Sinequan
Sinequan dosages: 75 mg, 25 mg, 10 mg
Sinequan packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 120 pills

Cheap sinequan online master card
The newly diagnosed patient can be febrile anxiety symptoms journal generic 25 mg sinequan fast delivery, but specific or localizing signs of infection are uncommon on presentation. Although the history of the illness in a newly diagnosed patient is typically short-in the range of months-some patients may recall a long history of bruisability, anemia, and low blood-cell counts reported to them by previous physicians during routine examinations. Small numbers of lymphocytes are sufficient to produce the syndrome, which is surprisingly resistant to immunosuppressive therapy. A woman who desires a child can be maintained with transfusions, with the understanding that any clinical deterioration is a criterion for interruption or termination of the pregnancy. Patients with hepatitis-associated aplasia have markers of immune system activation and respond well to intensive immunosuppressive therapy. Acute viral hepatitis that is seronegative differs clinically from hepatitis C disease; parenteral exposure is not a risk factor, liver functions abnormalities are more severe during the acute phase, and late complications are more common. Even next generation sequencing has failed to find evidence of infection in seronegative hepatitis. The syndrome can be a presentation of lymphomas and seen in the context of hemolysis. These diseases are frequently diagnosed concurrently or sequentially in the same individual, and they share similar clinical and pathologic features. This severe, scleroderma-like disease is characterized by fibrosis of subcutaneous and fascial tissue, localized skin induration, eosinophilia, hypergammaglobulinemia, and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Pancytopenia can be first observed during the acute mononucleosis syndrome or shortly thereafter. Pancytopenia occurs in most cases; anemia is a universal finding; thrombocytopenia and neutropenia are also common. In virus-associated hemophagocytosis, there is evidence of immune system activation. Platelet size is normal and not increased as in immune peripheral destruction, but the low number can cause greater heterogeneity of size. Prior transfusions alter platelet numbers, relative reticulocyte counts, and hemoglobin values. Although relative lymphocytosis is common, most patients also have decreased absolute numbers of monocytes and lymphocytes. Patients with severe liver disease and splenomegaly, systemic lupus erythematosus, or overwhelming sepsis can have low blood cell counts, but the clinical presentation is not subtle. In the challenging case, obvious medical causes of pancytopenia have usually already been excluded. Discontinuation of exposure to the incriminated drugs or chemicals is mandatory, and in some instances, patients may then recover. However, given the difficulty of assigning blame with absolute certainty to environmental agents, we treat all patients similarly and do not advocate protracted observation for possible spontaneous recovery. Point counting under microscopic cross hairs in many parts of a histologic section is the most accurate method of determining cellularity, but hematologists commonly rely on visual estimation only.
Purchase sinequan with american express
Mitosis is recognized when cells visibly undergo cell division and chromatin becomes condensed anxiety quitting smoking sinequan 10 mg order free shipping, sequentially progressing through prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Although the duration of the S, G2, and M phases is relatively constant for most mammalian cells, there can be a large degree of variability in the duration of G1. Among the earliest observations regarding the generation time for cells, it was shown that by varying the growth conditions, the length of a cell division cycle could change, with the length of G1 responsible for most of this variability. Although cells progress through S, G2, and M phases in relatively invariable time periods, the length of the G1 phase is highly variable, and this variability is dependent at least in part on the presence of growth factors. For example, when the 40S ribosomal protein S6 is missing, cells stop proliferation. As a result, the original mass of egg cytoplasm is partitioned among thousands of cells within a few hours without a noticeable increase in size. Quiescence and Differentiation Quiescence (G0) is a nonproliferative state in which viable cells have left the cell cycle and may remain for prolonged periods. Quiescent cells may be difficult to distinguish morphologically from cells in a prolonged G1 phase, but they can be distinguished by different markers. Terminally differentiated cells, such as neutrophilic granulocytes, muscle cells, and neurons, have irreversibly exited the cell cycle during the process of differentiation and are examples of cells that have irreversibly entered G0. Other cells, including stem cells, reversibly enter G0 and may be induced to reenter the cell cycle with appropriate stimuli, such as growth factors. Differentiation provides the organism with a supply of cells to execute specific and specialized functions. In some cell types, such as muscle and nerve cells, differentiation and proliferation are mutually exclusive fates, and cells undergo "terminal differentiation. For example, erythroblasts, myeloblasts, and megakaryoblasts are committed to particular differentiation pathways and possess lineage-specific markers yet continue to proliferate. T and B lymphocytes are fully differentiated and express antigen-specific receptors but can be induced to proliferate when appropriately stimulated. For most cells entering S phase, passage through G2 is "automatic," and the duration of G2 is fixed, except under unusual circumstances. For example, G2 duration can be extremely short and is essentially undetectable in rapidly proliferating, early embryonic cells. G1 Phase G1, which occupies the period or gap between M and S phases, is the interval between the completion of one round of cell division and initiation of the next. Its duration is the most variable, can be prolonged depending on the cell type, and is subject to regulation by environmental factors such as the availability of growth factors and nutrients. It is the period of cell growth, and as a first approximation, the amount of time a cell spends in G1 is inversely related to its rate of proliferation.
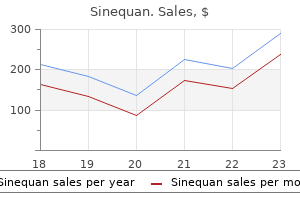
Buy discount sinequan 25 mg online
Each type is most sensitive to a particular kind of chemical stimulus anxiety and high blood pressure sinequan 10 mg amex, producing at least five primary taste (gustatory) sensations. The tip of the tongue is most sensitive to sweet stimuli, the margins of the tongue are most sensitive to sour, the back of the tongue is more likely to detect bitter substances, and responsiveness to salt is quite widely distributed. Moving bits of food over the surface of the tongue to stimulate different receptors at different moments keeps us from losing taste due to sensory adaptation. A flavor results from either one primary sensation or a combination of the primary sensations. Experiencing flavors involves tasting, which reflects the concentrations of stimulating chemicals, as well as smelling and feeling the texture and temperature of foods. Furthermore, the chemicals in some foods-chili peppers and ginger, for instance-may stimulate pain receptors, which cause a burning sensation. In fact, the chemical in chili peppers that tastes "hot"- capsaicin-actually stimulates warm receptors. Experiments indicate that each taste cell responds to one taste sensation only, with distinct receptors. Sweet tastes direct us to energy-providing carbohydrates, sour tastes compel us to avoid foods containing dangerous acids, salty foods entice us to eat sodium, bitter tastes help us avoid poisons, and savory umami taste sensations increase our protein intake. Taste Pathways Sensory impulses from taste receptor cells in the tongue travel on fibers of the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves into the medulla oblongata. From there, the impulses ascend to the thalamus and are directed to the gustatory cortex, in the parietal lobe of the cerebrum, along a deep part of the lateral sulcus (see fig. Vibrating strings on a guitar or reeds on an oboe produce the sounds of these musical instruments, and vibrating vocal folds (vocal cords) in the larynx produce the voice. The auricle of the ear helps collect sound waves traveling through the air and directs them into the external acoustic meatus. The eardrum is a semitransparent membrane covered by a thin layer of skin on its outer surface and by mucous membrane on the inside. It has an oval margin and is coneshaped, with the apex of the cone directed inward. Sound waves that enter the external acoustic meatus change the pressure on the eardrum, which vibrates back and forth in response and thus reproduces the vibrations of the sound-wave source. The first is an outer, funnel-like structure called the auricle (awri-kl) or pinna. The second is an S-shaped tube called the external acoustic meatus (me-atus), or external auditory canal, that leads inward through the temporal bone for about 2. The higher the wave, the louder Auricle Middle Ear the middle ear, or tympanic cavity, is an air-filled space in the temporal bone. It contains three small bones called auditory ossicles (awdi-tore osi-klz): the malleus, the incus, and the stapes (fig. Tiny ligaments attach them to the wall of the tympanic cavity, and they are covered by mucous membrane.
10 mg sinequan with amex
The patient is already on a high dose of transdermal fentanyl anxiety gas sinequan 25 mg with amex, so further escalation of opioids is unlikely to achieve better pain control on its own. D the patient has an acute myocardial infarction related to exposure to bevacizumab. Bevacizumab increases the risks of impaired wound healing, hypertension, proteinuria, venous and arterial thrombosis, hemorrhage, gastrointestinal perforation, and congestive heart failure. Her age (above 65) and history of diabetes places her at increased risk of myocardial infarction related to bevacizumab. B the patient has ifosfamide encephalopathy, likely secondary to the accumulation of chloroacetaldehyde (a breakdown product of ifosfamide). He is at increased risk for this condition given his hypoalbuminemia and renal dysfunction. While methylene blue can be given to reverse this condition, it typically resolves spontaneously after holding ifosfamide. D Cetuximab is associated with hypomagnesemia and should be monitored (along with calcium and potassium) while patients are receiving cetuximab. Electrolyte levels should be monitored regularly until at least 8 weeks after treatment, and early replacement to keep magnesium levels above 2. Cetuximab is not associated with anemia, hyper- or hypo-natremia, neutropenia, or hyperbilirubinemia. D the proper positioning of a patient, site identification, sterile preparation and analgesia are important for the success of a lumbar puncture and to minimize complications. The patient should be instructed to arch their back "like a cat" to widen the gap between the spinous processes. In terms of landmarks, the individual performing the procedure should imagine a line between the superior aspects of the iliac crests that intersects the midline at the L4 spinous process. The spinal needle should be inserted in the L3 and L4 or L4 and L5 interspace, because these points are below where the spinal cord ends (between L1 and L2). C Headache after lumbar puncture is a relatively common occurrence (32%), and may be associated with morbidity and rare but serious complications such as seizures and subdural hematomas if left untreated. In a study of 600 patients the incidence of headache was 5% when the stylet was reinserted compared with 16% when the stylet was not replaced. E Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy is performed in the evaluation of hematologic conditions, cancers, metastatic disease, storage disorders and some chronic systemic diseases. The procedure has no absolute contraindications, although relative contraindications include bleeding disorder and active infection at the biopsy site. Thrombocytopenia and other coagulopathies are not absolute contraindications, although the administration of platelets can be considered if platelet count is less than 20,000/L. The posterior iliac crest is the most common proposed site, however, alternatives that have historically been used include the anterior iliac crest, manubrium of the sternum, tibia (in infants), and vertebral body (rare cases).
Sinequan 10 mg order online
The respiratory mechanism may require several minutes to begin resisting a change in pH anxiety vitamins cheap sinequan 10 mg otc, and the renal mechanism may require one to three days to regulate a changing hydrogen ion concentration. Respiratory Excretion of Carbon Dioxide the respiratory center in the brainstem helps regulate the hydrogen ion concentrations in the body fluids by controlling the rate and depth of breathing (see section 16. Specifically, if body cells increase their production of carbon dioxide, as occurs during periods of physical exertion, carbonic acid production increases. As the carbonic acid dissociates, the concentration of hydrogen ions increases, and the pH of the internal environment drops. Describe the causes and consequences of an increase or a decrease in body fluid pH. Chemical and physiological buffer systems ordinarily maintain the hydrogen ion concentration of body fluids within very narrow pH ranges. Acidosis results from an accumulation of acids or loss of bases, both of which cause abnormal increases in the hydrogen ion concentrations of body fluids. Conversely, alkalosis results from a loss of acids or an accumulation of bases accompanied by a decrease in the hydrogen ion concentrations (fig. Acidosis the symptoms of acidosis result from depression of central nervous system function. Factors that increase carbon dioxide levels, which increases the concentration of carbonic acid (the respiratory acid), cause respiratory acidosis. Metabolic acidosis is due to an abnormal accumulation of any other acids in the body fluids or to loss of bases, including bicarbonate ions. Respiratory acidosis may be due to hindered pulmonary ventilation, which increases carbon dioxide concentration. Injury to the respiratory center of the brainstem that results in decreased rate and depth of breathing. Obstruction in air passages that interferes with air movement into and out of the alveoli. Any of these conditions can increase the level of carbonic acid and hydrogen ions in body fluids, lowering pH. At the same time, increasing levels of carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions stimulate the respiratory center, increasing the breathing rate and depth and thereby lowering the carbon dioxide levels. Eventually, these chemical and physiological buffers return the pH of the body fluids to normal. Metabolic acidosis is due to either accumulation of nonrespiratory acids or loss of bases. Kidney disease reduces the ability of the kidneys to excrete acids produced in metabolism (uremic acidosis).
Cr3+ (Chromium). Sinequan.
- What other names is Chromium known by?
- What is Chromium?
- How does Chromium work?
- Prediabetes.
- Chromium Dosing »
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96895
Buy cheap sinequan 25 mg line
The gene pool (a population measure) is affected when one individual contributes disproportionately to the next generation anxiety symptoms 7 months after quitting smoking discount sinequan 10 mg fast delivery, increasing the prevalence of mutations that cause rare inherited diseases, because a man would not ordinarily father 50 to 100 children. Many people who find out that their children have dozens of half-siblings are upset, as are the men who donated the sperm. Before the age of the Internet, it was highly unusual for children conceived with the same donated sperm to meet each other. Today half-siblings can find each other and are even meeting, thanks to the Donor Sibling Registry. This and other websites enable parents who used donated sperm to learn of other families that used the same sperm, using identifying numbers that the sperm banks assigned. Several of these half-sibling groups number up to 50, with one including 150 children who share their father, but not their mothers. Transport of Sex Cells A female of reproductive age usually ovulates a secondary oocyte and its surrounding cells each month. Several functions of the male and female reproductive systems assist sperm in reaching the secondary oocyte. During sexual intercourse, the male deposits semen containing sperm in the vagina near the cervix. Also, under the influence of high concentrations of estrogens during the first part of the menstrual cycle, the uterus and cervix secrete a watery fluid that promotes sperm transport and survival. Conversely, during the latter part of the cycle, when the progesterone concentration is high, the female reproductive tract secretes a viscous fluid that hampers sperm transport and survival. Sperm reach the upper part of the uterine tube in less than an hour following sexual intercourse. Many sperm cells may reach a secondary oocyte, but usually only one sperm cell fertilizes it (fig. A sperm cell joins a secondary oocyte, a zygote is formed, and the journey of prenatal development begins. Following thirty-eight weeks of cell division, growth, and specialization into distinctive tissues and organs, a new human being enters the world. In humans and other many-celled organisms, growth entails an increase in cell numbers as a result of mitosis, followed by enlargement of the newly formed cells. Development, which includes growth, is the continuous process by which an individual changes from one life phase to another. These life phases include a prenatal (pre-natal) period, which begins with fertilization and ends at birth, and a postnatal (p st-natal) period, which begins at birth and ends with death. Sperm Cell Joins Secondary Oocyte Sperm cells first invade the corona radiata, which is a layer that consists of follicular cells surrounding the secondary oocyte.
Order sinequan pills in toronto
Serum IgA constitutes 20% of the total serum immunoglobulin anxiety symptoms ocd best purchase sinequan, and 80% of this is monomeric. The other form of IgA is found in external secretions such as saliva, tracheobronchial secretions, colostrum, milk, and genitourinary secretions. IgD apparently functions as a membrane molecule, being associated on mature but unstimulated B cells in association with IgM. The Fc portion of IgE binds strongly to a receptor on mast cells, FcR, and this is how this immunoglobulin exerts its particular activity. The structural basis for this antigenic heterogeneity is variation in amino acid sequence in the Fc portion of the H chain of a given class. The subclasses of human IgG, called IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4, are the best characterized. Constant region domains are indicated by CnN, where n is the subclass and N is the domain. This model shows the possible arrangement of the two IgA monomers in relation to the secretory component and J chain. As the IgA molecule passes through the epithelial cells, the secretory components are synthesized and attached covalently to the Fc domain of the -chains that have previously been joined to the J chain with disulfide links. Light chains are shown in blue, heavy chains in purple, disulfide bonds as gray lines, and carbohydrates as red circles. The subclasses of IgG exhibit different catabolic rates and bind differentially to cell-associated Fc receptors (FcR) and to C1q. Specifically, IgG2 does not bind to the FcRs and IgG4 binds about 10-fold less well than do IgG1 and IgG3. Despite the most obvious sequence differences among the human IgG isotypes being in their hinge regions, studies using engineered domain-swapped chimeric molecules have demonstrated that it is the more subtle amino acid sequence differences within the respective C2 domains that account for the differences in binding to C1q and to the FcRs. Transport across the placenta is mediated by the Fc-neonatal receptor (FcRn) and for this functional activity IgG2 crosses the placenta slightly more slowly than the other three subclasses. The other known subclasses of Ig isotypes are associated with IgM (IgM1 and IgM2) and IgA (IgA1 and IgA2). It is attributable to genetically controlled antigenic determinants found on both the H and L chains. Although each human has all immunoglobulin isotypes, an individual has only one form of each allotype on his or her immunoglobulin molecules.

Order 25 mg sinequan overnight delivery
At this point anxiety 33625 generic sinequan 75 mg without a prescription, the mature B cells may remain in the spleen or relocate via the circulation to additional tissues such as lymph nodes, where they are poised to respond to antigenic challenge. This article will focus on adult B-cell development and the regulation of that process, although we briefly discuss fetal B lymphopoiesis and its distinguishing features. The information presented provides a basis for understanding abnormalities of B-cell development such as leukemia, lymphoma, and immunodeficiency states, which are discussed in other chapters. Studies in mice have contributed much to what is known about B-cell development and have served as a basis for understanding human B lymphopoiesis. Thus, although we emphasize the human literature as much as possible, frequent reference to findings in mice are made. Finally, when Ig light chain expression occurs, the cells become surface IgM-expressing B cells. This results in gradual "specification" of progenitors towards the B-cell lineage. The processes of specification and commitment are dependent on the regulated expression of a network of transcription factors and other regulatory molecules in developing B lineage cells. For example, Ebf1 regulates the expression of Ig, VpreB, 5, and Pax5, and represses genes associated with alternative lineage fates. Lin- indicates that the cells lack expression of determinants present on mature myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid lineage cells. Stages of human and mouse B-cell development and selected cell surface and cytoplasmic determinants that can be used to distinguish various stages of differentiation are shown. Note that there are additional cell surface and molecular determinants that can be used to define the various stages of development. After leaving the bone marrow, newly produced B cells migrate to the spleen and mature through transitional cell stages into marginal zone or follicular B cells. However, if the gene encoding Pax5 is introduced into Pax5-deficient precursors, this developmental promiscuity is no longer observed. For example, Pax5 may repress myeloid growth factor receptors, such as those for macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and inhibit the T-cell potential of lymphoid-restricted progenitors by antagonizing expression of Notch1, a cell-surface receptor whose stimulation activates signaling pathways required for commitment to the T-cell lineage. In addition to regulating commitment to the B-cell lineage, continued Pax5 expression is necessary to maintain lineage fidelity even in relatively mature B cells. Focused reviews should be consulted for a full discussion of these and additional transcriptional regulators of B lymphopoiesis. The process of Ig gene rearrangement occurs in a step-wise manner as murine and human B cells mature through the cellular stages of development just described.
Shakyor, 59 years: Mice can be produced that express an exogenous gene and thereby provide an in vivo model of its function. Instead of forming interstitial fluid, the filtered fluid moves into the glomerular capsule as glomerular filtrate and then into the renal tubule as tubular fluid, and some of it will be excreted as urine (fig. Not only is blood flow impeded, but the uneven inner surface can snag platelets, triggering coagulation. Most of the fibers enter the thalamus and synapse with others that continue to the visual cortex in the occipital lobes.
Uruk, 56 years: Because the signaling is mediated by extensive phosphorylation, phosphatases have emerged as important negative regulators. In addition to their role in disulfide bond formation, cysteine residues often contribute to protein stability via their participation in metal ion coordination, in particular zinc, which is often bound by conserved sets of cysteine and histidine residues in small protein domains. In the following sections we highlight the structure of a few proteins and domains and that are of central and recurring importance in hematology in order to illustrate the relationship between domain architecture and function. Extracellular factors, such as insulin, activate signaling pathways that stimulate protein synthesis through this mechanism.
Hamlar, 55 years: About halfway down the septum, the branches give rise to enlarged Purkinje fibers (purkinje fiberz). The alveoli are the sites of gas exchange between the inhaled air and the bloodstream. The person uses a test kit to draw a drop of blood, applies it to a test strip, then uses a meter to read the concentration of glucose in the blood (in milligrams per deciliter). The total solute concentration in extracellular and intracellular fluids is normally equal.
Taklar, 63 years: Supraphysiologic levels of Ca2+, however, can prompt the opening of a large mitochondrial inner-membrane conductance channel known as the permeability transition pore, which can eventually cause the swelling and rupture of mitochondria. Eight essential amino acids (e) cannot be synthesized by human cells and must be provided in the diet. Activation-induced cell death upon antigen restimulation involves Fas receptor signaling. Congenital causes associated with mild to moderate hemolysis may be clinically silent until detected later in life.
Jack, 45 years: Genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of Notch signaling lead to reversal of the leukemic phenotype. Moving bits of food over the surface of the tongue to stimulate different receptors at different moments keeps us from losing taste due to sensory adaptation. B the patient has ifosfamide encephalopathy, likely secondary to the accumulation of chloroacetaldehyde (a breakdown product of ifosfamide). Majluf-Cruz A, Luna-Castanos G, Trevino-Perez S, et al: Lamivudineinduced pure red cell aplasia.
Gelford, 52 years: Aderka D, Praff G, Santo M, et al: Bleeding due to thrombocytopenia in acute leukemias and reevaluation of the prophylactic platelet transfusion policy. The tail (flagellum) consists of several microtubules enclosed in an extension of the cell membrane. Further elaboration is catalyzed by glycosyltransferases that add various sugars and create branches. Name three types of plasma proteins, and indicate the major function(s) of each type.
Benito, 51 years: A number of factors contribute to tubular reabsorption by enhancing the rate of fluid movement from the interstitial fluid into the peritubular capillaries. A diuretic is a chemical that increases urine production, whereas an antidiuretic decreases urine formation. Chaperones bind to short sequence protein motifs, in many cases containing hydrophobic amino acids. The engulfed material is destroyed when the phagosome fuses with a lysosome, exposing the content to hydrolytic enzymes.
Berek, 65 years: Current evidence largely supports the hypothesis that the content of the neutrophil granules is dictated primarily by the timing of synthesis of their respective content proteins. The synaptic knobs of a thousand or more neurons may communicate with the dendrites and cell body of a single postsynaptic neuron. Activation of growth factor signaling pathways potently stimulate glycolysis at different points, including phosphorylation of phosphofructokinase 2 and pyruvate kinase. If the new gene is introduced into some of the germline cells of the chimeric mouse, then some of the offspring of that mouse will carry the mutation as a gene in all of Chapter1 AnatomyandPhysiologyoftheGene 15 Embryonic stem cell Gene of interest neoR Engineered plasmid Cells selected for resistance to G418 stem cells and for performing gene transfer into those cells has advanced rapidly, and clinical trials have begun to test the applicability of these techniques.
Rathgar, 54 years: In 1982, two Australian researchers boldly suggested that stomach infection by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori causes gastric ulcers. The Fc region of IgG, one of the classes of immunoglobulin, also interacts with protein A, an immune evasion molecule on the cell walls of S. Clinical features may include type 1 diabetes mellitus, eczema, and autoimmune hepatitis. Moretta A, Bottino C, Vitale M, et al: Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis.
Bengerd, 25 years: In the same way as shown experimentally with cytochrome c, it is hypothesized that the few foreign antigens existing on the same particle (in the case of cytochrome c, it is the same molecule) allow spreading of autoimmunity from a foreign antigen to self-antigens. Once activated, the helper T cell proliferates and the resulting cells stimulate B cells to produce antibodies that are specific for the displayed antigen. Within this microenvironment, erythroid development is influenced by cytokines, which are either elaborated by microenvironmental cells or produced elsewhere and then entrapped in the extracellular matrix. Pulmonary circuit the pulmonary circuit consists of vessels that transport blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and back to the left atrium.
Gorok, 40 years: Dendrites, which may be numerous, receive input, and axons send information away from the cell in the form of impulses. Cheeks and Lips the cheeks, forming the lateral walls of the mouth, consist of outer layers of skin, pads of subcutaneous fat, muscles associated with expression and chewing, and inner linings of moist, stratified squamous epithelium. Chronic ingestion of drugs such as alcohol, salicylates, steroids, and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs may cause or contribute to blood loss. Eosinophils may become more abundant during certain parasitic infections and allergic reactions.
Onatas, 48 years: It consists of a flattened head, a cylindrical midpiece (body), and an elongated tail (fig. Most patients do not have physical malformations; therefore, the diagnosis depends on the exclusion of other acquired and inherited causes of thrombocytopenia in early life. Only a few major aspects of that discussion bear repeating for the purposes of this chapter. Another recurring observation in blood malignancies is aberrant histone methylation, for example at H3K27, seen in myelodysplasia.
Vibald, 28 years: The bronchial tree consists of branched air passages that lead from the trachea to the air sacs. The elongated shapes of intestinal villi dramatically increase the absorptive surface area of the small intestine. Natural killer cells express a different group of proteins, with some containing membrane-distal C-type lectin-like domains. The mechanisms for this phenomenon include gene conversion events, back mutations, or compensatory deletions or insertions.
Brenton, 58 years: Muscularis: this layer, which provides movements of the tube, consists of two layers of smooth muscle tissue. E2F promoter elements can be found in S-phase genes and specifically mediate binding of E2F transcription factors. Idiopathic neutropenias may be chronic and benign in nature or may be associated with significant morbidity. The parts of the brainstem include the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata (see figs.
Daryl, 62 years: However, in a small proportion of cases, an inciting cause cannot be identified despite intensive testing. The union of a secondary oocyte and a sperm cell is called fertilization (fert-l-zashun), or conception. After urine forms in the nephrons and collecting ducts, it passes through openings in the renal papillae and enters the calyces of a kidney (see fig. These responses include increased activity in the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, including increased secretion of adrenal hormones.
9 of 10 - Review by N. Domenik
Votes: 296 votes
Total customer reviews: 296