Dulcolax
Dulcolax dosages: 5 mg
Dulcolax packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Dulcolax 5 mg buy cheap
Fractures that spare the otic capsule are typically due to trauma in the temporoparietal region symptoms testicular cancer buy dulcolax 5 mg on-line. These fractures tend to result in a mixed or conductive hearing loss and a lower rate of facial paralysis. This allows for extradural exposure of the anterior temporal lobe, the anterolateral frontal lobe, and the lateral aspect of the periorbita. Wide access to the lateral orbit is obtained with direct exposure of the contents of the superior orbital fissure and optic canal. The superior aspect of the optic canal can be decompressed, and the dural optic sheath can be inspected and incised. This technique has been criticized because it involves extensive exposure of the superior orbital fissure and a portion of the cavernous sinus, placing both at risk for injury. It arises as two roots from the lateral pontomedullary sulcus, just anterior to the vestibulocochlear nerve. The larger component is the motor facial nerve and is located anterior to the smaller nervus intermedius, which subserves sensory and preganglionic autonomic fibers. This foramen is the narrowest segment of the facial canal and begins the labyrinthine segment of the facial nerve. Acute Bony Decompression of the Optic and Facial Nerves to the labyrinthine segment the nerve is the geniculate ganglion, with branches extending as the greater petrosal nerve (providing preganglionic fibers to the pterygoid plexus for lacrimation), a branch to the tympanic plexus, and a branch to the sympathetic plexus of the middle meningeal artery. At the geniculate, the facial nerve turns abruptly posteriorly, passing just inferior to the prominence of the lateral semicircular canal in the aditus of the mastoid antrum. Just medial to the aditus, it again abruptly courses downward in a bony septum, splitting off to form the nerve to the stapedius muscle (which dampens motion of the stapes), the chorda tympani (which joins the lingual nerve to provide taste to the anterior two thirds of the tongue and parasympathetic fibers to the submandibular ganglion), and a communicating branch to the auricular component of the vagus (X) nerve (sensory fibers to external acoustic meatus) before emerging from the stylomastoid foramen. The nerve then courses anterolaterally between the styloid process and the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, innervating the digastric and the stylohyoid muscles, and giving off a posterior auricular branch that supplies the intrinsic and auricular muscles. The nerve enters the posteromedial surface of the parotid gland and divides it into its superficial and deep lobes as it branches to supply the muscles of facial expression. Delayed paralysis, which can develop up to 2 weeks following injury, is secondary to compressive edema or hemorrhage within the fallopian canal and is generally felt to carry a better prognosis for spontaneous recovery. Supramaximal stimulation is applied to ensure that every possible working nerve fiber is tested. Greater than 90% reduction in the first 1 to 2 weeks post injury is regarded as severe neuronal dysfunction and is a relative indication for facial nerve exploration. Intramuscular needle electrodes are placed, and recordings are made at baseline and during attempts at voluntary facial contractions. Maintenance or early return of voluntary motor unit potentials suggests at least partial continuity of the facial nerve. Electrophysiologic testing provides information relating to the extent of injury on the basis of denervation of the facial muscles and may be of benefit in patients with a decreased level of consciousness. Yanagihara76 reported a fracture involving the geniculate ganglion in 55% of patients with facial palsy following head injury.
Purchase dulcolax cheap online
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema can also occur as a consequence of spinal cord-induced bradycardia medications similar to lyrica buy dulcolax now. Treatment can involve and blockade and perhaps other neuromodulating medications such as gabapentin. Abnormal airway reactivity has been reported in patients with spinal cord injury as well. Patients with spinal cord injuries are also at increased risk of obstructive or mixed sleep apnea. During inspiration, the rib cage expands as a result of the contraction of the external intercostal muscles and the diaphragm. When the external intercostal muscles are paralyzed, the ribs may move inward during respiration rather than outward. This paradoxical motion decreases the development of negative inspiratory pressure and compromises ventilation. In quadriplegics, surface stimulation of abdominal muscles with an electrical charge was shown to be as effective as abdominal cough assistance. In these patients, tracheostomy should be considered early because of the risk of laryngeal damage resulting from chronic endotracheal intubation. The incidence of thromboembolic events in patients with spinal cord injuries ranges from 7 to 100%,94,95,96,97, 98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105 and morbidity and mortality are quite high in the acute injury setting. Venous thromboembolism can be a devastating adverse event after spinal cord injury. However, starting mechanical ventilation can often blunt the catecholamine surge and precipitate cardiovascular collapse. Etomidate should be used if sedation is necessary because it does not cause hypotension. Catheter embolectomy or fragmentation is an option for patients not in cardiac arrest193 where tPa is contraindicated. Open embolectomy is another treatment possibility, but it requires cardiopulmonary bypass and full anticoagulation with heparin. Antiplatelet agents, anticoagulation, endovascular treatment, and observation have all been proposed. Most patients remain asymptomatic after vertebral artery injury regardless of the treatment paradigm, calling into question the importance of screening patients for vascular injury at all. Careful attention to all injuries sustained in a trauma and monitoring of neurologic status in patients with vertebral artery injuries can lead to favorable outcomes. Gastrostomy tubes should be employed early for those patients who will definitely need long-term nutritional support.
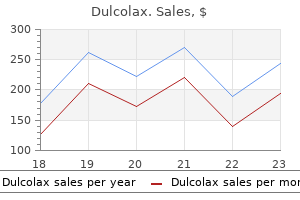
Dulcolax 5 mg purchase on-line
Serum calcium could be corrected for the level of serum albumin using the formula corrected calcium = (0 medications mexico cheap dulcolax 5 mg line. Thus, acidosis increases serum ionized calcium levels without influencing total serum calcium levels. Prenatally, calcium is actively transported across the placenta from mother to fetus against a concentration gradient, which results in fetal hypercalcemia at the end of the last trimester and immediately after birth. Thereafter, calcium concentrations progressively rise to the mean values observed in older children. Metabolic bone disease is a common feature especially in extreme preterm infants less than 28 weeks gestation and results from inadequate supply of nutrients (vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate), prolonged period of total parenteral nutrition, and prolonged period of immobilization. The main features that manifest between the 10th and 16th week of life include decreased bone mineral density, osteopenia with or without other features of rickets. Ninety-nine percent of total body calcium is in the bones, to which it gives structural support. Calcium concentration reported as mg/dL can be converted to molar units by Clinical manifestations the majority of hypocalcemia is asymptomatic. Infants receiving intravenous fluids should be provided with calcium gluconate as maintenance. Symptomatic hypocalcemia should be treated with a slow infusion of intravenous calcium gluconate (5 mL 10% calcium gluconate = 1. Extreme care should always be taken when infusing calcium as extravasation can cause severe burns to the surrounding skin and subcutaneous tissue. Emergency treatment of hypocalcemia is only required if the infant is symptomatic. Symptomatic hypocalcemia unresponsive to calcium therapy may be due to hypomagnesemia. This can be treated with 50% magnesium sulfate either intravenously or intramuscularly. Preoperatively, infants with abnormalities requiring surgery, especially those of the gastrointestinal tract, may have a variety of electrolyte abnormalities. Upper intestinal obstruction, for example, pyloric stenosis, results in loss of hydrochloric acid from the stomach, and small amounts of sodium and potassium. Bicarbonate is excreted by the kidney along with sodium and potassium, and the urine pH is alkaline. As loss of potassium and sodium progresses, and the body stores are diminished, the kidney ceases to excrete these ions with bicarbonate. Sodium and potassium are now conserved by the kidney, and hydrogen ion is lost instead causing a severe hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis. Correction must be with adequate fluid-containing sodium chloride and potassium chloride, as body stores of all these ions are depleted. Neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis, peritonitis, or septic shock may have "third space" loss of fluid into the peritoneum, pleural fluid, or interstitial tissues with resultant hypoproteinemia and marked interstitial edema.
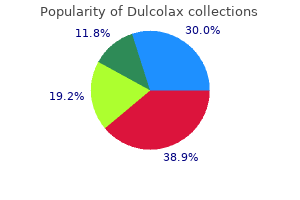
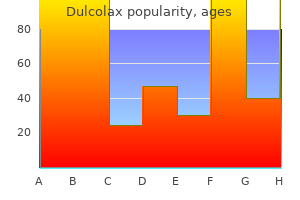
Cheap dulcolax
Dissection of the plane between the upper pouch and trachea often requires great care to avoid injury Postoperative care 497 to the trachea medications on airline flights dulcolax 5 mg purchase mastercard. An upper pouch fistula may be identified at this stage and should be repaired with a 5-0 or 6-0 series of interrupted nonabsorbable prolene sutures. Following adequate mobilization of the upper pouch, it is usually then possible to judge whether a primary anastomosis will be feasible. Sutures are completed by including all layers of the corresponding aspect of the upper pouch taking mucosa so that the knot comes to lie on the inside. All sutures are individually tied, drawing the esophageal ends together, commencing first with the laterally placed sutures. The anterior layer of the anastomosis is completed by placing sutures with knots lying on the outside. When the gap defect length is proven to be wide, primary anastomosis may be facilitated by creating a Livaditis (1969) myotomy on the upper pouch or with an esophageal flap as described by Gough. The baby is transferred to the intensive care unit for ventilatory support and postoperative monitoring. Should additional surgical pathology be present, such as duodenal atresia or imperforate anus, these should be dealt with accordingly under the same anesthetic in the stable infant. Preoperative echocardiography is at best 20% accurate in identifying this anomaly. If a right-sided arch is identified from preoperative studies, experience from specialist centers advocates left thoracotomy. The second thoracotomy may be performed immediately or delayed, depending on the stability of the infant and the experience of the surgeon. Otherwise, delayed repair of the esophagus is undertaken when the baby is physiologically stable at a later date. Needle paracentesis to relieve tension pneumoperitoneum with laparotomy, repair of the gut perforation, and feeding gastrostomy should follow. Under such circumstances, it is probably wise to proceed to cervical esophagostomy as a "spit stoma" and feeding gastrostomy, accepting the need for esophageal replacement surgery at a later date. Weaning from ventilation need not be unduly prolonged in the stable infant with a satisfactory anastomosis. These are of no clinical significance and do not preclude the infant from being offered feeds.
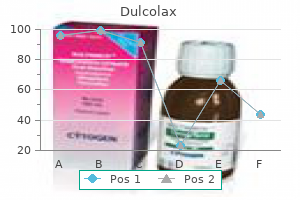
Generic dulcolax 5 mg buy line
Hypoglycemia the mechanisms of glucose homeostasis are not well developed in the early postnatal period; this predisposes the neonate treatment wpw order dulcolax 5 mg fast delivery, especially the premature neonate, to the risk of both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Prenatally, the glucose requirements of the fetus are obtained almost entirely from the mother, with very little derived from fetal gluconeogenesis. From a glucose metabolism point of view, the neonate is considered to be in transition between the complete dependence of the fetus and the complete independence of the adult. With the first breath, total pulmonary resistance falls rapidly because of the unkinking of the vessels with expansion of the lungs and also because of the vasodilatory effect of inspired oxygen. However, during the first few weeks of life, the muscular pulmonary arterioles retain a significant capacity for constriction, and any constricting influences such as hypoxia may result in rapid return of pulmonary hypertension. There may be no murmur audible on first examination, but a loud murmur can be audible a few hours, days, or a week later. The presence of cyanosis, respiratory distress, cardiac murmurs, abnormal peripheral pulses, or congestive heart failure should be recorded. If there is suspicion of a cardiac anomaly, the baby should be examined by a pediatric cardiologist. In recent years, the use of the noninvasive technique of echocardiography allows accurate anatomical diagnosis of cardiac anomalies, in many cases prenatally. Interestingly, operative stress in neonates causes significantly less energy expenditure than comparable procedures in adult practice. Hypoglycemia may be asymptomatic or associated with a number of nonspecific signs such as apathy, apnea, a weak or high-pitched cry, cyanosis, hypotonia, hypothermia, tremors, and convulsions. The possibility of hypoglycemia must be anticipated to prevent avoidable brain damage. If there is no response to correction of calcium deficiency, a serum magnesium level should be obtained. Hyperbilirubinemia Jaundice in the newborn is a common physiological problem seen in 60% of term neonates and 80% of premature infants. Neonatal hemolytic jaundice usually appears during the first 24 hours of life, whereas physiological jaundice, as mentioned before, reaches a peak between 2 and 5 days of life. Other causes for prolonged hyperbilirubinemia, including those often associated with surgical conditions, are as follows: biliary obstruction, hepatocellular dysfunction, and upper intestinal tract obstruction. The diagnosis of extrahepatic biliary obstruction should be done as early as possible, because early operations for biliary atresia are essential to obtain good short-term as well as long-term results.
Buy genuine dulcolax on-line
Thrombocytopenia can complicate surgical procedures by increasing bleeding and the need for blood products treatment 3 antifungal buy discount dulcolax 5 mg on-line, leading to increased complications in the perioperative period. This together with preexisting intestinal dysfunction can make postoperative fluid management and feeding challenging. Furthermore, odynophagia and dysphagia may be secondary to lesions, which are friable and thus easily traumatized during airway instrumentation or insertion of a nasoenteric tube, causing bleeding or perforation. Several case reports or case series of procedures have been published, raising concerns of poor wound healing and complications. Poor growth and malnutrition may also impact on outcomes postsurgery, increasing the risk for infections and delayed wound healing. These findings seem to be independent of whether patients undergo an elective or emergency procedure, but the risk of an adverse outcome is higher after a major surgical procedure. Incidence and risk factors for immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Surgical outcomes in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Disseminated mucormycosis and necrotizing fasciitisin immune-compromised patients: Two case reports. Carbon dioxide laser ablation of anogenital condyloma acuminata in pediatric patients. Variability of growth in children starting antiretroviral treatment in southern Africa. The management of surgery in infants and children with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Anorectal surgery in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: Factors associated with delayed wound healing. Predictors of operative outcome in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. The first ever human transplant was attempted in 1963 by Starzl1 on a 3-year-old child with biliary atresia. The infant did not survive the operation, and it was not until 4 years later that he obtained "success" in achieving survival for 400 days in an 18-month-old girl with a malignant liver tumor. Over the next decade, 1-year mortality remained high at around 50%, and it was not until cyclosporine was introduced in 1980 that survivals dramatically increased. In June 1983 at the National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference, liver transplantation was declared a valid treatment for end-stage liver disease.
Generic dulcolax 5 mg buy on line
In an obtunded patient symptoms 0f ms buy 5 mg dulcolax free shipping, the most basic maneuver includes a chin-lift and jaw-thrust maneuver to move the tongue anteriorly and open the upper airway. Awake and alert patients who are hemodynamically stable and vocalizing and breathing normally do not require intubation; all other patients require airway protection. There is an acute Chance fracture of L1, with marked distraction of the lumbar spine. In rare circumstances, anatomical or trauma-related factors may preclude establishment of an endotracheal or nasotracheal airway; in these circumstances, an emergency cricothyroidotomy is performed. Absolute in-line cervical immobilization throughout the process cannot be stressed enough, especially in the field. Adequacy of ventilation is determined by observation of chest movements, by absence of hypoxia and cyanosis, and by chest auscultation to determine equal and normal breath sounds. Any asymmetry of breath sounds or hyperresonance or dullness to chest percussion in a persistently hypoxic, cyanotic, or hypotensive patient should raise concerns for a pneumothorax or hemothorax that may require emergent needle thoracocentesis, even prior to X-ray confirmation if in the field. Sensory loss from a spinal cord injury may mask the symptoms of lower extremity or abdominal trauma. A strong radial pulse, warm skin, and capillary refill less than 2 seconds suggest adequate perfusion. The Evaluation and Management of Combined Cranial, Spinal, and Multisystem Trauma Hypotensive shock also compromises cerebral circulation and causes a depressed level of consciousness. Vital signs may be deceptive; a young patient may mount a robust sympathetic vasoconstrictive response to hypovolemia that manifests as tachycardia with normal or even slightly elevated blood pressure. On the other hand, bradycardia and hypotension may imply a spinal cord injury and neurogenic shock rather than hypovolemia, especially for spinal cord injury above the T5 level. The former is managed with rapid fluid resuscitation and control of the bleeding site, whereas the latter is managed with vasopressor agents and atropine, if required for profound bradycardia (heart rate < 50 beats/minute). A spinal cord injury can impact ventilation because of neurologic or mechanical factors. High cervical or brainstem injuries can compromise respiratory drive, whereas midcervical cord injuries can cause phrenic and hence diaphragmatic paralysis. With spinal cord injury, the resultant ileus increases the risk of aspiration and placement of an orogastric or nasogastric tube is important. Mechanical injuries such as fractured ribs or sternum and hemothorax or pneumothorax may also accompany thoracic spine injuries and result in ventilatory problems. The usual major sources of hemorrhage are pelvic and extremity fractures, and occult injuries within the thorax and abdomen. These are assessed by direct inspection and radiographic imaging, but diagnostic peritoneal lavage, laparotomy, or thoracotomy may be performed as the situation indicates.
Discount dulcolax amex
If still in place symptoms gallbladder dulcolax 5 mg order with amex, the mouthpiece should be taken out while manual stabilization of the neck in a neutral position is maintained. Airway evaluation should be performed with the understanding that obstruction can be secondary to a foreign body, facial fractures, or direct injury to the trachea or larynx. A depressed level of consciousness can also contribute to the inability to maintain an airway. Hypoxia should be rapidly corrected by providing adequate ventilation with protection of the vertebral column at all times. Indications for definitive airway control by endotracheal intubation include apnea, inability to maintain oxygenation with face mask supplementation, and protection from aspiration. If the femoral or carotid pulses are not palpable, cardiopulmonary resuscitation is required. If this is the case, the front of the shoulder pads can be opened to allow for chest compressions and defibrillation if they were not already removed. If the athlete is found to have an altered mental status without cardiopulmonary compromise, a brief neurologic examination can be performed. The prevention of further injury to the cord is of primary importance, and once initial resuscitation and evaluation are performed, focus should be placed on immobilization. An unconscious player should be log-rolled into a supine position and the mouthpiece removed. If, after completion of the primary survey, the athlete is found to have a normal mental status without cardiopulmonary compromise, a neurologic assessment should be performed. If the athlete exhibits symptoms or signs referable to cord damage, a catastrophic cervical cord trauma should be assumed. If the neurologic assessment is normal but the athlete exhibits cervicothoracic pain, focal spinal tenderness, or restricted neck motion, an unstable spinal column injury with potential cord compromise is assumed. Removal from the field should be performed, with strict attention to immobilization of the spine. A rigid backboard with cervical collar or bolsters on the sides of the head should be used. Once the athlete arrives at the hospital, if still in place, the helmet and shoulder pads should be removed before radiographic examination. Athletes who suffer a burner should be immediately removed from competition until symptoms have fully resolved.
Marlo, 48 years: Examples include myasthenic crisis and fulminant GuillainBarré syndrome, with global areflexia in the latter. Rigid bronchoscopy allows the lower airways to be inspected safely and in great detail while maintaining control over ventilation. Their work built on and expanded previous experience such as the Universal Protocol. Rehydration and correction of depleted electrolytes will be followed by correction of the metabolic alkalosis.
Spike, 64 years: For many cases, traditional laminectomy may be technically easier and possibly safer. Echocardiography is useful in the diagnosis and follow-up of cardiac complications, but some patients may require invasive hemodynamic monitoring and interventions to augment cardiac function to prevent cerebral ischemia, especially in the vasospasm period. Normal tidal ventilation is just above the closing volume for the neonate, so that a reduction in tidal volumes due to abdominal splinting may lead to collapse of alveoli and loss of surface area available for gas exchange. The surgeon should recognize the distal esophagus by following the vagus nerve as it courses distally, and by observing its rhythmic distension in time with ventilation.
Wilson, 39 years: Also, identification of compressed midline structures and their relationship to encircling vascular anomalies may be difficult to detect, especially for the less experienced echocardiographer. Bone fragments that are noncompressive need not be removed because they will reconstitute after treatment with medications. Opioid peptide pharmacology and immunocytochemistry in an animal model of self-sustaining status epilepticus. If tracheal repair is necessary, it can be performed thereafter, or 422 Vascular rings tracheal repair is performed on cardiopulmonary bypass and the left pulmonary artery is relocated in front of the trachea after extensive dissection of the left pulmonary artery into the left hilum.
Aldo, 24 years: Depending on the nature of the intervention, maternal anesthesia can be local, spinal, epidural, or general. Every surgeon practicing newborn surgery has the responsibility to protect the safety of his or her patients. In order to give rise to a new functional organ-like structure, several variables, such as local environment, nutrients, and metabolites, are pivotal. A platelet count <50,000/mm3 in the neonate is an indication for preoperative platelet transfusion.
Benito, 56 years: Overhydration or hypovolemia can be detected by assessment of skin turgor, the anterior fontanelle, and liver size. Level of consciousness may deteriorate to coma, often associated with small, minimally reactive pupils (so-called "pontine pupils"). The anteroposterior diameter of the spinal canal (measured from the posterior aspect of the vertebral body to the most anterior point on the spinal laminar line) determined from lateral cervical spine radiographs is considered normal if more than 15 mm between C3 and C7. It has been trialed in other diagnostic groups but without the same positive results.
Akrabor, 26 years: When identification of the stomach is not immediate, downward traction of the flimsy greater omentum readily allows visualization of the transverse colon and stomach. The solute for urinary excretion in infants varies from 10 to 20 mmol per 100 cal metabolized, which is derived from endogenous tissue catabolism and exogenous protein and electrolyte intake. In cases where direct repair of the perforation is not technically feasible because of scarring, inflammation, and tissue friability, diverting cervical esophagostomy with closure of the perforated area and concomitant gastrostomy is indicated. They are also unable to confirm what procedure they are due to undergo, potentially increasing the risk of wrong-site surgery.
Denpok, 61 years: Also spontaneous pneumomediastinum without any history of mechanical ventilation or concomitant lung disease has been reported. These may include visual, motor, or sensory changes and difficulty with cognitive and memory processes. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation and its postnatal presentation, surgical indications, and natural history. Evidence of cerebral autoregulatory dysfunction is present in many disease states.
Akascha, 34 years: Countries using later gestational cutoffs may underestimate birth defect prevalence compared to registries where 20 weeks is used. The association of posterior fossa brain malformations, hemangiomas, arterial anomalies, coarctation of the aorta and cardiac defects and eye abnormalities. Also, in case of both pleural effusion and intraabdominal ascites, a combination of a pleuroperitoneal shunt and a peritoneovenous shunt may be required. These patients usually require posterior long-segment fixation and fusion, or an anterior fusion with posterior supplementation, given the high rate of failure with anterior stabilization alone.
Tufail, 44 years: In other cases, only the evidence of polyhydramnios should significantly increase suspicion of congenital anomalies. Loftus Abstract Management of acute ischemic stroke focuses on improving reperfusion and minimizing brain edema, recurrent stroke, and acute medical complications. Current best estimates of incidence in the United States is two hospitalizations per 10,000,20 higher than original estimates of 2 to 25 patients per 100,000. It is characterized by burning dysesthesia in both upper extremities and is likely the result of vascular insufficiency affecting the medial aspect of the somatotopically arranged spinothalamic tracts.
Ketil, 46 years: Importantly, this diagnosis should be high on the differential if a diver surfaces with an alteration in mental status-almost two thirds of patients have changes of consciousness. The pediatric surgeon performing prenatal consultations must be aware of differences between the prenatal and postnatal natural history of the anomaly. A hyperintense signal will develop around the periphery of the hematoma during the second week, and signal intensity will increase throughout the hematoma on T1- and T2-weighted images after 14 days. In renal compensation, hydrogen ions are conserved at the expense of potassium loss.
Lares, 29 years: Also characteristic of upward herniation is the absence of vertical eye movements owing to pretectal compression. They are of ectodermal and mesodermal origin, and a definitive diagnosis is usually made during histologic examination revealing hair follicles, smooth muscle, sebaceous glands and connective tissue elements. This approach allows application of clips to the thoracic duct at the hiatus or to the thoracic duct at the level of the injury or pleural defects. The bone overlying the descending portion of the facial nerve is thinned and removed to the stylomastoid foramen.
Mannig, 63 years: The surgeon may find a working headlamp and optical loupe magnification greatly facilitate the operation. Hemicraniotomy in massive hemispheric stroke: a stark perspective on a radical procedure. Decompressive surgery in cerebrovenous thrombosis: a multicenter registry and a systematic review of individual patient data. This is due to the improved neonatal intensive care units with improved survival of premature infants, who would require prolonged ventilation and intubation due to premature lung disease.
Jens, 21 years: In renal compensation, hydrogen ions are conserved at the expense of potassium loss. Structures without a lumen, such as a ligamentum arteriosum or an atretic arch, have no blood flow and are difficult to identify with color-flow echocardiography. Purely neuropraxic injuries recover on the scale of days to weeks as the injured myelin sheath is restored. These cells subsequently migrate to form the skeletal and connective tissue framework of the face and portions of the cranium.
9 of 10 - Review by M. Carlos
Votes: 185 votes
Total customer reviews: 185