a virus, they are released into the environment and must find a new cell to infect. Although some plasmids can be transferred from one host cell to another, they have no extracellular phase and so unlike viruses or viroids, they do not destroy their host cell. Plasmids are widely used to carry genes during many genetic engineering procedures. They contain no nucleic acid and possess genetic information only in the sense of being gene products. Prions infect cells in the nervous systems of animals and cause diseases, the most famous of which is bovine spongiform encephalopathy, better known as mad cow disease. The prion protein is actually a misfolded version of a normal protein found in nerve cells, especially in the brain. When the prion infects a nerve cell, it promotes the misfolding of the corresponding normal proteins, which causes the cell to die. The prion protein is actually encoded by a gene belonging to the host animal that it infects. Cells have a membrane layer that separates the inside portion or cytoplasm from the external environment. Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall, cytoplasmic membrane, soluble cytoplasmic enzymes, and a nucleoid region that holds a single chromosome. Eubacteria are the most familiar prokaryotes since the members of this domain tend to cause human diseases. Archaea and eubacteria are both considered prokaryotes since they lack a nucleus surrounding their chromosome(s). Eukaryotes have nuclear envelopes to surround their chromosomes, a cytoskeleton to give the cells shape, and organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Eukaryotes include a great variety of species that are classified into: kingdoms, phyla, class, order, family, followed by genus and species. Model organisms are used to investigate how life develops, exists, and reproduces. Model organisms can be grown easily and reproduce fast, have their genomes completely sequenced, can be studied in each stage of their development, and are amenable to genetic manipulations.
Purchase prometrium with mastercard
How might changing the conditions of the purification change the outcome of the experiment Do you think the authors could have missed some of the binding proteins for Oct4 simply because of the purification method Hence symptoms vaginal yeast infection prometrium 100 mg purchase with mastercard, transcription will not occur unless interaction of the two proteins occurs. In co-immunoprecipitation, the gene for the protein of interest is expressed in animal cells and isolated using antibodies either to the protein itself or to a fusion tag. Any proteins intracellularly associated with the protein of interest are also purified as long as the isolation conditions are conducive for such interactions. Protein Arrays l Protein arrays are built using tagged proteins and are screened by a variety of approaches. Protein Interactions and the Interactome e313 Protein arrays are used for the global analysis of proteins within cells. Analysis of proteins includes the biochemical and enzymatic analysis as well as protein-protein interactions. These arrays are constructed by tagging proteins with chemical groups (for example, by genetic engineering of their genes) which are then used to anchor the fusion proteins to a solid surface. These bound proteins are then assayed for enzymatic activity or protein interactions with the help of an easily detectable substance, such as a fluorescent dye. Protein arrays use fusion tagged proteins for immobilization of the protein on the solid surface. Metabolomics provides a means to analyze differences in mutant strains of bacteria and growth conditions by identifying different metabolic intermediates present within the samples. Conceptual questions the field of functional genomics attempts to assign function to an unknown gene whose physiological role is not well-understood. However, protein sequence similarity does not necessarily translate into functional similarity. The authors used a recombinant protein with unknown function and incubated it with cellular extract from Mtb. How does the field of metabolomics change the assignment of putative functions to unknown gene products Discussion points In this paper, the researchers used a metabolomics approach to reassign the function of an Mtb enzyme based upon the metabolic intermediates. Do you think that changing the growth conditions could affect the outcome of their experiment Although some genes are expressed all the time, most are expressed only under conditions where they are needed. Transcription is the first step in gene expression and, not surprisingly, is the site of a great deal of regulation, which is the topic of the present chapter. However, the mere presence of a protein is not sufficient to ensure a correct physiological response and the activity of many proteins is regulated after they are made, as discussed in Chapter 14. Gene Regulation Ensures a Physiological Response In bacteria such as Escherichia coli, about 1,000 of the 4,000 genes are expressed at any given time.
Boss, 32 years: This prevents the enhancer elements from reaching the Igf-2 gene, and so they loop around to interact with the H19 gene.
Mason, 41 years: Rotation of the myocardial wall of the outflow tract is implicated in the normal positioning of the great arteries.
Carlos, 64 years: Not surprisingly, the ribosomes themselves are rarely modified, except in such general cases as putting whole ribosomes on standby to reduce the overall rate of protein synthesis in non-growing cells, as discussed in Chapter 13.
Orknarok, 24 years: For example, in 1997 the Hudson Foods plant in Columbus, Nebraska was forced to shut down and 25 million pounds of ground beef were recalled.
Kulak, 61 years: Nuclear medicine gastric emptying studies tend not to add further information if contrast studies and endoscopy are performed.
Riordian, 29 years: In still other cases, some mutations will have different penetrance, that is, the mutation will be expressed differently in different individuals or environments.
Rasarus, 37 years: As the cell divides, the restored purple pigment gene is inherited in the daughter cells, and a patch of purple forms on the white kernel.
Rozhov, 48 years: Not only does the virus avoid using capdependent translation itself, but it shuts it down, thus preventing host protein synthesis (see Focus on Relevant Research).
Gancka, 39 years: The World Health Organization preoperative surgical checklist reduced major complications from 11 to 7 %.
Miguel, 23 years: These viruses infect animals and in both cases the outermost viral membrane is derived from the membrane of the previous host cell.
Brontobb, 45 years: In higher animals, aneuploidy is often lethal for the organism as a whole, although certain aneuploid cells may survive in culture under some conditions.
Sulfock, 47 years: Two relatively widespread cases of this are known-alternative splicing and polyproteins.
Nafalem, 43 years: For gain of function mutations to become clinically relevant, the individual needs to be heterozygous.
Moff, 33 years: A graduate student wanted to design her own sequencing chip to determine the sequence of the viral genome she has been studying.
Taklar, 49 years: Other similarities between Archaea and Eubacteria include the presence of a single circular chromosome and the method of cell division is through binary fission.
Gunnar, 22 years: Since each individual nucleotide reduces the voltage across the membrane to a different extent, the actual sequence is determined by measuring the current across the membrane.
Tufail, 27 years: In the following chart, fill in the expected phenotype for each of the genetic mutants using your knowledge of lac operon control.
Kor-Shach, 53 years: The sites that these enzymes typically recognize are four to eight base pair palindromic sequences.
Mortis, 26 years: This switch is postulated to account for the decrease in calcium sensitivity and pH responsiveness found in the adult heart as compared to the neonatal heart (40,41).
10 of 10 - Review by N. Rathgar
Votes: 77 votes
Total customer reviews: 77