Mesalamine
Mesalamine dosages: 800 mg, 400 mg
Mesalamine packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills

Generic mesalamine 400 mg visa
Fever treatment of strep throat order generic mesalamine online, exercise, obesity, sleep apnea, emotional stress, and congestive heart failure can explain transient proteinuria. Proteinuria only seen with upright posture is called orthostatic proteinuria and has a benign prognosis. Isolated proteinuria sustained over multiple clinic visits is found in many glomerular lesions. Affected individuals can have vasculitis, thrombotic microangiopathy, antiphospholipid syndrome, or, more commonly, a systemic disease such as atherosclerosis, cholesterol emboli, hypertension, sickle cell anemia, and autoimmunity. These infectious diseases produce a variety of inflammatory reactions in glomerular capillaries, ranging from nephrotic syndrome to acute nephritic injury, and urinalyses that demonstrate a combination of hematuria and proteinuria. These six general categories of syndromes are usually determined at the bedside with the help of a history and physical examination, blood chemistries, renal ultrasound, and urinalysis. The bedside history and physical examination can also help determine whether the glomerulonephritis is isolated to the kidney (primary glomerulonephritis) or is part of a systemic disease (secondary glomerulonephritis). When confronted with an abnormal urinalysis and elevated serum creatinine, with or without edema or congestive heart failure, one must consider whether the glomerulonephritis is acute or chronic. This assessment is best made by careful history (last known urinalysis or serum creatinine during pregnancy or insurance physical, evidence of infection, or use of medication or recreational drugs); the size of the kidneys on renal ultrasound examination; and how the patient feels at presentation. Patients who quickly develop renal failure are fatigued and weak and often have uremic symptoms associated with nausea, vomiting, fluid retention, and somnolence. Primary glomerulonephritis presenting with renal failure that has progressed slowly, however, can be remarkably asymptomatic, as are patients with acute glomerulonephritis without much loss in renal function. Once this initial information is collected, selected patients who are clinically stable, have adequate blood clotting parameters, and are willing and able to receive treatment are encouraged to have a renal biopsy. High-resolution electron microscopy can clarify the principal location of immune deposits and the status of the basement membrane. By light microscopy, glomeruli (ideally 20) are reviewed individually for discrete lesions; <50% involvement is considered focal, and >50% is diffuse. Injury in each glomerular tuft can be segmental, involving a portion of the tuft, or global, involving most of the glomerulus. Immunofluorescent and electron microscopy can detect the presence and location of subepithelial, subendothelial, or mesangial immune deposits, or reduplication or splitting of the basement membrane.
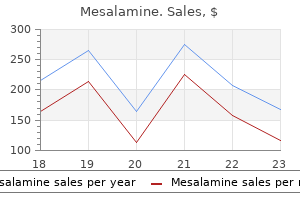
Order mesalamine from india
The process is limited to the mucosa and superficial submucosa medications zopiclone purchase mesalamine 800 mg line, with deeper layers unaffected except in fulminant disease. First, the crypt architecture of the colon is distorted; crypts may be bifid and reduced in number, often with a gap between the crypt bases and the muscularis mucosae. Second, some patients have basal plasma cells and multiple basal lymphoid aggregates. Mucosal vascular congestion, with edema and focal hemorrhage, and an inflammatory cell infiltrate of neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages may be present. Ileal changes in patients with backwash ileitis include villous atrophy and crypt regeneration with increased inflammation, increased neutrophil and mononuclear inflammation in the lamina propria, and patchy cryptitis and crypt abscesses. In the 75% of patients with small intestinal disease, the terminal ileum is involved in 90%. Endoscopically, aphthous or small superficial ulcerations characterize mild disease; in more active disease, stellate ulcerations fuse longitudinally and transversely to demarcate islands of mucosa that frequently are histologically normal. This accompanied by fissures that penetrate deeply into the bowel wall and 2263 sometimes form fistulous tracts or local abscesses. Occasionally, diarrhea and bleeding are so intermittent and mild that the patient does not seek medical attention. Patients with proctitis usually pass fresh blood or blood-stained mucus, either mixed with stool or streaked onto the surface of a normal or hard stool. They also have tenesmus, or urgency with a feeling of incomplete evacuation, but rarely have abdominal pain. With proctitis or proctosigmoiditis, proximal transit slows, which may account for the constipation commonly seen in patients with distal disease. When the disease extends beyond the rectum, blood is usually mixed with stool or grossly bloody diarrhea may be noted. Colonic motility is altered by inflammation with rapid transit through the inflamed intestine. When the disease is severe, patients pass a liquid stool containing blood, pus, and fecal matter. Although severe pain is not a prominent symptom, some patients with active disease may experience lower abdominal discomfort or mild central abdominal cramping. Other symptoms in moderate to severe disease include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fever, and weight loss. Physical signs of proctitis include a tender anal canal and blood on rectal examination. With more extensive disease, patients have tenderness to palpation directly over the colon. Patients with a toxic colitis have severe pain and bleeding, and those with megacolon have hepatic tympany.
Diseases
- Infantile convulsions and paroxysmal choreoathetosis, familial
- Histiocytosis X
- Scholte Begeer Van Essen syndrome
- Hereditary ceroid lipofuscinosis
- Devriendt Legius Fryns syndrome
- Ollier disease
- Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans of Flegel
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type V
- Endocarditis, infective
- Cholestatic jaundice renal tubular insufficiency
Buy mesalamine 400 mg on-line
Eosinophilia >10% is one of the defining features of this illness and may be as high as 75% of the peripheral white blood cell count medicine cabinet home depot effective 800 mg mesalamine. It is present at the time of diagnosis in >80% of patients, but may respond quickly (often within 24 h) to initiation of systemic corticosteroid therapy. Reticulonodular and nodular disease without cavitation can be seen, as can pleural effusions and hilar adenopathy. Angiography may be used diagnostically and may show signs of vasculitis in the coronary, central nervous system, and peripheral vasculature. Recent data suggest that clinical remission may be obtained in >90% of patients treated; ~25% of those patients may relapse, often due to corticosteroid tapering, with a rising eosinophil count heralding the relapse. The asthma can often be severe, and oral corticosteroids are often required to control symptoms but may lead to suppression of vasculitic symptoms. In addition to the more common symptoms of cough, dyspnea, sinusitis, and allergic rhinitis, alveolar hemorrhage and hemoptysis may also occur. Mononeuritis multiplex most commonly involves the peroneal nerve, but also involves the ulnar, radial, internal popliteal, and occasionally, cranial nerves. Although survival does not differ between those treated or untreated with cyclophosphamide, cyclophosphamide is associated with a reduced incidence of relapse and an improved clinical response to treatment. Other possible findings on chest imaging include patchy infiltrates and evidence of mucus impaction. Cardiac involvement includes myocarditis and/or endomyocardial fibrosis, as well as a restrictive cardiomyopathy. Infectious etiologies of pulmonary eosinophilia are largely due to helminths and are of particular importance in the evaluation of pulmonary eosinophilia in tropical environments and in the developing world (Table 282-4). These infectious conditions may also be considered in recent travelers to endemic regions. Loffler syndrome refers to transient pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia that occurs in response to passage of helminthic larvae through the lungs, most commonly larvae of Ascaris species (roundworm). Symptoms are generally self-limited and may include dyspnea, cough, wheeze, and hemoptysis. Loffler syndrome may also occur in response to hookworm infection with Ancylostoma duodenale or Necator americanus. Lung involvement occurs in 40% of these patients and is characterized by cough and dyspnea, as well as pulmonary infiltrates. In immunocompromised hosts, including patients on glucocorticoids, a severe, potentially fatal, hyperinfection syndrome can result from Strongyloides infection. Paragonimiasis, filariasis, and visceral larval migrans can all cause pulmonary eosinophilia as well. Therefore, drug reaction must always be included in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary eosinophilia. Although the list of medications associated with pulmonary eosinophilia is ever expanding, common culprits include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications and systemic antibiotics, most specifically nitrofurantoin.
Buy mesalamine 400 mg mastercard
These patients are at risk of a variety of micronutrient deficiency diseases in addition to the symptoms and disability created by continuing in-hospital starvation medicine 223 buy mesalamine in united states online. They include inadvertent or physician-ordered food deprivation, psychologic depression or distress, poorly controlled pain or nausea, badly presented unappealing food, communication barriers, anorexia nervosa, physical or sensory disability (including dysgeusia), thrush, dysphagia and other mechanical difficulties ingesting food, partial obstruction of the esophagus, stomach or intestinal tract, intestinal angina, and very commonly, combinations of these causes. The body normally adapts to starvation by reducing energy expenditure and curtailing protein catabolism, partly by hormone- and nervous system-regulated alterations in cellular metabolism, and partly by reducing its muscle mass. These adaptations enable prolonged survival during sub-lethal starvation, but survival comes at a cost that includes lethargy, a tendency to hypothermia, muscle atrophy (including of the cardiac and respiratory muscles), skin thinning, and functional disability. Until this terminology is better standardized, we suggest that health care workers explicitly distinguish among (1) situations that create a risk of inadequate nutrient intake, (2) situations in which inadequate intake of specific nutrients actually occurs and creates a discernable risk of developing a specific nutritional disease, and (3) the specific diseases themselves, as enumerated below. Old age is irreversible, but adequate protein and energy provision combined with physical rehabilitation can be lifesaving. As well, their reduced muscle protein mass is unable to release amino acids into the circulation at a rate sufficient to meet the need for protein synthesis at sites of injury and healing, and within the central protein pool to regulate the immuno-inflammatory process. The modern obesity epidemic has created a population of obese patients with chronic inflammation and starvation whose muscle atrophy outpaces their fat loss. Intravascular albumin pool redistributes into this large volume, decreasing the serum albumin concentration. Muscle atrophy and dietary protein deficiency perpetuate inflammation-induced hypoalbuminemia, because muscle protein and the diet provide the amino acids required for hepatic albumin synthesis. Hypoalbuminemia will not improve as long as systemic inflammation persists, even with prolonged optimal nutritional therapy. After systemic inflammation has subsided, several weeks of optimal nutrition may be required for serum albumin concentrations to renormalize. Conditions that increase body protein loss can be identified by measuring the rate of body N loss. Most N leaves the body in the urine (almost all of it in urea, ammonium, and creatinine), the feces, skin, and by other minor routes. Total N is not usually measured in hospital laboratories, but urinary urea concentrations are routinely available. Formulas are available that estimate that total N loss solely from 24-h urinary urea excretion. A recent, validated formula estimates daily total N loss (g) = g N in urinary urea/0. Net muscle protein catabolism follows approximately first-order ("decay") kinetics, such that the rate of N loss from muscle is proportional to the existing total amount of N available to be lost. Muscle atrophic, protein-catabolic patients lose less body N/day in absolute terms than an equivalently catabolic patients with normal muscle mass, but they are at nevertheless at greater risk of succumbing to their critical illness.
Purchase mesalamine 400 mg with mastercard
Recurrent episodes of bacterial lymphangitis symptoms genital warts safe 400 mg mesalamine, usually caused by streptococci, are a very common cause of lymphedema. The most common etiology of secondary lymphedema worldwide is lymphatic filariasis and affecting >120 million children and adults and causing lymphedema and elephantiasis in 14 million of these affected individuals (Chap. Recurrent bacterial lymphangitis by Streptococcus may result in chronic lymphedema. Lymphedema characterized by swelling of the leg, nonpitting edema, and squaring of the toes. Advanced chronic stage of lymphedema illustrating the woody appearance of the leg with acanthosis and verrucous overgrowths. Stage I Early accumulation of fluid relatively high in protein content that subsides with limb elevation. Source: Adapted from the 2013 Consensus Document of the International Society of Lymphology: Lymphology 46:1, 2013. Diagnostic Testing the evaluation of patients with lymphedema should include diagnostic studies to clarify the cause. Lymphoscintigraphy and lymphangiography are rarely indicated, but either can be used to confirm the diagnosis or differentiate primary from secondary lymphedema. Lymphoscintigraphy involves the injection of radioactively labeled technetiumcontaining colloid into the distal subcutaneous tissue of the affected extremity, which is imaged with a scintigraphic camera to visualize lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes. Findings indicative of primary lymphedema include absent or delayed filling of the lymphatic vessels or dermal back flow caused by lymphatic reflux. Findings of secondary lymphedema include dilated lymphatic vessels distal to an area of obstruction. In lymphangiography, iodinated radiocontrast material is injected into a distal lymphatic vessel that has been isolated and cannulated. In secondary lymphedema, lymphatic channels often appear dilated beneath the level of obstruction. The complexities of lymphatic cannulation and the risk of lymphangitis associated with the contrast agent limit the utility of lymphangiography. A novel technique of optical imaging with a near-infrared fluorescence dye may enable quantitative imaging of lymph flow. Occasionally, intermittent pneumatic compression devices can be applied at home to facilitate reduction of the edema. Diuretics are contraindicated and may cause depletion of intravascular volume and metabolic abnormalities. Liposuction in conjunction with decongestive physiotherapy may be considered to treat lymphedema, particularly postmastectomy lymphedema. Other surgical interventions are rarely used and often not successful in ameliorating lymphedema.
Generic mesalamine 800 mg with visa
Short-acting dihydropyridines should be avoided because of the risk of precipitating infarction symptoms your having a boy order mesalamine 400 mg online, particularly in the absence of concomitant beta blocker therapy. Choice Between Beta Blockers and Calcium Channel Blockers for Initial Therapy Since beta blockers have been shown to improve life expectancy after acute myocardial infarction (Chaps. A comparison of the common side effects, contraindications, and potential drug interactions of many of the frequently presented antianginal agents is shown in Table 267-7. Antiplatelet Drugs Aspirin is an irreversible inhibitor of platelet cyclooxygenase and thereby interferes with platelet activation. Clopidogrel combined with aspirin reduces death and coronary ischemic events in patients with an acute coronary syndrome (Chap. Ranolazine, a piperazine derivative, may be useful for patients with chronic angina despite standard medical therapy (see Table 267-7). The major drug in this class is nicorandil, which typically is administered orally in a dose of 20 mg twice daily for prevention of angina. If the symptoms and signs of heart failure are controlled, an effort should be made to use beta blockers not only for angina but because trials in heart failure have shown significant improvement in survival. A trial of the intravenous ultrashort-acting beta blocker esmolol may be useful to establish the safety of beta blockade in selected patients. Revascularization should be employed in conjunction with but not replace the continuing need to modify risk factors and assess medical therapy. However, case selection is essential to avoid a prohibitive risk of complications, which are usually due to dissection or thrombosis with vessel occlusion, uncontrolled ischemia, and ventricular failure (Chap. Oral aspirin, a P2Y12 antagonist, and an antithrombin agent are given to reduce coronary thrombus formation. Restenosis is more common in patients with diabetes mellitus, arteries with small caliber, incomplete dilation of the stenosis, long stents, occluded vessels, obstructed vein grafts, dilation of the left anterior descending coronary artery, and stenoses containing thrombi. In diseased vein grafts, procedural success has been improved by the use of capture devices or filters that prevent embolization, ischemia, and infarction. The use of drug-eluting stents that locally deliver antiproliferative drugs can reduce restenosis to much less than 10%. Of note, however, the delayed endothelial healing in the region of a drug-eluting stent also extends the period during which the patient is at risk for subacute stent thrombosis.
Chinese Jujube (Jujube). Mesalamine.
- Liver disease, muscular conditions, ulcers, dry skin, wounds, diarrhea, fatigue, and other conditions.
- How does Jujube work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Jujube?
- Dosing considerations for Jujube.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96108
400 mg mesalamine buy with mastercard
Hypotension during dialysis can frequently be prevented by careful evaluation of the dry weight and by ultrafiltration modeling symptoms 1dp5dt order mesalamine without prescription, such that more fluid is removed at the beginning rather than the end of the dialysis procedure. Excessively rapid fluid removal (>13 mL/kg per h) should be avoided, as rapid fluid removal has been associated with adverse outcomes, including cardiovascular deaths. Additional maneuvers to prevent intradialytic hypotension include the performance of sequential ultrafiltration followed by dialysis, cooling of the dialysate during dialysis treatment, and avoiding heavy meals during dialysis. Midodrine, an oral selective a1 adrenergic agent, has been advocated by some practitioners, although there is insufficient evidence of its safety and efficacy to support its routine use. Strategies that may be used to prevent cramps include reducing volume removal during dialysis, ultrafiltration profiling, and the use of sodium modeling (see above). Anaphylactoid reactions to the dialyzer, particularly on its first use, have been reported most frequently with the bioincompatible cellulosic-containing membranes. Type A reactions are attributed to an IgEmediated intermediate hypersensitivity reaction to ethylene oxide used in the sterilization of new dialyzers. A nighttime dwell is frequently instilled at bedtime and remains in the peritoneal cavity through the night. The number of exchange cycles required to optimize peritoneal solute clearance varies by the peritoneal membrane characteristics; as with hemodialysis, solute clearance should be tracked to ensure dialysis "adequacy. The major difference between the dialysate used for peritoneal rather than hemodialysis is that the hypertonicity of peritoneal dialysis solutions drives solute and fluid removal, whereas solute removal in hemodialysis depends on concentration gradients, and fluid removal requires transmembrane pressure. Typically, dextrose at varying concentrations contributes to the hypertonicity of peritoneal dialysate. Studies have demonstrated more efficient ultrafiltration with icodextrin than with dextrose-containing solutions. The most common additives to peritoneal dialysis solutions are heparin to prevent obstruction of the dialysis catheter lumen with fibrin and antibiotics during an episode of acute peritonitis. Catheters used for maintenance peritoneal dialysis are flexible, being made of silicone rubber with numerous side holes at the distal end. The scarring that occurs around the cuffs anchors the catheter and seals it from bacteria tracking from the skin surface into the peritoneal cavity; it also prevents the external leakage of fluid from the peritoneal cavity. The peritoneal equilibrium test is a formal evaluation of peritoneal membrane characteristics that measures the transfer rates of creatinine and glucose across the peritoneal membrane. High transporters also tend to lose larger quantities of albumin and other proteins across the peritoneal membrane. In general, patients with rapid transporting characteristics require more frequent, shorter dwell time exchanges, nearly always obligating use of a cycler. The efficiency of solute clearance also depends on the volume of dialysate infused. Several observational studies have suggested that higher rates of urea and creatinine clearance (the latter generally measured in L/week) are associated with lower mortality rates and fewer uremic complications. In general, patients on peritoneal dialysis do well when they retain residual kidney function. Rates of technique failure increase with years on dialysis and have been correlated with loss of residual function to a greater extent than loss of peritoneal membrane capacity.
Discount mesalamine 400 mg fast delivery
Certainly shinee symptoms mp3 400 mg mesalamine order amex, imaging and further study is appropriate in patients whose evaluations are suggestive but not convincing. All patients should be fully prepared for surgery and have any fluid and electrolyte abnormalities corrected. Either laparoscopic or open appendectomy is a satisfactory choice for patients with uncomplicated appendicitis though most procedures are performed in a minimally invasive fashion. Management of those who present with a mass representing a phlegmon or abscess can be more difficult. Such patients are best served by treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics, drainage if there is an abscess >3 cm in diameter, and parenteral fluids and bowel rest if they appear to respond to conservative management. Laparoscopic appendectomy now accounts for the majority of all appendectomies performed in Western cultures and is associated with less postoperative pain, shorter lengths of stay, faster return to normal activity and likely fewer superficial wound complications-although the risk of intraabdominal abscess formation may be higher. Continuation of these findings beyond 5 days should raise concern for the presence of an intraabdominal abscess. The mortality rate for perforated appendicitis or other complicated disease is much higher, ranging from 3% overall to a high as 15% in the elderly. This is called secondary peritonitis, as opposed to primary or spontaneous peritonitis, when a specific intraabdominal source cannot be identified. Physical findings may only be identified in a specific region of the abdomen if the intraperitoneal inflammatory process is limited or otherwise contained as may occur in patients with uncomplicated appendicitis or diverticulitis. Most patients present with tachycardia and signs of volume depletion with hypotension. Laboratory testing typically reveals a significant leukocytosis, and patients may be severely acidotic. Radiographic studies may show dilatation of the bowel and associated bowel wall edema. Free air, or other evidence of leakage, requires attention and could represent a surgical emergency. In stable patients in whom ascites is present, diagnostic paracentesis is indicated, where the fluid is tested for protein and lactate dehydrogenase and the cell count is measured. Secondary peritonitis most commonly results from perforation of the appendix, colonic diverticuli, or the stomach and duodenum. It may also occur as a complication of bowel infarction or incarceration, cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, and intestinal obstruction or volvulus. Conditions that may cause secondary bacterial peritonitis and their mechanisms are listed in Table 324-5.
Buy discount mesalamine 800 mg line
Patients with emphysema often have a quiet chest with diffusely decreased breath sounds medicine pacifier buy mesalamine 400 mg line. A pneumothorax or pleural effusion may present with an area of absent breath sounds. Jugular venous distention may also be a sign of volume overload associated with right heart failure. Pulsus paradoxus is an ominous sign in a patient with obstructive lung disease, as it is associated with significant negative intrathoracic (pleural) pressures required for ventilation and impending respiratory failure. Owing to this association, particular attention should be paid to joint and skin examination. Cyanosis is seen in hypoxemic respiratory disorders that result in >5 g of deoxygenated hemoglobin/dL. Acute respiratory symptoms are often evaluated with multiple tests performed at the same time in order to diagnose any life-threatening diseases rapidly. In contrast, chronic dyspnea and cough can be evaluated in a more protracted, stepwise fashion. A plateau of the inspiratory and expiratory curves suggests large-airway obstruction in extrathoracic and intrathoracic locations, respectively. Restriction can result from parenchymal disease, neuromuscular weakness, or chest wall or pleural diseases (Table 278-1). Additional testing, such as measurements of maximal inspiratory and expiratory pressures, can help diagnose neuromuscular weakness. Patients with diseases that cause ventilation-perfusion Pulmonary Function Testing (See also Chap. A12) Most patients with disease of the respiratory system undergo imaging of the chest as part of the initial evaluation. Clinicians should generally begin with ultrasound of the chest or a plain chest radiograph, preferably posterior-anterior and lateral films. Ultrasound is often readily available and can help rapidly diagnose pneumothorax, pleural effusion, and consolidation of lung parenchyma. Chest radiographs give additional detail and can reveal findings including opacities of the parenchyma, blunting of the costophrenic angles, mass lesions, and volume loss. However, many diseases of the respiratory system, particularly those of the airways and pulmonary vasculature, are associated with a normal chest radiograph. If the test includes administration of contrast, the pulmonary vasculature can be assessed with particular utility for determination of pulmonary emboli.
400 mg mesalamine purchase with amex
Psychological stress and anxiety can increase the release of proinflammatory cytokine medicine wheel teachings discount 400 mg mesalamine free shipping, and this in turn may alter intestinal permeability. Most of these patients demonstrated exaggerated symptoms in response to visceral distention, and this abnormality persists even after exclusion of psychological factors. These may modulate brain networks related to emotional arousal and/ or central autonomic control, salience and somatosensory integration. Abuse is associated with greater pain reporting, psychological distress, and poor health outcome. The microbes involved in the initial infection are Campylobacter, Salmonella, and Shigella. These abnormalities may contribute to abnormal epithelial secretion and visceral hypersensitivity. This finding, however, has been challenged by a number of other studies that found no increased incidence of bacterial overgrowth based on jejunal aspirate culture. Abnormal H2 breath test can occur because of small-bowel rapid transit and may lead to erroneous interpretation. A temporary reduction in lactobacilli has been reported in animal models of early-life stress. On the other hand, Firmicutes is the dominant phylum in adults consuming a diet high in animal fat and protein. It is conceivable that gut dysbiosis acting in concert with genetic susceptibility and environmental insults may alter mucosal permeability and increase antigen presentation to the immune cells in the lamina propria. A careful history and physical examination are frequently helpful in establishing the diagnosis. Gut dysbiosis acting in concert with genetic and environmental factors may alter intestinal permeability, increase antigen presentation resulting in mast cell activation. The cytokines and chemokines generated from mucosal inflammation may cause symptoms such as fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue, and mood changes. The quality, location, and timing of pain may be helpful to suggest specific disorders. Postprandial pain accompanied by bloating, nausea, and vomiting suggests gastroparesis or partial intestinal obstruction. Intestinal infestation with Giardia lamblia or other parasites may cause similar symptoms. When diarrhea is the major complaint, the possibility of lactase deficiency, laxative abuse, malabsorption, celiac sprue, hyperthyroidism, inflammatory bowel disease, and infectious diarrhea must be ruled out. On the other hand, constipation may be a side effect of many different drugs, such as anticholinergic, antihypertensive, and antidepressant medications.
Eusebio, 27 years: The infiltrative process is primarily in the body of the stomach and consists of mature T cells and plasmacytes.
Sebastian, 44 years: The dose of alteplase can be markedly reduced, usually to a range of 2025 mg, instead of the peripheral intravenous systemic dose of 100 mg.
Flint, 26 years: Ongoing assessment is indicated when parenteral or enteral feedings are initiated, because it is necessary to discern what amount of formula is actually being administered to and received by the patient.
Peratur, 64 years: It is important to remember that prognosis and treatment vary widely by disorder (and disease extent).
Raid, 40 years: It is relatively simple, safe, inexpensive, and maintains the digestive, absorptive, and immunologic barrier functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Basir, 33 years: The addition of tricuspid valve repair, consisting usually of insertion of an annuloplasty ring, adds little time or complexity to the procedure and is well tolerated.
Hamlar, 37 years: In these diseases, mild chronic zinc deficiency can cause stunted growth in children, decreased taste sensation (hypogeusia), and impaired immune function.
Grimboll, 56 years: If the bleeding emanates from a laceration of the pleura, apposition of the two pleural surfaces is likely to stop the bleeding.
Corwyn, 61 years: It accounts for a substantial portion of admissions to emergency wards and occurs on all hospital services.
Sugut, 47 years: Initiation of Inflammation Over the past decade, our knowledge of pathogen recognition has increased tremendously.
Ingvar, 35 years: Functional neurologic assessment for neurologic recovery is generally deferred for at least 72 h after return to normothermia, typically 45 days after the cardiac arrest.
Yussuf, 32 years: Affected individuals will often have circulating eosinophilia with clinical manifestation of systemic allergy.
Seruk, 22 years: Low doses of theophylline may be helpful in some patients, and theophylline withdrawal has been found to worsen in many patients.
Darmok, 54 years: Other toxins normally cleared by the kidney may be responsible for the symptom complex known as uremia.
Javier, 25 years: Selected patients should have assessment for diabetes mellitus (fasting serum glucose or oral glucose tolerance test), dyslipidemia (fasting lipid panel), and thyroid abnormalities (thyroid-stimulating hormone level).
Rozhov, 28 years: Beyond the clinical manifestations above, laboratory findings include rising creatinine, transient eosinophilia (6080%), elevated Thrombotic occlusion of renal vessels or branch arteries can lead to declining renal function and hypertension.
Bengerd, 49 years: In the consideration of the processes involved in crystal formation, it is helpful to view urine as a complex solution.
Kadok, 65 years: Repair usually consists of valve reconstruction using a variety of valvuloplasty techniques and insertion of an annuloplasty ring.
10 of 10 - Review by B. Tjalf
Votes: 30 votes
Total customer reviews: 30