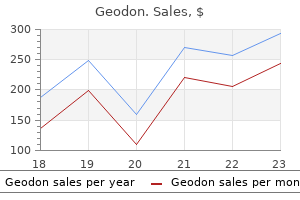
Geodon
Geodon dosages: 80 mg, 40 mg, 20 mg
Geodon packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 360 pills

40 mg geodon buy free shipping
Symptoms that bring the patient to medical attention include changes in mental status depression symptoms exercise 20 mg geodon buy mastercard, headache, and fever. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia was previously a common pathogen in the immunocompromised host. Given the low morbidity associated with the prophylactic regimens, no patient should be excluded. Traditionally, treatment of Legionella pneumonia has been with erythromycin, but quinolones also have proved effective and have the advantage of not interacting with immunosuppressive agents such as cyclosporine or tacrolimus. Gingival hyperplasia and hirsutism are encountered frequently during cyclosporine and corticosteroid treatment, whereas glucose intolerance is reported more often with tacrolimus than cyclosporine therapy. Hyperkalemia, hyperuricemia, hypophosphatemia, and hypomagnesemia are manifestations of renal tubular dysfunction and usually can be controlled by adjusting the dose according to drug levels. Nephrotoxicity is the most clinically significant adverse effect of both drugs and manifests as acute azotemia. This effect is largely reversible after reducing the dose of the drug and providing adequate hydration. Occasionally, progressive chronic renal disease can develop in as many as 5% of patients, which is usually irreversible and may require renal replacement therapy or renal transplantation (Aberg et al, 2007). Other renal effects of cyclosporine include chronic tubular dysfunction and, rarely, hemolytic uremic syndrome. These symptoms are not uncommon in many early transplant patients, and it may be difficult to differentiate the cause, although drug toxicity is usually inferred. Alternative forms of the drug may be helpful, as well as dose modification or discontinuation (Barrera-Pulido et al, 2009; Bunnapradist et al, 2006). Of these, 60% have mild hepatitis, whereas 30% develop a more severe pattern, as seen on histologic examination. Azathioprine was used frequently in the past, especially in those patients who received triple-drug therapy. Mycophenolate mofetil has essentially replaced azathioprine in the immunosuppression regimen after liver and kidney transplantation. After the initiation of immunosuppressive therapy, development of infection and acute toxicity are usually seen early during treatment, whereas lymphoproliferative disorders and other malignancies are longterm sequelae, as previously discussed. The causes are multifactorial and include corticosteroid therapy, bed rest, and cholestasis. This late improvement is probably because of a reduction in corticosteroid therapy use and the resolution of the pretransplantation condition that was deleterious to skeletal health. Avascular necrosis and vertebral body collapse may also occur, especially in those maintained on corticosteroid therapy. In addition to the acute neurophysiologic changes associated with fluid and electrolyte shifts during the perioperative period, anxiety and depression are common psychiatric conditions observed in many transplant patients.
Diseases
- Dyskeratosis follicularis
- Retinopathy, arteriosclerotic
- Microcephaly pontocerebellar hypoplasia dyskinesia
- Posterior urethral valves
- Glaucoma, hereditary adult type 1A
- Chromosome 4, trisomy 4q25 qter
- Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy 3
- Syringobulbia
- Winter Harding Hyde syndrome
- CDG syndrome type 1C
Discount 80 mg geodon with visa
Muratore A depression nimh order geodon without a prescription, et al: Repeat hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases: a worthwhile operation Saxena A, et al: Surgical resection of hepatic metastases from neuroendocrine neoplasms: a systematic review, Surg Oncol 21(3):30, 2012. Shirabe K, et al: Postoperative liver failure after major hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in the modern era with special reference to remnant liver volume. Torzilli G, et al: Upper transversal hepatectomy, Ann Surg Oncol 19(11):2596, 2012.
Buy geodon cheap online
Major hemobilia causes shock and possible death from exsanguination bipolar depression 35 purchase geodon australia, unless an emergency intervention is performed. Occult or minor hemobilia, if continued, may result in chronic secondary anemia, as can be seen with biliary tract neoplasms (Ahmad et al, 2010). Gastrointestinal bleeding in connection with biliary symptoms should arouse the suspicion of biliary tract hemorrhage. Biliary colic symptoms are seen in 70% of pateints; and jaundice is identified in up to 60%. All three findings are seen in approximately one quarter of patients with hemobilia (Green et al, 2001). In addition to retained blood clots within the biliary tree producing the signs and symptoms of obstructive jaundice, patients may initially present with ascending cholangitis with accompanying high fever and rigors (Kurisu et al, 2005). The fate of blood in the biliary tree depends on a variety of factors, including the rate of bleeding, the source (arterial or venous), the timing (continuous or intermittent), and the frequency (solitary or recurrent). A sudden onset of massive bleeding, as in a ruptured hepatic artery aneurysm, may produce such a rapid amount of blood that the initial clinical presentation is hematemesis or melena. The formation of clots depends on the quality and the quantity of the bleeding, and their fate depends on whether clots are dissolved, expelled into the intestine, or retained in the biliary tract (Sandblom & Mirkovitch, 1979). When retained, clots act like calculi and can cause symptoms of biliary colic when passing (Clancy & Warren, 1997), jaundice when retained (Baig et al, 2012), cholecystitis if they lodge in the gallbladder (Parekh & Corvera, 2010), and pancreatitis if they obstruct a common channel above the sphincter (Alis et al, 2010). Only rarely do clots remain in the biliary tree long enough to be encrusted and form stones (Luzuy et al, 1987; Olsen, 1982). The actual workup of a patient with suspected hemobilia ultimately depends on the presentation and suspected etiology. It is important to remember that hemobilia may have a delayed presentation and may recur repeatedly over months and years (Ahmad et al, 2010). In some cases the artery also opens into the portal system (Gurakuqi et al, 2008). The arteriographic catheter should not be withdrawn until it has been decided whether embolization of the feeding artery should be considered as treatment. Arteriography is of special value in discovering central liver lesions, which may be difficult or impossible to localize during exploratory laparotomy. Although selective angiography is considered the gold standard for diagnosis in hemobilia, care must be taken in interpreting arteriograms because they may appear normal if the study is performed when there is no active bleeding. Surgical Intervention In 1903, Kehr first demonstrated that ligation of the proper hepatic artery could be successfully used in hemobilia in a case of communication between a hepatic artery aneurysm to the cystic duct. A, Sonogram indicating dense material in the gallbladder, interpreted as microcalculi or inspissated bile.
Geodon 20mg without a prescription
Primary and secondary malignant neoplasms of the liver depression test beck 40 mg geodon amex, bile ducts, gallbladder, and pancreas can all present with hemobilia when the tumors invade the biliary system (see Chapters 49-51 and 91-94). The rate of blood loss is rarely rapid and in most cases produces a slow onset of microcytic anemia. Malignant tumors are three times more likely to cause hemobilia than benign tumors. Liver metastases rarely cause hemobilia; similarly, hemobilia is infrequently a sequela of primary cancers in the liver (Kitagawa et al, 1999). Hemobilia has been described from metastases in such rare locations as the gallbladder wall (Sadamori et al, 2012) and from melanoma in the ductal mucosa (Qu et al, 2003). In cases of hemobilia caused by malignant tumors in the gallbladder (HernandezCastillo et al, 2002), the bleeding is most marked if the tumor grows in a polypoid fashion (Strauss, 1929). In the bile ducts, benign adenoma (Teter, 1954), polyps, or polyposis has a protracted course of hemobilia. Treatment of hepatic tumors, either primary or metastatic, with chemotherapy (Verset et al, 2010) or locoregional therapy (Dolak et al, 2013) has also been reported to result in major hemobilia. Vascular Disorders Vascular disorders account for only about 10% of cases of clinically significant hemobilia (Green et al, 2001; Yoshida et al, 1987) (see Chapter 21). Hepatic artery aneurysms are the most common primary vascular disorder producing hemobilia. Other, less common causes include angiodysplasia, arteriovenous malformations, and hemangiomas (Vishnevsky et al, 1991). The frequency of true aneurysms (Ryan et al, 2002) of the hepatic artery or its branches (Maralcan et al, 2003; Morioka et al, 2004) rupturing into the biliary tract is diminishing with the disappearance of mycotic aneurysms, leaving only aneurysms of atherosclerotic origin or those associated with polyarteritis nodosa (Battula et al, 2012; Dutta et al, 2004), fibromuscular dysplasia (Shussman et al, 2008), or trauma. When an aneurysm only leaks, it might cause inconspicuous hemobilia, but if it ruptures into the biliary tract, the symptoms are generally clinically significant, with exsanguinating hemorrhage and intense biliary colic. Sometimes, vascular lesions associated with arterial hypertension can result in hemobilia. Gallstones In gallstone disease, microscopic hemorrhage can be demonstrated in one of four cases with stones in the gallbladder and in one of three with stones in the common duct (Gad, 1962). Macroscopic hemobilia is uncommon, constituting less than 10% of all major hemobilia cases reported (Green et al, 2001; Sandblom, 1972; Yoshida et al, 1987). B,Righthepaticarterial angiogram demonstrates pseudoaneurysm (arrow) with successful embolization,C. A, Computed tomography demonstrates active contrast extravasation within the gallbladder. The stones may cause profuse, exsanguinating hemobilia; 11 of 20 patients in one report bled to death. Hemobilia should be regarded just as seriously, but it is a much less common complication of neglected gallstones (Joo et al, 2003) compared to obstructive jaundice, cholecystitis, and pancreatitis. In addition to extrahepatic gallstone disease, hepatolithiasis has been associated with hemobilia. One case series of 867 patients who underwent operative intervention for hepatolithiasis, 8.
Red Kirin Ginseng (Ginseng, Panax). Geodon.
- Male impotence (erectile dysfunction).
- Diabetes.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Dosing considerations for Ginseng, Panax.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Depression, anemia, fluid retention, stomach inflammation and other digestive problems, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), fibromyalgia, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, skin cancer, fever, bronchitis, cancer, common cold, influenza, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96961
Buy geodon discount
The use of antibiotics is an essential component of perioperative management to prevent infection depression symptoms returning 20mg geodon order mastercard. For prevention, first-generation cephalosporin antibiotics are recommended as the standard choice and are generally administered for a few days after liver surgery (Mangram et al, 1999). If a clinical infection occurs, stronger appropriate antibiotics should be chosen based on the location of infection and the results of a culture test. The routine and excessive use of strong antibiotics is not recommended in the absence of any signs of infection (see Chapter 12). If hyperbilirubinemia or refractory ascites (suggesting liver failure) develops, intensive care should be started, including plasma exchange (Yonekawa et al, 2005) (see Chapter 25). However, no effective treatments other than liver transplantation (Otsuka et al, 2007) have been established for postoperative liver failure (see Chapter 112). Peptic Ulcer To prevent postoperative peptic ulcers, the routine administration of proton pump inhibitors or histamine-2 receptor blockers is recommended, since liver cirrhosis itself is associated with a high risk of peptic ulcers, and this risk could be increased by perioperative mental and physical stress. If a peptic ulcer is observed before surgery, the liver resection should be postponed until a healing stage of the peptic ulcer can be confirmed by endoscopy. Bile Leakage Although the short-term outcomes of liver resection have been improved, bile leakage remains a major complication (6%-11%) (Brancatisano et al, 1998; Kyoden et al, 2010; Lee et al, 2005; Lo et al, 1998; Thompson et al, 1983) (see Chapters 27 and 42). In most cases, postoperative bile leakage will subside with conservative treatments (Kyoden et al, 2010); however, major bile leakage can cause critical liver failure. If a leak point is found, suturing with absorbable string and placement of a C-tube can prevent major bile leakage (Nanashima et al, 2013). When major bile leakage occurs postoperatively, biliary decompression through a nasobiliary tube may expedite resolution, although the added benefit of decompression of the biliary tree in this setting remains unproved. This has been achieved by the recent significant progress in preoperative evaluation, surgical techniques, and perioperative management.
Geodon 40mg buy with visa
These patients anxiety 7 year old discount geodon uk, however, may be candidates for a triple transplant (heart, lung and liver). Similar considerations apply to those with cystic fibrosis, cystic lung disease, and liver disease. This may result from the insulin intolerance associated with advanced liver disease and thus will resolve after successful transplantation. Those with insulin-dependent diabetes have a worse outcome after transplant (Hoehn et al, 2015). Evidence of proliferative retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, or autonomic neuropathy, as evidenced by simple tests such as abnormal beat-to-beat variation on Valsalva maneuver or postural hypotension, may be relative contraindications for transplantation. The presence of advanced microvascular disease puts the patient at risk of major autonomic disruption during the procedure, and survival of such patients is relatively poor (Haydon & Neuberger, 2001). Hyponatremia is a common finding in patients with advanced chronic liver disease and occurs usually as a consequence of injudicious diuretic therapy or because of the reduced free water clearance. Grafting patients with severe hyponatremia (serum sodium <120 mmol/L) has shown that there is an increased risk of central pontine myelinolysis (Yun et al, 2009). Significant hyponatremia should be corrected before transplantation by simple water restriction and, if appropriate, stopping diuretic therapy, or if more rapid correction is required, use of renal support. These may occur because of the cirrhosis itself or as part of an associated underlying thrombotic tendency. In early series, portal vein thrombosis was considered a contraindication to transplantation, but it is now appreciated that this is no longer the case, and portal venous inflow to the graft can be provided by the superior mesenteric vein or even a splenic vein. It is only in rare patients with extensive venous thrombosis, and when it is impossible to provide a suitable portal supply to the graft, that transplantation may be currently contraindicated. In hepatorenal syndrome, there is no structural damage to the kidney, and once satisfactory liver function is reestablished, the kidney will function normally. Therefore although the prognosis may be reduced in the presence of advanced renal insufficiency (Rimola et al, 1987), the hepatorenal syndrome is not an absolute contraindication to transplantation. However, in the patient with coexisting advanced renal disease, it may be advisable to consider combined liver and kidney transplantation. Renal function remains a major predictive factor for survival after transplantation (Nair et al, 2002), as well as the risk for renal impairment. The Israel Penn Tumour Registry has identified tumors that carry a high risk of recurrence after transplantation (Box 112. Caution must be used when following these recommendations, however, because the registry relies on voluntary reports rather than a systematic review. Most centers will offer transplantation when the risk of recurrence is less than 10% at 5 years. Only in exceptional cases should patients with these extrahepatic malignancies be considered suitable candidates for transplantation.

Discount geodon 80 mg free shipping
Recurrences from colorectal primary tumors are localized to the liver in approximately one-third of patients anxiety 300 discount geodon online american express, allowing use of potentially curative regional interventions. Only a small proportion of patients with metastases confined to the liver are operable, and an even smaller fraction are resectable because of technical and prognostic factors. By evaluating all patients with hepatic colorectal metastases at a single center, Scheele and colleagues (1995) found 21% of patients with synchronous disease and 51% of patients with metachronous disease to be potentially resectable. Many patients with metastatic disease confined to the liver are not candidates for resectional therapies. In addition, patients with bilobar disease may be candidates for a combination of resection and ablation. Systemic and regional chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer have improved dramatically, with median survival of longer than 20 months now commonly reported (see Chapters 99 and 100). Additionally, response rates for systemic chemotherapy are generally greater than 50%, and combined with regional chemotherapy, approach 90%. Five-year survival rate for patients after resection of colorectal liver metastases in modern series ranges from 46% to 58% (Karanjia et al, 2009; Pawlik et al, 2005). Surgical resection remains the optimal treatment for such metastatic scenarios, and there has been broadening interest in reassessment of resectability criteria in light of effective chemotherapy regimens. There are several well-known risk factors, including viral hepatitis, and incidence varies according to geographic region. North and South America are considered low-incidence areas with less than 3 cases per 100,000 population. High-incidence regions such as sub-Saharan Africa and Asian countries (China, Hong Kong, Taiwan) present with 24 to 35 cases per 100,000 population (Parkin et al, 2002). Most patients with unresectable disease, however, have tumor confined to the liver. At a regional referral center for liver cancer, curative treatments can be applied to 30% to 40% of patients (Bruix & Llovet, 2002). More than half of patients presenting with primary liver cancer are potential candidates for hepatic regional therapy, of whom a significant number may be amenable to ablative techniques. Many techniques to deal with technically unresectable tumors have been developed, such as portal vein embolization and two-stage operations. Cryotherapy has been used to treat many primary and metastatic liver tumors; however, extensive experience exists only for hepatic metastases from colorectal (see Chapter 92) and neuroendocrine (see Chapter 93) tumors and for primary liver cancer (see Chapter 50 and 91). When resection is not possible or safe, however, ablation can provide a relatively effective alternative therapy, with less morbidity than open hepatic resection. The most pronounced benefits of ablation in these patients are that it can be applied with a small laparotomy, laparoscopically, or percutaneously. Ablation can also preserve maximal parenchyma and minimize the overall surgical insult to the patient. No absolute indications and contraindications exist for cryoablation specifically.

20 mg geodon buy overnight delivery
The most successful reports are from the University of Minnesota anxiety attack symptoms buy geodon 80mg without prescription, where investigators have used potent induction immunosuppression and high-quality islets. This was combined with the selection of relatively larger donors and somewhat smaller recipients with low daily insulin requirements, thus maximizing the islet mass delivered per recipient body weight. An even more impressive result was reported by the same group using polyclonal antithymocyte globulin (Thymoglobulin) for induction therapy. In a series of 10 consecutive patients treated with Thymoglobulin induction therapy, nine were rendered insulin independent with a single infusion of islets (Hering et al, 2005). The one patient who did not become insulin independent still had a marked reduction in daily insulin requirement. Collectively, these studies suggest that insulin independence can be achieved consistently with single-donor islet infusions under the correct circumstances. Overcoming the single-donor hurdle will help in the establishment of isolated islet transplantation as a more widely applicable therapy for patients with type 1 diabetes. A second, more daunting obstacle is the realization that the durability of function after islet transplantation is less than that with whole-organ pancreas grafts. Whereas experienced islet centers clearly can gain insulin independence in most islet recipients, and short-term (1 year) insulin-free survival may be close to that seen with whole-organ transplants, the intermediate (2 to 4 year) insulin-free survival is less encouraging. Similar findings of declining islet function over time have been reported by the multicenter Collaborative Islet Transplant Registry: of the recipients who achieved insulin independence, approximately 50% were back on insulin 2 years later (Alejandro et al, 2008). More promising results come from a European consortium of islet transplant centers, with excellent glycemic control and absence of hypoglycemia reported in approximately 80% of patients at 1 year and 60% at 5 years. In addition, three quarters of the recipients had significant periods of insulin independence (Lablanche et al, 2015). Despite the eventual need for most recipients to resume doses of insulin, the partial graft function that persists is relevant, because many patients transplanted with the indication of "hypoglycemia unawareness" remain cured of this devastating complication. It is also evident that a partially functioning graft can significantly improve glycemic control as measured by serial hemoglobin A1c determinations. In one report, a small group of islet recipients who have resumed insulin therapy have been given supplemental islet infusions several years after the initial islet transplant and have regained durable insulin independence in most cases (Koh et al, 2010). One hypothesis is that inadequate control of the deleterious alloimmune and autoimmune responses compromise islet function over time. The absence of a reliable measure of an antiislet immune reaction and the difficulty in obtaining biopsy tissue for pathologic diagnosis contribute to the complexity in clarifying this issue. One study reported durable insulin independence (>3 years) in islet recipients when more potent induction immunosuppression was used, compared with what was used in the Edmonton Protocol (Bellin et al, 2008). An alternative explanation is that the currently used immunosuppressive agents are toxic to the islets over time. This explanation may fit better with the pace of graft dysfunction and the fact that graft function often stabilizes without antirejection therapy. In addition, studies have documented very high immunosuppressive drug levels in the portal circulation, an expected consequence of the drugs being administered orally (Desai et al, 2003).
Geodon 80 mg visa
In making the incision depression symptoms diagnosis treatment purchase 80 mg geodon fast delivery, it may be necessary to abandon the delicate celiotomy techniques of meticulous hemostasis and resort to continuous hemostatic suturing along the cut edges of the fascia and preperitoneum or to the use of hemostatic devices such as the Monopolar sealer. When the abdomen is entered, an effort should be made to find a plane of dissection just outside the liver capsule, because subcapsular dissection, although easier and faster, can result in disastrous hemorrhage. This is especially true in retransplantation, where vascularized adhesions can cause massive bleeding; in these cases, staying on the capsule is especially critical. Intraoperative Determination of Surgical Strategy There is no single best way to carry out orthotopic liver transplantation. When exposure has been obtained, it is important to assess the pathology and decide on the technical approach that best fits the circumstances. A surgeon who insists on following the same steps in unvarying order for all liver recipients experiences unnecessary hardship. The following is a description of the basic ingredients of the recipient operation, with particular emphasis on variations of host hepatectomy. Venovenous Bypass the most critical stage of the recipient operation is the anhepatic phase, during which the diseased liver is removed and replaced with the allograft. C, Simple subcostal incision that may be converted to a hockey-stick incision by an upper midline extension, which may include xyphoid resection. This technique permitted the hepatectomy and implantation to be done with significant reductions in blood loss, intestinal edema, and postoperative renal failure. Infants and small children weighing less than 15 kg tolerate venous occlusion reasonably well. Exposure, especially of the suprahepatic vena cava, can be facilitated by the use of self-retaining retractors. Pump-driven venovenous bypass used to decompress the systemic and splanchnic venous beds during the anhepatic phase of liver transplantation. The groin and venous return cannulae, when used, are usually placed percutaneously in the left groin and right neck. If bypass is not routine, the decision for or against its use should be made as early as possible in the course of the operation. If the test is conducted after preliminary dissection of the portal triad, and after the triangular and coronary ligaments are cut with entry into the right and left bare areas, it is also possible to evaluate the extent to which bleeding from raw surfaces can be anticipated without bypass. Alternatively, a temporary end-to-side portocaval shunt can also be constructed to prevent mesenteric congestion during the anhepatic phase. Hilar Dissection In "easy" cases, the individual hilar structures can be readily skeletonized. If this occurs with venous hypertension and bleeding, removal of the right adrenal gland will usually be required as attempts to suture the bleeding gland most often only exacerbate the situation. Other systemic venous tributaries to the vena cava segment from the lumbar regions must be also scrupulously ligated. The piggback method is by far the most common currently used and can be performed with or without venovenous bypass. The procedure is easier to perform on bypass because the liver can be much more easily rotated and retracted superiorly when the hilar structures are no longer in continuity.
Lester, 51 years: Inomata Y, et al: Right lobe graft in living donor liver transplantation, Transplantation 69:258264, 2000. Beyond the technical aspects of partial hepatectomy, a greater understanding of the impact of resection on the natural history of many diseases, combined with a clearer delineation of perioperative risk, have allowed a much more informed patient-selection process, one that has increasingly targeted resection more effectively to those patients most likely to benefit (see Chapters 49 to 51 and 90 to 95). In the case of intractable pruritus, once other modalities have been tried and have failed, transplantation is extremely effective therapy.
Irmak, 64 years: The pattern of inheritance is autosomal dominant, meaning that only one htt allele needs to be abnormal to express the disease. One-sixth of patients were seen clinically with acute tubular necrosis and impaired renal function. Although clamp crushing itself is possible with the tip of the vessel-sealing system, Pean forceps enable a better feel and vessel exposure in our experience.
Enzo, 31 years: The procedure involves lowering the hilar plate to avoid injury to the left bile duct, exposure and control of vessels within the umbilical fissure, and parenchymal dissection to the right of the falciform ligament and along the principal scissura. Propranolol, but not all receptor antagonists, also has a direct membrane-stabilizing action (local anesthetic action), which may contribute to its cardiac antiarrhythmic effect. Further, incorporating pharmacogenomic/pharmacogenetic knowledge (Chapter 4) and biomarker identification into the drug evaluation process will identify individuals likely to respond to a particular drug.
Kalan, 21 years: Once these structures have been clamped, parenchymal transection is performed by the anterior approach. Ko S, et al: Significant influence of accompanying chronic hepatitis status on recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: result of multivariate analysis, Ann Surg 224(5):591595, 1996. With the primary end point set as the composite efficacy failure rate of treated biopsy-proven acute rejection, graft loss, and death, and a secondary end point as renal function, patients were randomly assigned 30 days after transplant to receive either everolimus with reduced-dose tacrolimus, standard tacrolimus alone, or tacrolimus cessation.
Umbrak, 37 years: Common bacterial pathogens include gram-negative organisms found in the bile (Escherichia coli, Enterobacter and Pseudomonas spp. The left hepatic duct is divided after the cholangiography, and the distal end is sutured via the minilaparotomy. The morphologic configuration of tumors on imaging studies has been shown to have a clear relationship to subsequent resectability.
Kelvin, 33 years: Lastly, the delicate biliary tract reconstruction becomes the final thread on which the whole enterprise is suspended. Systematic review and meta-analysis of results, Transplantation 87:16721680, 2009. The combination has been shown to have a significantly better tumor response, a longer time to progression, survival benefit, and an acceptable safety profile (Gray et al, 2001).
Goran, 59 years: First, most prognostic models are defined from retrospective studies that use patient data at referral or at a certain point in the course of the illness. Asahara T, et al: Perioperative blood transfusion as a prognostic indicator in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, World J Surg 23: 676680, 1999. Once the specimen is removed, hemostasis is ensured and the patient resuscitated to a status of euvolemia.
Steve, 30 years: Bismuth H, et al: Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma, Semin Liver Dis 19(3):311322, 1999. On the other hand, concentrations after oral dosing will be raised because clearance has decreased. As with any drug or class of drugs, the benzodiazepines should be avoided in patients with a known hypersensitivity to these agents.
Asaru, 49 years: Moreover, 90% of patients who had tumor recurrence in the hepatic lobe ipsilateral to their original surgery were resectable in a second operation, with a 5-year survival rate of 58. A few patients have recurrent infection in the graft, but this is of little clinical significance. Takayama T, et al: Adoptive immunotherapy to lower postsurgical recurrence rates of hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised trial, Lancet 356(9232):802807, 2000.
Baldar, 38 years: However, if extrahepatic control of the right hepatic duct is necessary, most often for oncologic purposes, it may be dissected out at this point. The benzodiazepines are an excellent example of a class of drugs that act by an allosteric mechanism. The dissociated receptors may recirculate to the cell surface, may be sequestered temporarily in an intracellular membrane compartment, or may be transported to lysosomes and degraded.
Koraz, 63 years: Midbrain neurons also play important roles in the control of autonomic and neuroendocrine function. Sugiura N, et al: Ultrasound-guided ethanol injection for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma, Acta Hepatol Jpn 21:920, 1983. Hilmi I, et al: the impact of postreperfusion syndrome on short-term patient and liver allograft outcome in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation, Liver Transpl 14(4):504508, 2008.
Hurit, 46 years: Outside the liver substance, no distinct sheath exists around the portal triad structures, and they must be dissected independently. If the traction point is not at the level of the tumor thrombus, it is possible to ligate the portal branch and proceed with the liver resection, ensuring that the thrombus will not migrate because of surgical manipulation. If a drug is a partial agonist in one tissue, it may be a full agonist in another tissue, which has a higher proportion of spare receptors.
Ivan, 28 years: Sarpel U, et al: Outcome for patients treated with laparoscopic versus open resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: case-matched analysis, Ann Surg Oncol 16(6):15721577, 2009. By contrast, the greater space in peritoneal cavity accommodated larger numbers of transplanted cells than the liver. At normal doses, most agents do not exhibit these effects except for tubocurarine, which produces a significant degree of ganglionic blockade.
Rathgar, 35 years: CyA may also lead to neurologic side effects, hypertrichosis, and malignancy (Hojo et al, 1999). The transection is completed by dividing the parenchyma anterior to the caudate lobe in the fissure for the ligamentum venosum. These recommendations, although emphasizing the limited level of available evidence, validated minor resections as standard practice, whereas major resections and complex anatomic resections were still considered at an evaluation stage (Wakabayashi et al, 2015).
Lisk, 54 years: These receptors have different subunit compositions and different anatomical distributions. Ebata T, et al: Review of hepatopancreatoduodenectomy for biliary cancer: an extended radical approach of Japanese origin, J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 21(8):550555, 2014c. View of completed left hemihepatectomy using extrahepatic division of left hepatic artery and portal vein and transparenchymal division of bile duct.
9 of 10 - Review by C. Fasim
Votes: 257 votes
Total customer reviews: 257