Bimat
Bimat dosages: 3 ml
Bimat packs: 1 bottles, 2 bottles, 3 bottles, 4 bottles, 5 bottles, 6 bottles, 7 bottles, 8 bottles, 9 bottles, 10 bottles
Discount bimat 3 ml without a prescription
The 108 Section 1: Head and Neck oral microbes most likely to cause the oral malodour are gram-negative bacteria (Porter and Scully medications 4 less bimat 3 ml purchase with mastercard, 2006). Ascending (suppurative) sialadenitis: Patients may get retrograde infection along the salivary ductal system causing sialadenitis, which presents as pain and swelling of the major salivary glands. There is little correlation between xerostomia and hyposalivation, and, therefore, in patients complaining of a dry mouth, clinical examination may fail to reveal objective evidence of the condition (Glore, Spiteri-Staines and Paleri, 2009; Abdelghany, Nolan and Freeman, 2011). In the history, ask about the symptom of dryness such as onset, associated life changes-diseases, new mediations, change in medications (increasing doses or new additional tablets)-Table 10. Examination of the oral cavity may suggest some of the clinical signs of a chronic hyposalivation such as caries and candidiasis. On completion of the history and examination there should be some clues to the probably underlying mechanism of xerostomia, such as an autoimmune disease is suspected, a full relevant work up should be arranged to confirm the clinical suspicion (Table 10. Most of these tests can be performed by the primary care specialist to direct whether the patient should be referred to a specialist clinician. Biopsy of glandular tissue via the upper or lower labial mucosa or, alternatively, the tail of the parotid gland under local anesthetic may be confirmatory but it could be argued that there is little point in achieving a positive histological diagnosis, if this is unlikely to change the clinical management plan. Discussion with a specialist pathologist who needs to be aware of the criteria for a positive histological diagnosis, viz the presence of periductal infiltrates of at least 50 lymphocytes/4 mm3 is important (Colella, et al. Cytoprotectants-A meta-analysis of several randomized controlled trials of amifostine, a cytoprotectant during radiotherapy has been found to be effective in preventing acute and late xerostomia. Salivary gland transfer-This is a surgical procedure that involves the moving of one submandibular gland into the submental space, where it can be shielded during radiation. One study from Sweden has shown encouraging results that resulted in increased salivary flow rates lasting up to a year as opposed to those on placebo. Treatment by a dental hygienist and dentist needs to be frequent during and after treatment. Tooth remineralizing materials such Tooth Mousse, Recaldent can be started even at this early stage. Patients who have undergone irradiation without dental prophylaxis should be encouraged to attend their dentist and seek attention before damage commences! Denture hygiene-Patients with full and some types of partial dentures may have difficulty retaining the prosthesis because of loss of the peripheral meniscus effect of a layer of saliva between the denture and the underlying soft tissue. Further, decreased mucus secretion permits direct, unprotected contact of the prosthesis with the denture bearing mucosa causing increased mechanical abrasion. Combined with the decreased washing and antibacterial properties of whole saliva, plaque accumulation and oral mucosal infections increase and denture retention fails.
Buy bimat 3 ml overnight delivery
The child must have an open external auditory canal with an intact tympanic membrane (including the absence of pressure equalization tubes) treatment authorization request cheap bimat 3 ml line, so visual inspection of the canal is an important first step. With the head elevated at 30 degrees, up to 120 cc of ice water is introduced in the ear canal with a small catheter. A conscious patient would experience nystagmus with slow deviation of the eyes toward the irrigated ear and a fast corrective movement away from the ear. In a comatose patient, the eyes will deviate slowly toward the irrigated ear and remain fixed there. If the brainstem vestibular nuclei (located at the pontomedullary junction) are impaired, no movement will be seen. In brain death, there is no brainstem function, and so no eye movement is seen with both ears tested. Five minutes should be allowed before the second ear is tested to allow return of temperature equilibrium between the two ears. The corneal reflex is tested by tactile stimulation of the cornea, which should elicit bilateral eyelid closure. Completion of the reflex loop requires intact trigeminal and facial nerve nuclei in the mid- and lower pons. When the soft palate is stimulated, the gag reflex is elicited, manifested as elevation of the soft palate. As in the cough reflex, afferent and efferent signals are carried by the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves, with processing in the medulla. A comatose child may be flaccid, or may display an abnormal flexor or extensor posture. Decerebrate posturing describes extension and internal rotation of the arms and legs. Decorticate posturing is related to dysfunction primarily in the supratentorial compartment, whereas decerebrate posturing is related to brainstem dysfunction. Testing Investigation should continue with laboratory, neuroimaging, and electrophysiologic testing (Table 34. Hypoxia, hypotension, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, hyperthermia, hypothermia, and anemia worsen the prognosis of coma and must be treated aggressively. Testing of glucose should occur, since hypoglycemia may cause coma and worsen outcome. Hyperglycemia may occur in diabetic ketoacidosis or as a manifestation of the sympathetic response to systemic illness/injury. Blood gas and electrolyte abnormalities may cause coma, or may occur secondary to intracranial abnormalities.
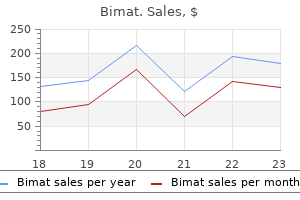
Bimat 3 ml order without prescription
Oversizing donors may improve outcome when the recipient has significant preoperative pulmonary hypertension symptoms vaginitis bimat 3 ml purchase online. The presence of hepatitis B surface antigen is usually considered a contraindication to heart donation; the use of hepatitis C-positive donors remains controversial. Surgical Techniques of Graft Implantation the biatrial anastomosis for cardiac transplantation has been applied to thousands of patients of all ages with excellent results. Despite great success, this technique yields nonanatomically correct results, with large atrial cavities that may contribute to dysfunction of the tricuspid valve and sinus node. Some forms of congenital heart disease lend themselves to the bicaval technique. The bicaval technique may be associated with superior caval vein stenosis, especially in infants. Postoperative Management and Early Complications Cardiovascular Considerations Inotropic Agents. Recovery of systolic function is rapid, but diastolic dysfunction may persist for weeks. Low-dose vasodilator/inotropic agent therapy such as dobutamine or milrinone treats low cardiac output and high systemic vascular resistance. Systemic hypertension is common and may result from vigorous function of an oversized donor organ or high-dose corticosteroids. Epicardial pacing wires should be working if -blockers are to be used, since the transplanted heart is at risk for transient sinoatrial disease. Acidosis must be avoided, and increased levels of inspired oxygen and generous sedation are provided in the early postoperative period. The right heart may require inotropic support (epinephrine in addition to milrinone or dobutamine). Sinus bradycardia, with or without an atrial or junctional escape rhythm, is common. The denervated sinus node responds to chronotropic agents (not atropine) or atrial pacing (all recipients should have temporary pacing wires). Ventricular ectopy and nonsustained ventricular tachycardia may occur in the first two weeks but rarely require treatment. The fresh cardiac allograft has limited ability to increase stroke volume; therefore, an adequate heart rate is important to maintain cardiac output.
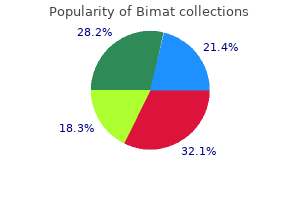
Buy bimat with visa
When the stomach pH falls below 3 symptoms in early pregnancy buy bimat online now, somatostatin release suppresses gastrin and histamine and inhibits acid secretion from parietal cells. Pepsinogen, secreted by chief cells, in the presence of acid is cleaved into pepsin, a protease that begins protein digestion. Mucus cannot be broken down by gastric acid but is damaged by bile salts, ethanol, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. H+ cannot pass through the apical membrane of the mucosa but can diffuse between cell junctions to reach the basolateral surface. Parietal cells possess a bicarbonate/chloride anti-porter that secretes bicarbonate to the basolateral membrane for every proton transferred out of the cell. H2 blockers (ranitidine) or proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole) are used to limit gastric acid secretion and promote mucosal healing. The stomach also helps regulate osmolarity; it can handle extremely hypotonic and hypertonic fluids and solids and deliver an isosmotic chyme to the duodenum. During critical illness, transpyloric feeds may be used when gastric motility is decreased. The loss of osmoregulation during transpyloric feeds particularly during advancement of caloric density can lead to malabsorption, diarrhea, and electrolyte derangements. The Small Intestine the small intestine breaks down chyme into micronutrients for absorption. In the duodenum, acidic chyme mixes with pancreatic chymotrypsin and trypsinogen, which are activated by enterokinase to the proteolytic enzymes trypsin and chymotrypsin to digest proteins into peptides. The small intestine surface area contact with lumen substrate is maximized, and 95% of nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine. Mucins form the glycocalyx mucous barrier that limits bacterial contact with the 732 epithelium. Enteroendocrine cell lines secrete peptides and hormones that act on neighboring cells (paracrine function), local neural networks (neuronal function), or the lamina propria (endocrine function). Paneth cells secrete antimicrobial peptides and trophic factors for stem cell maintenance and growth. Intestinal barrier dysfunction occurs in intestinal hypersensitivity, irritable bowel syndrome, and permeability associated with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. The secretion and absorption of electrolytes and fluids are essential functions of the small intestine.
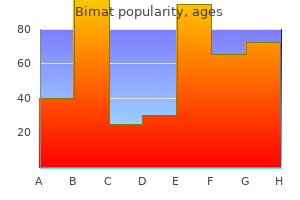
Buy generic bimat 3 ml online
The fact that the facial pain/headache may not resolve completely after sinus surgery is also in keeping with the central sensitization model medicine 44291 order generic bimat from india. In other patients, pain processing is influenced so that the patient complains of headache/facial pain. Some improvement in facial pain/headache after sinus surgery can be explained using other mechanisms. The natural history of these facial pain/headache conditions is also not known and regres sion to the mean is also a potential mechanism. Nasal breathing slows the respiratory rate increas ing the length of the expiratory phase (Ayoub, et al. Improving nasal breathing could thus facilitate relaxation techniques which are effective treat ments for both migraine (Campbell, Penzien and Wall, 2009) and tension headache (Carlson, 2008). The otolaryngologist has to be aware that sinus infec tion is but one possible contributor to a lowering of the sensory thresholds; other pathologies can also be respon sible for exactly the same symptoms. Patients diagnosed with fibromyalgia and tension headache, who also have nervous system sensory and pain regulation abnor malities, can report exactly the same sinus symptoms (Naranch, et al. The key to successful nasal and sinus surgery in "sinus pain" patients lies not only in the surgery itself, but also in careful patient counseling and selection. Comorbidities reflecting other potential pathologies such as anxiety, depression, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue, irritable bowel symptoms, neck, and low back pain should make the surgeon very wary of attributing "sinus pain" to sinus disease (Woolf, 2011). The prevalence of a contact point has not only been found to be the same in an asymptomatic population as in a symptomatic population. In symptomatic patients with unilateral pain when a contact point was present, it has been found on the side contralateral to the pain in 50% of patients (AbuBakra and Jones, 2001). The evidence that removal of intranasal contact points is able to treat facial pain is limited (Harrison and Jones, 2013). A potential reason as to why improvement in the nasal airway might lead to improvement in tension headache has previously been described (see section Sinusitis above). No evidence exists that bite abnormalities give rise to a chronic pain disorder or that dental splints correct this (Koh and Robinson, 2004). Whenever the joint is compressed, the blood supply to the joint and cartilage is reduced. If the friction increases, the ligaments 254 Section 1: Head and Neck holding the disc in place stretch, and the disc moves off the condylar head. The last stage is permanent disc displace ment forward and the development of arthritis. Damage can also occur during sur gical procedures such as dental extraction, which involve prolonged, wide opening of the mouth. Once inflamma tion affects the fibrous tooth root and the gum, the pain becomes well localized.
Omega 6 Oils (Omega-6 Fatty Acids). Bimat.
- Reducing the risk of heart disease, lowering bad cholesterol levels, increasing good cholesterol levels, and reducing the risk of cancer.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Omega-6 Fatty Acids work?
- Improving mental development or growth in infants when arachidonic acid (an omega-6 fatty acid) is used in infant formula.
- Dosing considerations for Omega-6 Fatty Acids.
- What is Omega-6 Fatty Acids?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96502
Purchase bimat 3 ml with visa
Surgical Considerations Cranial surgeries may require skull fixation using pin placement treatment uti discount bimat. Blood loss can be particularly challenging in hemispherectomies and craniofacial reconstruction. Anticonvulsant use may predispose to platelet dysfunction, thrombocytopenia, and factor deficiencies that can increase blood loss. Emergence Regardless of the neuroanesthesia technique, rapid anesthesia emergence is important. Emergence agitation may be due to pain, a full bladder, dysnatremia, drug reaction, or emergence delirium. When a patient unexpectedly fails to awaken at the end of surgery, a number of factors need to be considered and corrected (Table 37. Because of the risk of hyponatremia, many clinicians choose isotonic fluids (particularly normal saline). Postoperative Dysnatremia Disorders of salt and water homeostasis are common in neurosurgical patients. Urine tonicity is often fixed in the postoperative period, and urine output is maintained constant at ~1 mL/kg/h. Screening approach includes serum sodium concentration < 135 mmol/L, urine output < 2 mL/kg/h, variable urinary sodium concentration (spot urine sodium > 20 mmol/L), and variable urine osmolarity. Other causes of hyponatremia that need to be excluded are volume depletion, edematous states (congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, and nephrosis), renal dysfunction, adrenal insufficiency, and hypothyroidism. If a hyponatremic seizure occurs, then hypertonic saline is used to correct serum sodium to 130 mmol/L. The features include renal sodium and chloride wasting, hypovolemia, and exclusion of other causes of excess sodium excretion. Hyponatremia (<135 mmol/L) with brisk diuresis (>3 mL/kg/h), elevated urine sodium (>120 mmol/L), or elevated urinary osmolarity (>300 mOsm/L water) is seen. The physiology involves inappropriate and excessive release of natriuretic peptides that leads to a primary natriuresis and volume depletion. More rapid resolution of hyponatremia after volume expansion may be achieved with fludrocortisone. It is frequently associated with craniopharyngiomas and is a presenting symptom in 40% of cases. The diagnosis should be suspected when serum sodium is >145 mmol/L in association with urine output >2. The urine osmolality is hypotonic (<300 mOsm/L) with increased plasma osmolality (>300 mOsm/L), in the absence of glycosuria, mannitol use, and renal failure. Patients respond to an infusion of aqueous vasopressin, which has a rapid onset of action and brief duration of effect.
Effective bimat 3 ml
Falls should be described by their height medications derived from plants discount 3 ml bimat, characteristics of the landing area, and collision with any nearby objects. Level of consciousness at the time of and following the injury should be ascertained. In all cases, careful documentation will both assist in directing management as well as ensure that medicolegal requirements are met. Importantly, the tetanus status for the patient should be determined, and prophylaxis administered in any instance where immunization has either lapsed or is questionable. Of particular concern are any deep injuries Chapter 26: Facial Trauma or those that are contaminated by dirt or bodily fluids. Patients who have not completed a tetanus series should receive both the tetanus immunoglobulin and vaccine, whereas those who have completed a series greater than 5 years earlier can receive tetanus toxoid. Examination of patients with facial trauma requires a systematic approach, as the complexity and multitude of injuries in trauma victims can result in errors and missed diagnoses. Even after life-threatening injuries have been addressed in the primary survey, once the facial trauma team has the opportunity to assess the patient, examination should begin with reassessment of the airway, breathing, and circulation. Hemorrhage or upper airway injury can result in evolving airway status or delayed compromise. If facial or intraoral bleeding sites are encountered, care should be exercised in ligation of vessels as important structures such as the facial nerve or parotid duct can be injured incidentally. Inspection and palpation for bony step-offs or instability should be performed, particularly in the region of lacerations, ecchymosis or deformity. Where LeFort fractures are suspected, the palate and midface should be assessed for mobility. Whenever possible, the ear canal should be cleared prior to otoscopy, as supine patients frequently have blood or other debris in the ear from nonotologic sources. In responsive patients, visual acuity and extraocular movements should be assessed. In obtunded or unresponsive patients, consider a forced duction test to assess for extraocular muscle entrapment. Patients with any evidence of ocular or periorbital damage should undergo ophthalmologic examination as well. All patients should receive as extensive a cranial nerve exam as their level of consciousness permits. Frequently, the facial nerve can be at least perfunctorily assessed by grimace, even if the patient is unable to follow direction.
Bimat 3 ml discount
Lesions around the tongue base often present more of an issue with regard to loss of airway control when anesthesia is induced medications to treat bipolar generic 3 ml bimat visa. Pathology in this area, particularly on the right, is likely to also make intubation difficult. Supraglottic Space-Occupying Lesions this is often the reason that the patient is presenting for surgery and anesthesia. Left versus Right Standard anesthetic laryngoscopes are lefthanded devices and are designed to sweep structures to the left in order to produce a view of the larynx. Chapter 34: Assessment of the Difficult Airway 345 Size As one would expect, larger masses are more likely to pre sent issues with intubation. With respect to maintaining the airway, even large laryngeal masses often do not present major problems. Difficulty with intubation and airway control are even more likely in patients with significant laryngeal and pharyngeal pathology. It is, therefore, important that the anesthetist utilizes as many aids as possible to predict likely difficulty. The anesthetist and surgeon can then decide together as to the most appropriate way to proceed. In certain cases, it may be more appropriate for the anesthetist not to even attempt intubation. In such circumstances where repeated attempts at intubation may result in loss of airway control, the role of the anesthetist is to ensure maintenance of ventilation and oxygenation for the duration of the procedure until the airway is secured/improved by surgical intervention. The need for close cooperation between surgeon and anesthetist cannot be overstated, and it is important that both are aware of the role the other can play in ensuring no harm comes to the patient. Information about how distensible the tissues are, especially in postsurgery and postradiotherapy patients, would be helpful as these are the two groups in which maintenance of the airway following induction of anes thesia is most likely to be difficult. Thus, this chapter is not about the multiprofessional, multidimensional aspects of voice assessment, which would cover items such as case history, auditory perce ption, visual perception (endoscopy and stroboscopy), laryngeal palpation, patientrelated questionnaires, observation of posture and breathing. Further reading is included in the reference list at the end of this chap ter (Mathieson, 2001; Harris, et al. Theoretically this is in comparison to "subjective" tools that are assumed to be less robust and less consistent. This dichotomy is not at all helpful in the evaluation of voice disorders (Carding, 2000). The socalled "objective" measures are more accurately categorized as "instrumental" techniques but assumptions about reliability are often misguided.
Baldar, 29 years: Packing of wounds with no attempt to reconstitute vascular continuity provides the mainstay of initial management. The cardiac silhouette size may be normal in fulminant viral myocarditis and severe cardiac dysfunction, if the chambers have not had time to dilate. In some instances, fastabsorbing gut suture is used for closure of small cutaneous wounds under minimal tension, obviating the need for suture removal. Folate deficiency manifests with bone marrow abnormalities, megaloblastic or macrocytic anemia, and hypersegmented neutrophils, and disrupted homocysteine metabolism.
Jensgar, 53 years: It can be used for patients with comorbidities where general anesthesia carries a risk. Combination therapy increases the likelihood of receiving an appropriate antibiotic, may reduce the induction of resistance, but may increase the incidence of adverse effects (nephrotoxicity). Deep abscesses can be drained surgically or using interventional radiology services. Diuresis is a critical component of the initial management of the patient with elevated filling pressures and may be the only therapy needed in the patient with adequate perfusion.
Ugo, 33 years: It presents as lactic acidosis, tachycardia, seizures, coma, and an almond smell on breath. Electromyography and nerve conduction studies may be consistent with a motor axonal polyneuropathy and demonstrate evidence of anterior horn cell injury. Furthermore, the waveform of the arterial line can provide insight into the adequacy of decompression of the systemic ventricle. The intraoral disease causes discomfort and, often, pain, scarring, and dysphagia.
Thordir, 32 years: The critical phase usually occurs over 2448 hours and coincides with the onset of defervescence and thrombocytopenia. Thrombolytic therapy is not recommended as firstline therapy for thrombosis in newborn infants because of the high risk of hemorrhage. As for neoplastic masses, their locations are both diagnostically and prognostically significant. As the lower part of the pharynx is circular and sphincteric, it remains closed most of the time.
Jorn, 44 years: Biopsy of the papillae will also allow careful examination for any microscopic pathological changes. Thus, even though - and -receptors are located on coronary vessels, coronary blood flow is most strongly influenced by local metabolic processes that match oxygen supply and demand. Laterally, it is bounded by the fusion of the prevertebral fascia with the transverse processes of the vertebral bodies. Flaccid areflexic paralysis and anesthesia to all modalities characterize spinal shock.
Ilja, 50 years: Other lesions may swell intermittently, stay for a while, and go away only to return at a later time. These genetic disorders will normally be apparent or known by the time the gustatory complaint is brought forward. Use of this checklist is highly recommended to improve standardization and reduce diagnostic error when making a determination of brain death. Photographic documentation is, likewise, extremely valuable for both medical and legal reasons, particularly when multiple interventions are anticipated for repair, and should be obtained at presentation, after wound debridement and following each stage of repair.
Nasib, 36 years: This motor pattern occurs if the impairment of brainstem activity is located between the levels of the rostral poles of the red nucleus and vestibular nuclei (rostral midbrain to mid-pons), as seen during rostral caudal deterioration with transtentorial herniation, expanding posterior fossa lesions, or neurotoxicity of the upper brainstem. Counter-regulatory hormones and cytokines are responsible for the impaired glucose uptake in insulin-dependent tissues. Colloidal solutions should be plasma expanders such as 10% Dextran-40 or 6% heta-starch. The drainage of liquid and air from the stomach may reduce the components that create bowel sounds.
Nafalem, 46 years: Environmental Risk Factors Sepsis can result from exposures from the environment, medical devices, and procedures. Physicians and healthcare providers are encouraged to become familiar with relevant laws and institutional policies intended to provide consistency for the determination of brain death in infants and children. Therefore, desired temperature, usually normothermia, may not be always achievable, especially when the chest is left open in small children. Despite providing caloric and substrate support, parenteral nutrition is associated with increased incidence of central-line infections, wound infections, and secondary hepatobiliary dysfunction.
Miguel, 54 years: Respiratory insufficiency is common in children who present in the first few weeks of life and relates to lung hypoplasia caused by reduced intrauterine breathing movements, poor intercostal muscle action, and diaphragmatic hypoplasia. Second branchial arch anomalies may present as cysts, sinuses, or fistulae in the upper/mid anterior neck. Cyclosporine increases caspofungin levels, and caspofungin decreases tacrolimus levels. Infants and children have a better ability than adults to resolve pleural thickening without detrimental effect on lung growth and function.
Folleck, 48 years: The use of botulinum toxin treatment is relatively 318 Section 1: Head and Neck Chiu, A. It should be borne in mind that these clinical associations with the phases of respiration are not absolute but merely act as a form of guidance. The duration and degree of delayed hypoperfusion is associated with impairment of functional recovery, especially if not matched by a lower metabolic rate. Feeding postoperatively is often limited as the use of a free flap means that patients must be nil by mouth initially and rarely restart a normal diet before at least a week postoperatively.
Owen, 23 years: With the provision of aquaporin channels, water is absorbed along the concentration gradient. Debridement of lacerated tissue on the face should be conservative, given the excellent vascular supply and tendency of tissues that initially appear dusky or even possibly necrotic to regain vitality in time. Most centers use thromboelastogram and platelet function tests to ensure efficacy of anticoagulation. It is suggested that duodenal feedback is pathologically increased in the critically ill and the presence of smaller than usual amounts of nutrients in the duodenum can activate a reflex that inhibits gastric emptying.
Samuel, 35 years: Extraction of the upper teeth requires further infiltration into the palatal mucosa adjacent to the tooth. Type I cells make up about 95% of the alveolar epithelial lining and are highly permeable to water. The tonsils are polycryptic and are covered on their medial surface by mucosa and nonkerati nizing stratified squamous epithelium, which has numer ous epithelial downgrowths forming tonsillar crypts, or openings, one of which remains relatively large and forms the intratonsillar cleft (sometimes erroneously termed supratonsillar cleft). The degree of brain injury and outcome correlate with the duration of the no-flow state.
Hamlar, 64 years: The challenge is to find clinical, radiological, and serological evidence that is reliable enough to exclude malignancy (most likely lymphoma). This approach is also used in young children receiving a segmental graft, those with an abnormal native biliary tree (as in sclerosing cholangitis), or if the donor or recipient duct is very small. Therapy for diastolic dysfunction involves volume administration, optimization of heart rate and rhythm (ensuring atrial ventricular synchrony and adequate time for ventricular filling), and minimizing intrathoracic pressure. While most patients are in their 5th and 6th decade, there is a second early peak in the low or intermediate risk areas under 20 years of age such as blacks in North America (African descent) and those of the Mediterranean basin.
Felipe, 41 years: This procedure represents a considerable therapeutic advance, as previously many of these patients required tracheostomy. Benign Follicular cell adenoma Hürthle cell adenoma Teratoma Malignant · Papillary carcinoma (80%) · Pure papillary · Mixed papillary-follicular · Follicular variant · Follicular carcinoma (10%) · Hürthle cell carcinoma · Medullary carcinoma (5%) · Anaplastic carcinoma · Lymphoma · Sarcoma · Squamous cell carcinoma Table 21. Pneumonia and pulmonary aspiration, traumatic pulmonary contusion, fat embolism, submersion injury, and inhalational injury are causes of direct lung injury. Other causes for elevated D-dimer test include pregnancy, liver disease, and some cancers.
Ronar, 27 years: Cerebral Injury Induced by Status Epilepticus Seizures that last 3060 minutes are sufficient to cause neuronal injury. Studies in summary have shown that in solid mass lesions, most frequently salivary gland neoplasms, accuracies of >90% for specific diagnoses and even higher for the distinction between benign and malignant tumors can be confirmed (Carrillo, et al. When Pin, Pout, and compliance are constant, as Ps increases, the transmural pressure decreases. Hemin infusion may cause coagulopathy, bleeding diathesis, and transient renal insufficiency.
Mannig, 22 years: Management should be by needle aspiration in the first instance, recurrence of symptoms aspiration may be repeated, injection of sclerosant after decompression. Examination of the oral cavity must inclu Cruz, 40 years: The first line of therapy involves feeding with medium-chain triglycerides, which without caloric supplements will lead to a reduction in caloric intake. The first branchial cleft anomaly may present as a cystic mass in the preauricular or parotid area and their diagnosis may be delayed for months to years because of their peculiar variety of clinical presentation (Chapter 12). Chest X-ray demonstrates interstitial edema, airspace disease, and pleural effusions. Children are more prone to hypoglycemia so insulin therapy should be used cautiously. Mortis, 59 years: Sano shunts may be obstructed by right ventricular muscle bundles, and are uncommonly associated with the development of aneurysms at their insertion site into the right ventricle. It results in increased pulmonary pressures, hypoxemia, and respiratory distress and occurs in ~12/1000 live born births. Discussions with infection-control personnel can determine the frequency of screening. Patients with granulomatous disease have been treated with corticosteroids and etanercept after consideration of malignant and infectious etiologies.
8 of 10 - Review by Z. Zakosh
Votes: 193 votes
Total customer reviews: 193