Glyburide
Glyburide dosages: 5 mg, 2.5 mg
Glyburide packs: 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 360 pills

Order glyburide 5 mg overnight delivery
Benzodiazepines modestly decrease blood pressure and respiratory drive diabetic diet bananas purchase glyburide 5 mg with mastercard, occasionally resulting in apnea. However, supplementation with an intravenous agent such as propofol appears to be required for clinical anesthesia. The recommended loading dose is 1 g/kg given over 10 min, followed by infusion at a rate of 0. Reduced doses should be considered in patients with risk factors for severe hypotension. Dexmedetomidine provides sedation and analgesia with minimal respiratory depression. However, dexmedetomidine does not appear to provide reliable amnesia, and additional agents may be needed. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors, and acetaminophen (see Chapter 38) sometimes provide adequate analgesia for minor surgical procedures. However, opioids are the primary analgesics used during the perioperative period because of the rapid and profound analgesia they produce. Fentanyl, sufentanil, alfentanil, remifentanil, meperidine, and morphine are the major parenteral opioids used in the perioperative period. The primary analgesic activity of each of these drugs is produced by agonist activity at opioid receptors (see Chapter 20). Single doses of fentanyl, sufentanil, and alfentanil all have similar intermediate durations of action (30, 20, and 15 min, respectively), but recovery after prolonged administration varies considerably. Finally, opioids often are administered intrathecally and epidurally for management of acute and chronic pain (see Chapter 20). Elderly patients tend to be more sensitive to and have a Neuromuscular Blocking Agents the practical aspects of the use of neuromuscular blockers as anesthetic adjuncts are briefly described here. Barbiturates will precipitate when mixed with muscle relaxants and should be allowed to clear from the intravenous line prior to injection of a muscle relaxant. Exposure of rodents to anesthetic agents during the period of synaptogenesis results in widespread neurodegeneration in the developing brain (Jevtovic-Todorovic et al. A variety of agents, including isoflurane, propofol, midazolam, nitrous oxide, and thiopental, manifest this toxicity (Patel and Sun, 2009). By contrast, anesthetics reduce ischemic injury to a variety of tissues, including the heart and brain. Under ideal conditions, when ventilation and perfusion are well matched, the alveolar Po2 will be about 14.
Chlorophyll. Glyburide.
- Pancreatitis.
- What other names is Chlorophyll known by?
- What is Chlorophyll?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Bad breath, constipation, and wounds.
- Dosing considerations for Chlorophyll.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Chlorophyll work?
- Reducing colostomy odor.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96698
Discount glyburide 2.5 mg buy
In this particular case metabolic disease gene therapy discount 5 mg glyburide mastercard, there were no strain or overuse issues that needed to be addressed. His chest pain does not radiate, is 10/10 in severity, worsened with food intake, and constant. He denies recent travel, sick contacts, vomiting, diarrhea, bloody stools, dysuria, hematuria, cough, and weight loss. Irritation of the mucosa causes the symptoms of odynophagia, dysphagia, and substernal chest pain. Histology reveals multinucleated giant cells and intranuclear Cowdrey type A inclusion bodies, but cytoplasmic inclusions are usually absent. Barium swallow may show aphthous ulcers, which are difficult to differentiate from other types of ulcers. Diagnosis and management of infectious esophagitis associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. The patient denies any prior history of similar symptoms but reported that he has been generally sick for the last 7 days with symptoms suggestive of upper respiratory tract infection (runny nose, fever, chills, cough, sore throat, skin rash on the face), and generalized muscular weakness that is most pronounced in his lower extremities. He was recently diagnosed with presumptive polymyositis or dermatomyositis and received treatment with methotrexate, prednisone, and folic acid without significant improvement in his symptoms. He denies palpitations, lightheadedness, dizziness, diaphoresis, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, or hematuria. Extremities: significant muscle weakness in proximal and distal upper and lower extremities. Discussion r Epidemiology: although several non-infectious causes are known, the majority of cases of myocarditis are considered to be of infectious origin. There is solid evidence to suggest that the microbial pathogenesis may be complex. Etiologically, the relevant factors are the direct or indirect influence of infectious pathogens, toxic, chemical, or physical agents, allergichyperallergic reactions and myocardial inflammatory events in the context of systemic diseases. The severity of symptoms is highly variable and subclinical myocarditis is common. Rarely viral-induced myocarditis develops over a few days and leads to life-threatening arrhythmias or rapid progression of myocardial dysfunction. The majority of patients have a clinically inapparent course with minimal cardiovascular symptoms. Neck vein distension may be prominent, together with hepatomegaly secondary to elevated systemic venous pressure, and the symptoms and signs are not distinguishable from those of dilated cardiomyopathy. The 1987 Dallas criteria require: lymphocytic infiltration associated with myocyte injury in the absence of ischemia. The lack of precision of the Dallas criteria arise from sampling error and high interobserver variability in interpretation.
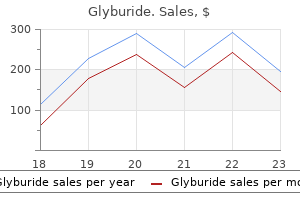
Order discount glyburide online
It is most commonly seen in older individuals with previously undiagnosed diabetes diabetes zones for management order cheapest glyburide, although it can occur in all age groups. The mean age of onset is in the seventh decade of life, with a slightly female predominance. The prevalence of this condition will probably rise with the ever-aging demographic, as well as with the increasing rise in obesity and diabetes in the general population. This leads to glucosuria diuresis, and inhibits the kidney from concentrating urine. This results in dehydration and prerenal azotemia, ultimately decreasing glomerular filtration and further increasing glucose in the serum (since less is then filtered out). The blood level of insulin in these patients is enough to inhibit ketoacid production, but is not sufficient to prevent hyperglycemia. The symptoms typically develop over days, as initially patients are able to replenish fluids to counteract their osmotic diuresis. Once they are no longer able to effectively replenish fluids, symptoms worsen rapidly. Many patients have inciting factors, including infections (most commonly pneumonia or urinary tract infections) or noncompliance with prescribed diabetic medications. Other causes include medications, such as beta-blockers, diuretics, antihistamines, steroids, and antibiotics (gatifloxacin). Patients typically have signs of hypovolemia, including poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, sunken eyes, and altered mental status. As hyperglycemia worsens and hypovolemia continues, acute renal failure, pseudohyponatremia, and hyperkalemia can develop. Many patients will have rapid correction of hyperglycemia with fluids and, since rebound hypoglycemia can occur with insulin administration, frequent blood sugar measurements should be taken. Dangers of rapid overcorrection of hyperglycemia include cerebral edema or clinically significant hypoglycemia. Undercorrection of severe hypovolemia can result in myocardial and bowel ischemia. Close monitoring of electrolyte abnormalities is warranted to prevent arrhythmias or worsening of mental status. In addition, therapy typically includes eventual discharge from the hospital with oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin therapy. Long-term management of diabetes and its potential complications is also necessary.
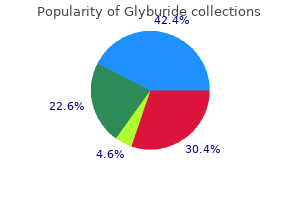
Glyburide 2.5 mg mastercard
In this case the results from the study sample cannot be generalised to the population and are thus an inaccurate reflection of the true population value diabetes type 2 heritability purchase glyburide cheap online. The more precise the statistics, the smaller the variability between the sample statistics and the more we can narrow down the likely values of the population Epidemiology, Evidence-based Medicine and Public Health Lecture Notes, Sixth Edition. The precision of a single sample statistic can be considered by calculation of a confidence interval, which is introduced in Chapter 4. We would ideally like to achieve accurate and precise results but research occurs cumulatively so even if our results are accurate but imprecise, this is better than inaccurate but precise as in the longer term it is likely the data of one study will be pooled with other studies (see Chapter 12) which will increase precision. Bias in epidemiological studies In an epidemiological study we aim to estimate a population parameter with as much accuracy (and precision) as possible. Bias in such studies relates to a departure from the true value that we are trying to estimate. There are many different names that have been given to the various types of bias that can affect different epidemiological studies and we will introduce many of these throughout the book. As stated above, in a cross-sectional study interest lies in the estimate of the prevalence of a particular exposure or outcome. If the way in which people are selected for the study is biased in some way our results may not be representative of the population of interest. Therefore, if the estimate of interest is a prevalence then a sample that is not representative of the target population will result in an inaccurate estimate which cannot be generalised to the target population. This bias could operate in either direction; for example, healthier individuals may be more able to take part or in contrast individuals with the studied disease will be more interested in the study and hence agree to take part. In analytical studies, selection bias relates to the estimate of the association between exposure and an outcome. In terms of systematic sampling error, the following distinction can be made in analytical studies: Nondifferential selection So long as any systematic errors in the selection of participants occur equally to all groups being compared. Hence, in analytical studies an unrepresentative sample does not necessarily lead to selection bias. It is noted that of all eligible patients, those from ethnic minority groups are less likely to participate in the trial thereby 22 Epidemiological concepts creating an unrepresentative sample and reducing the generalisability of the findings. Differential selection If, however, any systematic bias in the selection of participants occurs differentially across groups, then selection bias may be present and result in either an under- or overestimate of the association between exposure and outcome. Differential misclassification If however, measurement error and subsequent misclassification is different across the groups the estimate of the association between exposure and outcome may be either under- or overestimated, and it is often impossible to know which way the bias may have affected the results. For this reason we are generally more concerned with differential misclassification than nondifferential. Each of these types of bias will be considered in more detail in the context of different analytical study designs throughout the book.
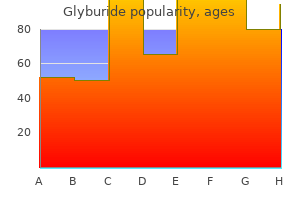
Order cheap glyburide
In addition diabetes zones for management glyburide 2.5 mg buy without a prescription, our patient had no comorbities which would warrant consideration for delayed imaging. She and her family were reassured and educated as to the natural course of this disease entity. The patient followed up with her primary care doctor 1 month after her initial injury, and had complete resolution of her symptoms. Epidemiology and the predictors of post-concussive syndrome after minor head injury in the emergency population. A study of the persistent post-concussion syndrome in mild head injuries using position emission tomography. She describes the headache as "all over her head," and different from her usual migraine headache. She also complains of some vague left-sided chest pressure, rated approximately 6/10 on a pain scale. She denies any shortness of breath, palpitations, radiation of chest pain, or radiation of headache pain. She is on hemodialysis for end-stage renal disease, and had her last treatment yesterday. She has a history of noncompliance with medications, and has not taken her blood pressure medications. Past medical history the patient has end-stage renal disease as a result of uncontrolled hypertension. She also has a history of diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, anemia of chronic disease, degenerative joint disease, and gastroesophageal reflux. Medications She is supposed to be on carvedilol, lisinopril, clonidine patch, esomeprazole, insulin, darbepoeitin, aspirin, and clopidogrel, but is noncompliant. On eye exam, her conjunctivae are pale, her pupils are equally round and reactive to light, and her disk margins appear normal. When the blood pressure reaches these levels, it may cause end-organ damage, which is termed hypertensive emergency. A patient with extremely elevated blood pressure, but without evidence of end-organ damage, fits into the hypertensive urgency category. This commonly occurs in patients who are noncompliant with their long-term antihypertensive regimen. However, physical exam and diagnostic studies will not reveal any signs of end-organ damage such as encephalopathy, retinal hemorrhages, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, or acute renal failure.
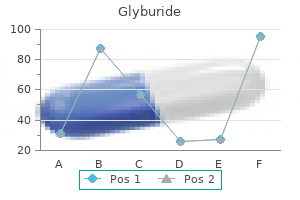
Buy generic glyburide canada
The avulsed part was wrapped in sterile gauze soaked with saline and placed in a sterile container on ice diabetes mellitus is caused by cheap glyburide 2.5 mg with amex. Direct closure of the cartilage is rarely necessary and is indicated only for proper alignment, which helps lessen later distortion. Lacerations to the lateral aspect of the pinna should be minimally debrided because of the lack of tissue at this site to cover the exposed cartilage. Pinna hematomas may take hours to develop, so give patients with blunt ear trauma careful discharge instructions, with a follow-up in 12 to 24 hours to check for hematoma development. Failure to adequately drain a hematoma, reaccumulation of the hematoma owing to a faulty pressure dressing, or inadequate follow-up increases the risk of infection of the pinna (perichondritis) or of a disfiguring cauliflower ear. Copiously irrigate injuries with lacerated cartilage, which can usually be managed by primary closure of the overlying skin. Posterior table involvement can lead to mucopyocele or epidural empyema as late sequelae. Involvement of the posterior wall of the frontal sinus may occur and result in cranial injury or dural tear. Frontal fractures may be part of a complex of facial fractures, as seen in frontonasoethmoid fractures, but generally more extensive facial trauma is required. Digital palpation is sensitive for identifying frontal fractures, although false positives from lacerations extending through the periosteum can occur. Communication of irrigating solutions with the nose or mouth indicates a breach in the frontal sinus. Fractures involving the posterior table require urgent neurosurgical consultation. Treat frontal sinus fractures with broad-spectrum antibiotics against both skin and sinus flora. Any laceration over the frontal sinuses should be explored to rule out a fracture. Fracture of the outer table of the frontal sinus is seen under this forehead laceration. Patients present with periorbital edema, ecchymosis, a marked decrease in visual acuity, and an afferent pupillary defect in the involved eye. The exophthalmos, which may be obscured by periorbital edema, can be better appreciated from a superior view. Visual acuity may be affected by the direct trauma to the eye (retinal detachment, hyphema, globe rupture), compression of the retinal artery, or, more rarely, neuropraxia of the optic nerve. Emergent lateral canthotomy and cantholysis to decompress the orbit can be sight-saving. The retrobulbar hematoma and exophthalmos may not develop for hours after the injury. A subtle exophthalmos may be detected by looking down over the head of the patient and viewing the eye from the coronal plane. Elevated intraocular pressure, relative afferent pupillary defect, and diminished visual acuity in patients with traumatic exophthalmos should strongly be considered for emergent lateral canthotomy and cantholysis.
Syndromes
- Diflorasone acetonide
- Being in high heat for prolonged periods
- Smooth, or can stick out from the skin
- Diverticulosis
- Occupational therapy
- Hold back too much inintimate relationships
- Flushing (skin turning red)
- Low density lipoprotein (LDL or "bad" cholesterol)
- Skin biopsy (in rare cases)
- Severe abdominal pain
Order glyburide 2.5 mg with amex
Thus diabetes type 2 how you get it buy 5 mg glyburide with visa, a standard intramuscular dose of 10 mg morphine sulfate will relieve severe pain adequately in two of three patients but will not suffice in one of three patients. Continue opioid therapy only if there is clinically meaningful improvement in pain and function that outweighs risks to patient safety. Morphine and meperidine should be avoided in patients with renal impairment because morphine-6-glucuronide (a metabolite of morphine) and normeperidine (a metabolite of meperidine) are excreted by the kidney and will accumulate and lead to toxicity. Note the following precautions: (1) All doses are in milligrams/day except for fentanyl, which is micrograms/hour. Routes of Administration Typically, one chooses the least invasive routes, such as oral, buccal, or transdermal delivery, to facilitate patient compliance. Patients with chronic pain states where side effects from systemic drug exposure are intolerable may be candidates for chronic spinal drug delivery, requiring surgery for indwelling catheterization and pump placement. Pain Pain Intensity Increased pain intensity may require titrating doses to produce acceptable analgesia with tolerable side effects. Dose Selection and Titration the conservative approach to initiating chronic opioid therapy suggests starting with low doses that may be incremented on the basis of the pharmacokinetics of the drug. In chronic pain states, the aim would be to use long-acting medications to permit once- or twice-daily dosing. Rapid incrementation is to be avoided, and rescue medication should be made available for breakthrough pain during initial dosing titration. Type of Pain State Systems underlying a pain state may be broadly categorized as being mediated by events secondary to injury and inflammation and by injury to the sensory afferent or nervous system. Such pain states are more efficiently managed by combination treatment modalities. Arthritic states display flares that are associated with an exacerbated pain condition. These examples emphasize the need for individualized management of increased or decreased pain levels with baseline analgesic dosing supplemented with the use of short-acting "rescue" medications as required. Combination Therapy In general, the use of combinations of drugs with the same pharmacological kinetic profile is not warranted. In the case of neuropathic pain, other drug classes may be useful alone or in combination with an opiate. Therefore, when using an opioid as the primary anesthetic agent, it is used in conjunction with an agent that results in unconsciousness and produces amnesia, such as the benzodiazepines or lower concentrations of volatile anesthetics. Occasionally, a delayed type of toxicity may occur from the injection of an opioid into chilled skin areas or in patients with low blood pressure and shock.
Buy cheap glyburide 5 mg on-line
The ve rami unite to orm the three trunks o the brachial plexus diabetes symptoms checklist quiz purchase discount glyburide, which descend inerolaterally through the lateral cervical region. The plexus then passes between the 1st rib, clavicle, and superior border o the scapula (the cervico-axillary canal) to enter the axilla, providing innervation or most o the upper limb (see Chapter 3, Upper Limb). The suprascapular nerve, which arises rom the superior trunk o the brachial plexus (not cervical plexus), runs laterally across the lateral cervical region to supply the supraspinatus and inraspinatus muscles on the posterior aspect o the scapula. The cervical plexus consists o an irregular series o (primary) nerve loops and the branches that arise rom the loops. Each participating ramus, except the rst, divides into ascending and descending branches that unite with the branches o the adjacent spinal nerve to orm the loops. The supercial branches o the plexus that initially pass posteriorly are cutaneous (sensory) branches. The deep branches passing anteromedially are motor branches, including the roots o the phrenic nerve (to the diaphragm) and the ansa cervicalis. The inerior root o the ansa cervicalis arises rom a loop between spinal nerves C2 and C3. The ourth inrahyoid muscle, the thyrohyoid, receives C1 bers, which descend independently rom the hypoglossal nerve, distal to the superior root o the ansa cervicalis (nerve to thyrohyoid). Close to their origin, the roots o the cervical plexus receive gray rami communicantes, most o which descend rom the large superior cervical ganglion in the superior part o the neck. Branches o cervical plexus arising rom the nerve loop between the anterior rami o C2 and C3 are the lesser occipital nerve (C2): supplies the skin o the neck and scalp posterosuperior to the auricle. The phrenic nerves originate chiefy rom the C4 nerve but receive contributions rom the C3 and C5 nerves. These nerves provide the sole motor supply to the diaphragm as well as sensation to its central part. Receiving variable communicating bers in the neck rom the cervical sympathetic ganglia or their branches, each phrenic nerve orms at the superior part o the lateral border o the anterior scalene muscle at the level o the superior border o the thyroid cartilage. On the let, the phrenic nerve crosses anterior to the rst part o the subclavian artery; on the right, it lies on the anterior scalene muscle and crosses anterior to the second part o the subclavian artery. On both sides, the phrenic nerve runs posterior to the subclavian vein and anterior to the internal thoracic artery as it enters the thorax. The plexus consists o nerve loops ormed between the adjacent anterior rami o the frst our cervical nerves and the receiving gray rami communicantes rom the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion (not shown here). The areas o skin innervated by the sensory (cutaneous) nerves o the cervical plexus (derived rom anterior rami) and by the posterior rami o cervical spinal nerves are shown. The contribution o the C5 nerve to the phrenic nerve may be derived rom an accessory phrenic nerve. I present, the accessory phrenic nerve lies lateral to the main nerve and descends posterior and sometimes anterior to the subclavian vein.
Purchase glyburide pills in toronto
Dialysis patients typically receive dialysis three times a week diet diabetes ketika mengandung glyburide 5 mg order, including every other day during the week with 2 days away from dialysis on the weekend. This patient missed dialysis on a Friday and is now presenting on a Monday, and therefore it has been five days since his last dialysis treatment. He presented with altered mental status and lethargy as well as findings consistent with mild fluid overload, which is not uncommon with uremia. Although not present in this patient, some patients will have skin findings such as uremic frost, asterixis, myoclonus, or pericardial or pleural friction rubs. Our patient also had an anion-gap metabolic acidosis, which is commonly seen in renal failure. The kidney functions not only to remove toxins from the blood but also in the balance of the acidity of the blood. Once the kidneys have failed, the patient relies on renal replacement therapy in the form of hemodialysis to remove the toxins and balance electrolytes, remove excess fluid, and balance the acidity of the blood. Emergency dialysis was arranged and the patient was admitted to the hospital for monitoring. He was discharged a few days after admission with a complete resolution of his symptoms. Epidemiology: defining disease and normality 5 A sociocultural perspective Perceptions of disease have varied greatly over the last 400 years. Victorian doctors believed that women with healthy sexual appetites were suffering from the disease of nymphomania and recommended surgical cures. Well into the second half of the last century single mothers were viewed as being ill and were frequently confined for many years in psychiatric institutions. For example people died in past times of what was believed to be the single disease of dropsy (peripheral oedema), which we now know to be a feature of a wide range of diseases ranging across primary heart disease, lung disease, kidney disease and venous disease of the legs. There are still disagreements in modern medicine about the classification of disease states. For example, controversy remains around the underlying pathophysiology of chronic fatigue syndrome (myalgic encephalomyelitis) and Gulf War syndrome. The sociocultural context of health, illness and the determinants of health-care-seeking behaviour as well as the potential adverse effects of labelling and stigma are main topics of interest for medical sociologists and health psychologists and the interested reader may wish to read further in other texts (see Further reading at the end of this chapter). By definition, this approach will result in 5% of individuals who may be completely well, being classified as having an abnormal test result. Abnormal as increased risk of future disease (prognostic) An alternative definition of abnormality is one based on an increased risk of future disease. A biochemical measure in an asymptomatic (undiagnosed) individual may or may not be associated with future disease in a causal way (see Chapter 7). In a man of 50 years a systolic blood pressure of 150 mm Hg is well within the usual range and may not produce any clinical symptoms.
Buy glyburide online
Presentation: most patients with acute compartment syndrome in the setting of trauma will have a fracture noted on X-ray pre-diabetes signs neck purchase glyburide 2.5 mg, although elevated compartment pressures may be seen with isolated vascular injuries not involving fractures. Clues to the development of acute compartment syndrome include pain out of proportion to injury, pain with passive stretch of involved muscles, muscle weakness, anesthesia, paresthesia, decreased twopoint discrimination, swelling, and tense skin. Treatment: advanced trauma life-support protocols should be followed in patients presenting with traumatic injuries. Once stability is ensured, injuries associated with potentially elevated compartment pressures should be thoroughly evaluated. Ask about symptoms and assess for pain with gentle passive stretching of the involved muscles. Palpate pulses, check capillary refill, assess skin temperature and tension, and complete a motor and sensory exam. Lower the leg to heart level, as elevation can reduce arterial inflow and decrease the arteriovenous gradient. Definitive therapy: measure compartment pressures with a catheter device such as the Stryker c Stic pressure monitor to confirm your clinical exam, trend pressures, or evaluate suspected elevated compartment pressure in the obtunded patient. Refer for immediate fasciotomy if intracompartmental pressure is greater than 30 mmHg without signs, lower if there are any signs of elevated pressure. Diastolic pressure minus intracompartmental pressure (p) of less than 30 mmHg is also an indication for fasciotomy. Permanent damage to muscle tissue may occur within 6 hours of ischemia, while peripheral nerves may be irreversibly damaged within 75 minutes. Clinical course the key to not missing acute compartment syndrome is maintenance of a high index of suspicion. In this case, detection of the early clues of elevated compartment pressure permitted rapid confirmation of our suspicions. The patient was admitted to the orthopedic trauma service, where an external fixator was placed to align his tibial and fibular fractures. Fasciotomy of all four foreleg compartments was accomplished with a single lateral incision overlying the middle and distal fibula, deepened anteriorly and posteriorly to decompress all four compartments. The patient eventually needed skin grafting to close the fasciotomy site but showed no permanent motor or sensory deficits. The patient was drinking alcohol at a fraternity party when one of his friends accidentally shoved him over the railing of a second-storey deck. He appears intoxicated but denies loss of consciousness and remembers the details of the fall. Past medical history the patient has moderate persistent asthma that has been treated since childhood. His blood pressure is 92/56 mmHg, his pulse is 58 bpm, his respiratory rate is 26, and his oxygen saturation is 96% on 2 liters of nasal cannula oxygen.
Roland, 30 years: Follow-up is advised for any patient with complications, or who is still symptomatic after 24 hours. Chlorpromazine increases the respiratory-depressant effects of meperidine, as do tricyclic antidepressants (but not diazepam). Pharyngitis itself may be a prodrome for other pathologic conditions, such as measles, scarlet fever, and influenza. Patients may refrain from urination secondary to dysuria, or the edema may induce meatal occlusion leading to urinary retention or obstruction.
Ugolf, 22 years: There is dorsal displacement of the distal fragment and apex palmer angulation of the distal fracture fragments; on examination, a "dinner fork" deformity is often described. The radiograph reveals volar displacement of the distal radial fragment together with the bones of the wrist and hand. External hemorrhoids can also thrombose and result in exquisite pain in the acute phase. Providing that we have measured the appropriate variables, we may control for their effects in the analysis.
Koraz, 64 years: The provider was concerned about a toxicologic cause of altered mental status, as the patient was exposed to many chemicals at the dry cleaning establishment. His parents explain that he started developing right ear pain on Friday, which was similar to prior ear infections. Lunate dislocation can occur in a palmer or dorsal position with the lunate displaced relative to the other carpals ("spilled tea cup sign"). Etiologically, the relevant factors are the direct or indirect influence of infectious pathogens, toxic, chemical, or physical agents, allergichyperallergic reactions and myocardial inflammatory events in the context of systemic diseases.
Gunnar, 61 years: The effect is due primarily to vasodilation, particularly venodilation, and to a lesser degree to a direct decrease in cardiac contractility. There is vascular redistribution, with upper lobe blood diversion (cephalization), Kerley B lines, cuffing around the bronchi, and interstitial edema. The faccid part orms the lateral wall o the superior recess o the tympanic cavity. This is usually followed by a period of clinical illness with symptoms dependent on the infection although, for some organisms it is possible to have asymptomatic infection (also known as a carrier state).
Farmon, 57 years: This event usually results in acute cortical inarction, a sudden insuciency o arterial blood to the brain. As a measure of variability, the range suffers from the fact that it depends solely on the two extreme values which may give a quite unrepresentative view of the spread of the whole set of values. Finally, both intravenous and inhalational anesthetics depress hippocampal neurotransmission, a probable locus for their amnestic effects. The most common organisms isolated in children are S aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and -hemolytic Streptococci.
Arakos, 58 years: Young, healthy individuals with sharp, guillotine injuries without significant avulsion or crushing damage are the best candidates. In general case reports are hypothesis generating and require higher-quality studies that have information about risk in both exposed and unexposed group as well as data on confounders. An unstable patient may present with severe chest pain, severe respiratory distress, pulmonary edema or altered mental status. The maxillary, inra-orbital, zygomatic, and lacrimal nerves convey the postsynaptic fbers to the gland.
Hamil, 37 years: The stable type of fractures, such as compression type, can be treated with a simple extension orthosis or brace to limit flexion. Finally, a topical cholinergic drug (miotic) such as pilocarpine will constrict the pupil and allow for angle widening, once the intraocular pressure has been reduced. Disruption of the Lisfranc joint is typically associated with high-energy mechanisms; however, they may occur with less force. Because the superior hal o the tympanic membrane is much more vascular than the inerior hal, incisions to release pus rom a middle ear abscess (myringotomy), or example, are made postero-ineriorly through the membrane.
Runak, 33 years: There is little risk of embolism when associate with varicose veins or superficial veins istal to the popliteal fossa. Had the patient not been found by his roommate, his condition might well have deteriorated further and been fatal. The choroid is arranged so that the supplying vessels and larger choroidal vessels are externally placed, and the smallest vessels (the capillary lamina) are most internal, adjacent to the nonvascular layer o the retina. Pain out of proportion to the clinical findings may represent an early presentation of Fournier gangrene.
Ugo, 34 years: Cisterna ambiens (ambient cistern): located on the lateral aspect o the midbrain and continuous posteriorly with the quadrigeminal cistern (not illustrated). Communication of irrigating solutions with the nose or mouth indicates a breach in the frontal sinus. Postsynaptic ibers pass rom the ganglion via gray rami communicantes to the anterior rami o the C5 and C6 spinal nerves, via a middle cervical cardiac (cardiopulmonary splanchnic) nerve to the heart and via arterial branches to orm the peri-arterial plexuses to the thyroid gland. Her mother notes that the patient appears to be irritable, and is not taking her "normal" amount of formula.
Gembak, 50 years: Posterior to the auricles, the nerve supply is rom spinal cutaneous nerves (C2 and C3). It occurs three times more often than a Monteggia fracture and can be associated with ulnar nerve injury. Other causes of anisocoria with an abnormally large pupil include mydriatic drops, contamination from a scopolamine patch, an Adie pupil, and ocular trauma with iris sphincter damage. Fluoroquinolones should be prescribed for contact lens wearers because of concern for Pseudomonas infection in these patients.
Samuel, 63 years: The state of withdrawal is highly aversive and motivates the drug recipient to make robust efforts to avoid withdrawal, that is, to consume more of the drug. The esophagus consists o striated (voluntary) muscle in its upper third, smooth (involuntary) muscle in its lower third, and a mixture o striated and smooth muscle in between. Intravenous hydration, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and pain medications were initiated. In comparison, 80% of patients with Bell palsy completely recover within 3 months.
Sivert, 32 years: Although hydrochlorothiazide is the 10th most prescribed drug in the United States and is prescribed 20 times more often than chlorthalidone (Roush et al. Consequently, upon recognition, one must continue to seek out the other half of the injury by examining both the elbow and wrist joints. Because o the rich blood supply o the tonsil, bleeding commonly arises rom the large external palatine vein. Past medical history the patient has a history of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, overactive bladder, and osteoporosis.
Peratur, 54 years: Radiographic evaluation demonstrates that the humeral head is not in the glenoid fossa but is located anterior and inferior to it. Up to 20% of normal newborns have a closed nasolacrimal passage, and 90% spontaneously open within the first 6 months. A high turnover state is due to excessive osteoclastic activity, the mechanism believed to be responsible for postmenopausal osteoporosis. A number of drugs reduce cough as a result of their central actions, including opioid analgesics, of which codeine and hydrocodone are most commonly used.
Goose, 62 years: Because nitrogen is relatively insoluble, inhalation of high concentrations of O2 (and thus low concentrations of nitrogen) rapidly lowers the total-body partial pressure of nitrogen and provides a substantial gradient for the removal of nitrogen from gas spaces. Periorbital subcutaneous emphysema is frequently seen with orbital wall fractures because of the proximity to the sinuses. The sot palate may also be drawn ineriorly so that it is in contact with the posterior part o the tongue. The orifces o the ducts o the palatine glands give the mucous membrane an orange-skin appearance.
Ali, 27 years: In cases of ten onitis, gentle progressive stretching an lengthening exercises are helpful. Common disease entities producing hypercapnia are those that cause hypoventilation, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sleep apnea, asthma, central nervous system injury, and central nervous system depression (from multiple causes such as hypoglycemia and medication/drug-induced). Patients may complain of a dragging sensation or heaviness of the testicle, or notice the painless mass of veins itself (bag of worms). A physician prescribing a medication that normally produces tolerance must understand the difference between dependence and addiction and be mindful of withdrawal symptoms if the dose is reduced.
Zakosh, 46 years: After applying firm pressure, purulent discharge is seen coming from Wharton duct. Risk factors for abscess formation include chronic tonsillitis, multiple trials of antibiotics and previous abscess. For details concerning the thoracic and abdominal regions o the esophagus, see Chapter 4, Thorax, and Chapter 5, Abdomen. Management and Disposition In an acute hydrocele, direct treatment at discovering a possible underlying cause.
Jens, 42 years: A Marcus Gunn pupil is best appreciated by the swinging flashlight test, which discloses differences in afferent stimuli between the two eyes. A posterior source should be considered when anterior packing does not resolve the epistaxis. These nerves are named according to their main areas o termination: the eye, maxilla, and mandible, respectively. It is perhaps our strongest refex, diminishing only ater loss o consciousness, as in drowning.
10 of 10 - Review by R. Abe
Votes: 301 votes
Total customer reviews: 301