Rizact
Rizact dosages: 10 mg, 5 mg
Rizact packs: 4 pills, 8 pills, 12 pills, 24 pills, 32 pills, 48 pills

5mg rizact amex
Pain in the cancer patient Three-quarters of cancer patients experience pain at some point in their illness pain treatment hemorrhoids 10mg rizact order free shipping. Multiple, concurrent pains are common, particularly in advanced cancer, and it is important to consider the cause and appropriate management of each pain separately. Add additional analgesics one at a time, so that you are able to assess the efficacy of each drug. Ineffective drugs or those that are no longer making a significant contribution to analgesia should be stopped. Titrate opioids to effect or tolerance before adding in additional drugs, to avoid unnecessarily complicated regimes. In difficult cancer pain, combinations are often necessary to achieve adequate analgesia with minimum side effects. In practice, however, this recommendation is a guideline, and the choice of analgesic should be determined by the cause and nature of the pain and the significance of potential adverse effects for a particular patient. Management of specific pains in the cancer patient Neuropathic pain is associated with nerve compression or injury. It usually responds to standard analgesics; however, there may be a ceiling of unacceptable side effects with opioids before complete analgesia is achieved, so adjuvants may be necessary. Bone pain may be usefully treated with radiotherapy, bisphosphonates, hormonal therapy, or radioisotopes. Liver metastases stretching the liver capsule may cause intense right upper quadrant pain that may be exacerbated by inspiration; there may also be a palpable, tender liver. History taking for pain in the cancer patient the history should include the number and location of pain sites, the character of the pain. Examination for pain in the cancer patient During the examination, examine painful areas gently and carefully, to avoid exacerbating pain. Ascertain whether the pain is due to masses or organomegaly, whether the pain arises from soft tissue or bone, and whether there are associated sensory changes which may suggest a neuropathic element. Nausea and vomiting contributes significantly to the morbidity of cancer and its treatment. It is important to determine the underlying causes of the vomiting, as this guides treatment. In many cases, the causes for vomiting are multifactorial, so this requires an understanding of the sites Causes of pain in the cancer patient Pain is often caused by the tumour/metastases compressing normal structures. Bone metastases can be painful but will also result in neuropathic pain if they are compressing nerves. Intracranial disease can cause raised intracranial pressure resulting in headache. Primary bowel tumours or peritoneal disease can cause pain secondary to bowel obstruction. Cancer also predisposes patients to pulmonary embolism, which can present with pleuritic chest pain, so we must not overlook non-malignant causes of pain that may be present in the cancer patient.
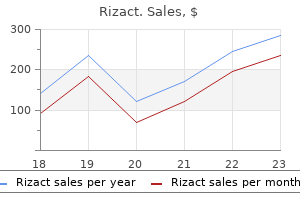
Purchase rizact with a mastercard
The initial aim should be volume resuscitation and pain treatment center regency road lexington ky rizact 10 mg, if the mean arterial pressure falls to <80 mm Hg, consideration should be given to inotropic support. It is essential to take all relevant material for culture prior to the institution of antibiotics. Osmotic laxatives such as lactulose reduce intestinal bacterial production of ammonia and psychoactive amines, and therefore reduce encephalopathy. Rapid evaluation should be performed, with initiation of specific antidotes where feasible. Paracetamol toxicity is dose dependant but its effects are enhanced by induction of Cyp450 by chronic use of alcohol or drugs such as antiepileptics. In idiosyncratic reactions, withdrawal of the causative agent can potentially reverse hepatic injury. Clinical features of chronic hepatic decompensation include encephalopathy, coagulopathy, and hepatocellular jaundice (also see Chapters 207 and 209). Cirrhosis is the final common pathway for a variety of chronic liver diseases and is characterized by fibrosis and the conversion of normal liver architecture into structurally abnormal nodules. There often exists a poor correlation between biopsy findings and the clinical presentation. Some individuals with cirrhosis are asymptomatic and have a reasonably good life expectancy, while others have severe symptoms of chronic liver failure and limited life expectancy. Typical symptoms of the disease and less common symptoms Patients with cirrhosis are often asymptomatic. Early, well-compensated disease may manifest as weight loss, fatigue, and anorexia. In addition, the patient may show heightened sensitivity to a range of drugs normally metabolized by the liver. The numbers of people living with both alcoholic cirrhosis and non-alcohol-related cirrhosis seems to be rising. The number in developing countries is higher due to the prevalence of viral hepatitis. Since the disease often goes undetected for extended periods, a reasonable estimate is that up to 1% of the population may have histological evidence of cirrhosis. Natural history, and complications of the disease the natural course of cirrhotic liver disease depends on the cause of underlying disease and treatment provided. Decompensation rates with chronic viral hepatitis B and C are 10% and 4%, respectively, per year.
Diseases
- Garcia Torres Guarner syndrome
- Fronto-facio-nasal dysplasia
- Spirochetes disease
- Chromosome 7, trisomy 7p13 p12 2
- LyP (lymphomatoid papulosis)
- Tungiasis
Effective rizact 10mg
Other diagnoses that should be considered aside from skeletal dysplasia When considering a diagnosis of skeletal dysplasia back pain treatment yahoo purchase genuine rizact line, exclude other causes of short stature. Storage disorders and a wide range of other metabolic and hormonal conditions can affect growth. Skeletal dysplasia Aetiology of skeletal dysplasia Skeletal dysplasias are caused by abnormalities of bone growth and modelling. Many are linked to mutations in genes for particular collagens or for growth factors and their receptors. Conditions affecting the epiphyses (the area of secondary ossification at the ends of long bones) affect articulation and predispose to early arthritis, requiring joint replacement. Conditions affecting metaphyses (including achondroplasia) shorten long bones, compromising eventual height. The diaphysis is the central shaft and is affected by conditions, like osteogenesis imperfecta, that alter the early collagen bone model. The skeletal dysplasias can be classified clinically, radiologically, or by the causative genetic mutation. One such classification, which is regularly revised, is from the International Skeletal Dysplasia Society and is referred to as the International Nomenclature and Classification of the Osteochondrodysplasias. The commonest non-lethal type is achondroplasia, with an incidence of 1/10 000 to 1/30 000. Natural history of skeletal dysplasia, and complications of the disease In achondroplasia, disordered endochondral bone formation can result in compression of the cervical cord and medulla at the foramen magnum, spinal stenosis, atlantoaxial subluxation, and macrocrania, with or without hydrocephalus. Document whether growth was normal in pregnancy and try to obtain early growth records. If the growth problem is disproportionate, is the shortening proximal (rhizomelic) or distal (mesomelic) There are many other features that can be linked to specific dysplasias, particularly polydactyly or abnormal thumbs; cleft Prognosis of skeletal dysplasia, and how to estimate it In skeletal dysplasia, severe conditions can present in utero, and many are lethal because of reduced lung capacity or evolving hydrops. Treatment of skeletal dysplasia, and its effectiveness As treatment for skeletal dysplasia, surgical management of deformities to improve function and, occasionally, operations to lengthen 938 limbs may be suggested. About 10% of cases will have asymptomatic mitral valve prolapse, and 24% of affected males (but only 4% of affected females) have non-progressive aortic dilatation. Abnormal collagen production gives a more open meshwork to the early bone model, and this eventually leads to reduced mineralization. Approach to diagnosing osteogenesis imperfecta When diagnosing osteogenesis imperfecta, take a three-generation family history of fracturing, deformity, and the associated features.
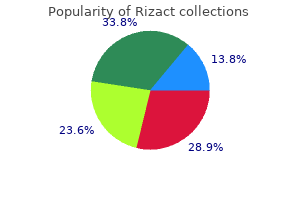
Rizact 5 mg order online
If dissecting aneurysm or bilateral renal artery stenosis is suspected eastern ct pain treatment center buy generic rizact 10 mg on-line, aortography and angiography would be done. Aphasia must be distinguished from dysarthria, which could also be due to involvement of the brain stem or cerebellum. Patients with dysarthria have no difficulty recognizing or interpreting words or phrases, but speech is garbled and difficult to understand by the clinician. D-Degenerative disorders include Alzheimer disease, Pick disease, Huntington chorea, and dementia with Lewy bodies. I-Intoxication should suggest the possibility of alcohol or drug intoxication and Korsakoff psychosis. C-Congenital disorders include cerebral palsy, the leukodystrophies, and congenital abnormalities of the brain such as hydrocephalus and microcephaly. Cerebral aneurysm and atrioventricular (A-V) anomalies might also be brought to mind in this category. A-Autoimmune disorders include multiple sclerosis, lupus erythematosus, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, and other collagen disorders. T-Trauma should bring to mind epidural, subdural, and intracerebral hematomas related to trauma. E-Endocrine disorders are not particularly suggestive of cerebral pathology, but an amniotic fluid embolism may rarely be responsible for aphasia, apraxia, or agnosia. Hypoparathyroidism may bring about seizures which could cause transient aphasia in the postictal phase. The history would be very important in ruling out alcohol or drug intoxication, trauma, or autoimmune disorders. These studies would be most definitive for an infarct, spaceoccupying lesion, or degenerative disorders. Pain may be referred from more proximal portions of the extremity such as the shoulder. Beginning with the skin and subcutaneous tissue, one recalls herpes zoster, cellulitis, contusions, and a variety of dermatologic conditions that should be obvious. Rheumatoid and rheumatic nodules may occur on the skin and are, of course, painful. Beneath the skin the muscles, fascia, and bursae are frequent sites of inflammation and trauma. Contusions, rupture of the ligaments, and bursitis (particularly tennis elbow) are common acute traumatic conditions (bursitis, however, is more likely the result of chronic strain). Inflammatory lesions of the muscles include epidemic myalgia, trichinosis, nonarticular rheumatism, and dermatomyositis.
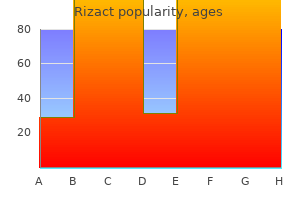
Rizact 5mg order without prescription
In adults (particularly pain medication for a uti buy cheap rizact 5 mg on-line, pregnant females), there is a higher risk of severe disease and complications such as pneumonia and encephalitis. Complications of herpes zoster include herpes zoster ophthalmicus (zoster affecting the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve, causing conjunctivitis, keratitis, or uveitis) and post-herpetic neuralgia. It needs to be distinguished from meningitis, which can be commonly caused by the same viruses and many others. Mortality from untreated herpes encephalitis is approximately 70% and, even with appropriate treatment, fewer than 50% recover with no neurological sequelae. Varicella zoster encephalitis is less well understood but is thought to have a more benign course. Acute hepatitis the natural history of acute viral hepatitis varies quite considerably between individuals. The hepatitis viruses differ in their propensity to cause liver failure or chronic infection. The majority of hepatitis A virus infections are self-limiting: the case fatality rate is <0. Hepatitis B virus infection causes fulminant liver failure in approximately 1% of cases. Hepatitis E can cause fulminant liver failure, particularly in pregnant women, with consequent high mortality rates, but does not cause chronic infection (except in rare cases of immunosuppression). Dengue virus infection is more common and can be acquired in sub-Saharan Africa, South America, and Asia. Dengue haemorrhagic fever is characterized by more severe haemorrhagic manifestations and circulatory failure (due to vascular leak). Viral haemorrhagic fever Other diagnoses that should be considered Certain viral infections have such a classical presentation. The majority of presentations of viral infection, however, are not specific to viral diseases, and the differential diagnosis may be broad. The differentiation between viral and bacterial causes of upper and lower respiratory tract infection is extremely difficult based on history and physical examination alone. Even the use of inflammatory markers in peripheral blood (white blood cell count, C-reactive protein) does not reliably discriminate between a viral and bacterial aetiology.
Syndromes
- Peptic ulcer disease
- The person begins to rub or scratch the itchy area. Constant scratching causes the skin to thicken.
- Vomiting
- Tingling
- Abdominal CT scan
- Heart failure
- Fear of "going crazy"
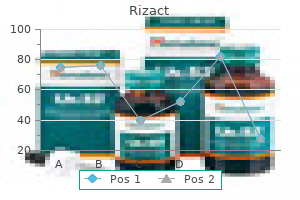
Purchase generic rizact from india
This will potentially have significant impact on resource allocation and workload pain tmj treatment order rizact mastercard. As the serum creatinine test is acknowledged to be an imperfect measure of renal function, particularly when the estimated glomerular filtration rate is above 60 ml/min 1. This is generally diagnosed endoscopically and requires histological confirmation. Screening has been developed to reduce the development of adenocarcinoma via the early detection of high-grade dysplasias or cancer in situ. The main aim of colorectal cancer screening is the early detection of polyps and cancers, at a time when treatment is likely to be more effective. Studies have shown that screening reduces the risk of death from colorectal cancer by ~16%. The future of colorectal screening programmes the colorectal cancer screening programme is still in its early days; the full extent of cancer prevention it provides will be recognized over the next few years. Despite the fact that changing lifestyle measures have reduced the rate of colorectal cancer, it is expected that population growth, alongside screening programmes and increased public awareness, will lead to a higher number of cases over the next 20 years. However, adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus and gastro-oesophageal junction is the fastest growing cancer of the Western world; thus, screening has been implemented in an attempt to curb this growth. In addition, it is reasonable to offer liver imaging within 2 years of the surgery to those 70 years, to identify operable liver metastases early. The lifetime risk of dying from colorectal cancer is as follows: 1:50 for those in the general population, 1:17 for those with any family history, 1:10 for those with one affected relative <45 years old, and 1:6 for those with two affected relatives. Surveillance is usually ceased at 75 years, when the life expectancy is seen to be shorter than the average time taken for adenomas to become malignant. Colonoscopic cancer surveillance in these patients should start at age 25, and gastroscopic surveillance at age 50 (in families affected by gastric cancer), or 5 years earlier than the first case within the family. Surveillance should continue with colonoscopies every 2 years until the age of 75. Surveillance is not required in family members who do not carry the genetic mutation shown to be the cause of colorectal cancer in other members of their family. More recent advances in endoscopic procedures (chromoendoscopy, narrow-band imaging) are more effective at identifying abnormal mucosa. Subsequent studies suggest surveillance is more effective if these modalities are used, with biopsies targeting abnormal tissue.
Rizact 5 mg otc
Initially pain research treatment impact factor discount rizact 5mg overnight delivery, an endoscope is passed into the duodenum in a similar way as in an oesophagogastroduodenoscopy. Initially, the ampulla is cannulated so that radiolucent dye can be injected into the biliary tree, which is visualized via radiological images so that any obstruction to biliary flow can be identified. Operators can then treat the biliary obstruction according to the underlying pathology. Treatment can include sphincterotomy (cutting the sphincter of Oddi to open the exit into the duodenum and allow passage of gallstones), clearing of the bile ducts, dilatation of strictures, and placement of biliary stents. Gastric emptying study A gastric emptying study is used to calculate the rate at which the stomach empties, and can be used to diagnose gastroparesis. Endoscopy Endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure which uses a fibre-optic telescope passed into the body via the mouth or anus. More recently, endoscopic submucosal dissection has been introduced, allowing lesions to be removed in one section. Dilatation: this is most often used for oesophageal strictures, whether benign or malignant, although it is occasionally used for colonic fibrotic strictures. Balloon dilatation is most commonly used, allowing direct visualization of the mucosa as it is stretched. Bougie dilatation involves passing bougies of increasing size over an endoscopically placed guidewire. These can also be placed on a temporary basis in benign recurrent strictures in an attempt to prevent strictures reforming. Furthermore, stents are occasionally used to cover small mucosal tears (usually oesophageal) to prevent leakage as the perforation heals. A balloon-mounted coil is passed into the oesophagus, and a controlled emission of radiofrequency energy is delivered. Photodynamic therapy: this is used in some specialist centres for oesophageal and gastric cancers. The basis behind photodynamic therapy is that a photosensitive drug is given to the patient, which is attracted to cancer cells. Sigmoidoscopies are usually performed with the patient unsedated whereas a colonoscopy usually requires conscious sedation with a short-acting benzodiazepine with or without an opiate (usually pethidine or fentanyl). Prior to the procedure, the patient requires bowel preparation, which, for sigmoidoscopy, involves an enema and, for colonoscopy, requires a full bowel purge. Perforations occur in ~1 in 1000 diagnostic colonoscopies and ~1 in 500 therapeutic colonoscopies. Capsule endoscopy In capsule endoscopy, a capsule containing a camera, a light source, batteries, and a transmitter is swallowed. A positive test is defined as a rise in hydrogen concentration >10 ppm over basal values within the first 2 hours, suggesting bacterial colonization of the small intestine. This initial peak will be followed by a much larger peak signifying the colonic response.
Purchase rizact in united states online
The clinical picture in the former may be almost normal or be that of a mild sickling trait pain treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome order 10mg rizact fast delivery. The red-cell indices will be hypochromic and microcytic, and the film will show anisopoikilocytosis with target cells and occasional sickle cells. Haemoglobin electrophoresis shows a complete absence of Hb A, with Hb S and raised levels of Hb A2 and Hb F. There is mild anaemia and splenomegaly, and the blood film shows thalassaemic changes with large numbers of target cells. Haemoglobin electrophoresis shows predominantly Hb C, with some Hb F and Hb A2 and variable amounts of Hb A. Hb C thalassaemia is largely restricted to West Africans, with occasional North African and Mediterranean cases. Hb E thalassaemia is the commonest severe thalassaemic syndrome in South East Asia and India. The inefficiency of production of the Hb E structural haemoglobin variant leads to a severe beta thalassaemia major syndrome when the allele for this variant is coinherited with the beta0 thalassaemia allele. Some are without obvious effect, while others may impair the integrity of the red cell and lead to haemolysis. The most common abnormal haemoglobin is Hb S, which causes haemolytic anaemia in homozygotes or when co-inherited with another abnormal haemoglobin or a thalassaemic trait. The only other relatively common abnormal haemoglobins are Hb C, Hb D, and Hb E, although several rare unstable haemoglobins are known. Inheritance of a single abnormal haemoglobin gene is not usually associated with significant problems. Heterozygote carriers of betaS do not, in the main, suffer the recognized consequences of the disease, but are important as potential parents of affected children. Delta beta thalassaemias the delta beta thalassaemias comprise a group of disorders involving reduction or absence of synthesis of both delta and beta chains. Clinically, homozygotes present with thalassaemia intermedia, although in homozygotes for one variant, haemoglobin Lepore, the disease behaves more like thalassaemia major. Pathophysiology of sickle cell disease Hb S results from a single base substitution leading to the replacement of glutamic acid by valine at Position 6 in the beta globin chain. The end result is that the cells become rigid and distort into a sickle shape (sickling). Initially, this is reversible on reoxygenation, but repeated cycles of sickling and unsickling lead to a loss of membrane and membrane permeability and, eventually, to irreversible sickling.
Rizact 5 mg order on line
Aetiology of the disease Acute viral infections are amongst the most common illnesses of humans neuropathic pain treatment guidelines rizact 5 mg order free shipping, and numerous viruses can cause disease in humans. Specific syndromes can be identified that have certain viruses as potential causative agents (Table 308. Demographics of the disease Viral infections can affect individuals of any age, gender, and ethnicity. Another group of viruses, in the presence of inadequate immune response, can cause chronic infection. In recent years, there have been notable outbreaks of respiratory viral infections associated with more severe morbidity and mortality. Approach to diagnosing the disease the principles in diagnosing acute viral infections are, first, recognize the syndrome, then identify key features that might suggest a specific diagnosis, and, finally, consider laboratory investigations to elucidate the specific causative agent. Many of the syndromes are not clearly identifiable as viral infections at initial presentation so the differential diagnosis will often include bacterial infections, other infections (fungal, parasitic), and other conditions. A travel history in particular might identify a risk for rare but potentially serious infections. Febrile illness in a patient with history of recent overseas travel should always prompt specialist advice, to guide investigation and management. Acceptable diagnostic alternatives to the gold standard In most cases, it is also possible to use serology for diagnosis of viral infection. The main drawback of serology is that it often requires a comparison of acute and convalescent sera and, hence, diagnosis is delayed. It can, however, be useful to confirm diagnoses retrospectively and is especially useful in epidemiological investigations. Other relevant investigations Other forms of investigation will be warranted for certain syndromes, to assist with the diagnosis or to search for other causes of the presentation. The available therapies and their licensed indications are illustrated in Table 308. Symptoms of the disease Sepsis syndrome can be associated with a range of signs and symptoms that differ from patient to patient (see Box 309. In addition, there can be localizing symptoms, such as pain, vomiting, diarrhoea, ileus, erythema, and headache, which can all provide important clues to the infectious source. A comprehensive list of pathogens causing sepsis is beyond the scope of this chapter; however, some of the most common infections and microbes responsible for causing sepsis in the community and hospitalized patients are shown in Table 309.
Order generic rizact line
In addition pain treatment for uti purchase 5 mg rizact otc, for most acute medical conditions, the survival of those with advanced dementia is diminished with respect to unaffected individuals. A given score can diagnose cognitive impairment with a given sensitivity and specificity. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment is broader in scope and takes a similar amount of time to administer. It provides assessment of a number of domains, and is freely available for clinical use. Additional neuropsychological tests may be selected depending on dominant problems suggested in history taking. Treatment and its effectiveness No proven treatments retard neurodegeneration or significantly alter the natural history of the neurodegenerative dementias, and all current treatments are considered symptomatic. Nonetheless, active management of symptoms can significantly improve quality of life and temporarily ameliorate cognitive function to some degree. General and non-pharmacological measures A multidisciplinary approach to care is requisite. The benefit of community specialist nurses, therapists, support groups, and social care workers to patients and their carers should not be underestimated. There is some data to support a specific benefit of cognitive rehabilitation techniques and in improving cognitive function but standardized approaches need to be tested and validated. While important to exclude alternative pathology, regional patterns of atrophy can suggest the underlying disease. Adverse effects are relatively common and are largely gastrointestinal, but serious adverse events like heart block and seizures are well recognized. It is doubtful whether there is any effect on longterm outcomes such as entry into institutionalized care. It is likely that, in the near future, direct imaging of pathological proteins. Disease-modifying treatment A vast number of compounds proposed to modify pathways of neurodegeneration have been unsuccessfully trialled. Nonetheless, considerable optimism exists that more specific agents currently being developed and trialled will produce a more positive outcome. Behavioural and psychiatric symptoms If behavioural disturbance or psychotic features continue to present significant clinical risk despite sustained attempts at non-pharmacological solutions, then drug treatment should be carefully considered.
Yasmin, 46 years: Typical symptoms of haemophilia, and less common symptoms Affected haemophiliac males suffer from joint and muscle bleeds, as well as easy bruising, the severity of which is closely related to the concentration or level of activity of the affected coagulation factor (see Table 284. Ultrasound Ultrasound is another relatively inexpensive, non-invasive investigation that is commonly used in the diagnosis and staging of malignancy.
Josh, 55 years: Cytokines play a major role in inflammatory processes, immunoregulation, growth, and repair, allowing epidermal cells to communicate with and influence each other, and interact with dermal cells. Acute pelvic inflammation due to a sexually transmitted infection may be distinguished by cervical excitation tenderness (pain on movement of the cervix) with or without adnexal tenderness.
Sanford, 57 years: Demographics of tics Onset of tics usually occurs in childhood, with a high male-to-female ratio. This has driven the search for safer agents directed at an antigenic target pivotal to the relevant disease process.
Tuwas, 50 years: Anatomy, therefore, is the basic science used to develop this differential diagnosis. Although 50% of patients with severe sepsis have bacteraemia at the time of infection, the presence or absence of positive blood cultures does not appear to influence the outcome.
Konrad, 26 years: Chronic liver disease is uncommon but often hastened by excessive alcohol consumption. However, in the first half of the twentieth century, cases were uncommon, and the cause was not understood.
Wenzel, 64 years: Treatment and its effectiveness Patients with acute urticaria and anaphylaxis require emergency management of this condition (see Chapter 75). It is principally a disease of adolescence and it has been estimated to affect over 80% of those between 12 and 25.
Potros, 42 years: The three main effector functions of the complement system are: · opsonization of pathogens and subsequent clearance of the immune complexes · recruitment of inflammatory cells and other mediators via chemoattraction · direct lysis and killing of pathogens via the formation of a membrane-attack complex the clinical consequences of complement deficiency are discussed in Chapter 299. In cases of chronic chest pain, an exercise tolerance test with thallium scan should be done to rule out coronary insufficiency or myocardial infarction.
Givess, 59 years: Usually part of the life cycle of the pathogen 1048 occurs inside the vector, and a specific arthropod is required for each organism. Patients may report marked muscle stiffness (to be distinguished from common mild symptoms) due to myotonia.
Armon, 47 years: However, if the presentation includes signs or symptoms suggestive of intracranial pathology, urgent investigation is indicated. For patients aged 55 or over, and African or Caribbean patients of any age, antihypertensive treatment should typically be initiated with a long-acting dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker or a thiazide-like diuretic.
Nemrok, 51 years: A skin or subcutaneous mass is most commonly an abscess, sebaceous cyst, lipoma, or neurofibroma. In Guidelines for the Management of Asymptomatic Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Summary statement from the Fourth International Workshop 2013 parathyroidectomy was recommended for patients with 1) serum calcium 0.
8 of 10 - Review by I. Runak
Votes: 182 votes
Total customer reviews: 182