Betahistine
Betahistine dosages: 16 mg
Betahistine packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills

Buy cheap betahistine online
Some hemorrhages are white centered; this should not be confused with the pinpoint white light reflex from the apex of a hemorrhage medications without a script best order for betahistine, or with hemorrhage around a leukemic deposit. The white area consists of platelet and fibrin deposits that occlude the vessel, or septic emboli. They result from retinal vascular occlusion in patients who have recently received bone marrow transplants, whether or not they have been treated with cyclosporin. They can recover spontaneously and are associated with retinal vascular endotheliopathy. Hard exudates: these small yellowish lesions are seen in relation to vessels that are chronically leaking noncellular blood elements and are most frequently seen in chronic leukemias with hyperviscosity. Retinal infarction in the acute stage: this gives rise to large areas of cloudy swelling of the retinal nerve fibers and ganglion cell layer. It is usually a feature of leukemia with a very high white blood cell count and hyperviscosity. Communicating hydrocephalus, chiasmal infiltration, and sixth nerve palsies may occur. Rarely, children may develop a leukoencephalopathy due to methotrexate and cranial radiation. With refinements in therapy, neurologic complications of leukemia and its treatment are now less common. Better supportive care has reduced the incidence of hemorrhage, and improved therapy has reduced leukoencephalopathy. Infection by measles, varicella, or mumps is less common since the introduction of vaccination programs and immunoglobulin prophylaxis in children with proven contacts. Vitreous cells Vitreous involvement with leukemic or blood cells is usually secondary to retinal or choroidal infiltration or hemorrhage. Vitreous organization is an unusual, but serious, sequela to widespread retinal or optic nerve infiltration. Other retinal manifestations Serous retinopathy15 and retinal pigment clumping occur as manifestations of choroidal ischemia. The response to irradiation at 2000 cGy may be dramatic22; whatever the treatment, optic atrophy is a frequent sequel. Optic neuropathy may also be caused by vincristine treatment23 or by radiotherapy. The neuropathy is dose related and usually starts as a peripheral neuropathy with abnormal deep tendon reflexes. L-Asparaginase may idiosyncratically be associated with a severe, sometimes fatal, encephalopathy. Cytarabine may cause blurred vision from keratoconjunctivitis (prophylaxis with topical steroids has been tried), corneal epithelial opacities, and microcysts. Methotrexate is a significant cause of neurologic problems including arachnoiditis from intrathecal administration, seizures, depression, and leukoencephalopathy with ataxia and Complications of treatment dementia.
16mg betahistine with visa
In the visually formative years medicine used to treat chlamydia generic betahistine 16mg with visa, alignment that allows for fusion and prevention of amblyopia is paramount. Fusion disruption for as little as 4 months can risk permanent loss of binocularity. Visual acuityis20/20ineach eyeandsheis orthotropicatnear anddistancefixation withhigh-grade stereoacuity. References For those patients that need correction beyond 10 years of age, contact lenses are a viable option and may improve compliance; additionally, refractive surgery has been used successfully in small series of older children and young adults. The deterioration of accommodative esotropia: frequency, characteristics, and predictive factors. Risk factors for abnormal binocular vision after successful alignment of accommodative esotropia. Primary inferior oblique overaction congenital esotropia, accommodative esotropia, and intermittent exotropia. Asymmetric inferior oblique overaction and its association with amblyopia in esotropia. Pharmacologic plus optical penalization treatment for amblyopia: results of a randomized trial. The long-term follow-up of accommodative esotropia in a population-based cohort of children. Clinical features predictive of successfully weaning from spectacles those children with accommodative esotropia. Hyperopic corneal refractive surgery in patients with accommodative esotropia and amblyopia. Comitant esotropia of the "Bielschowsky" type: these patients have up to 5 diopters (D) of myopia. The mechanism of a causal relationship between the myopia and esotropia is debated. In groups 1 and 3 there is generally a clear cause for loss of fusion and investigation is not indicated in the absence of any other abnormalities. In group 2, there is no clear cause for the breakdown of fusion and there is concern about underlying neurological disease. History and examination should determine whether there is evidence of a pre-existing cause for the esotropia and whether there is evidence of any associated neurological disease. Patching can precipitate a manifest squint in a child with a pre-existing microtropia or esophoria. Features suggesting neurological disease include age of onset after the age of 5 years and distance diplopia prior to the onset of the esotropia.
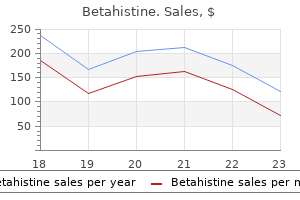
Order 16mg betahistine amex
It is said that sporadic aniridia is associated with Wilms tumor in up to one-third of cases treatment 4 water purchase betahistine no prescription. A chromosomal deletion involving both loci results in the association of Wilms tumor with aniridia. In Denmark,44 patients with sporadic aniridia have a relative risk of 67 (confidence interval: 8. None of the patients with smaller chromosomal deletions or intragenic mutations were found to develop Wilms tumor. Familial aniridia patients are said not to be at risk for Wilms tumor; however, one case has been reported in a child with familial aniridia, but this probably represents a familial 11p13 deletion. Defining the accurate breakpoints of the 11p13 deletion may contribute to the genetic counseling, disease prognosis, and prevention. Multisystem syndromes and chromosomal abnormalities such as ring chromosome 6 can also include aniridia. Until the result is known, all children with sporadic aniridia should have repeated abdominal ultrasonographic and clinical examinations. One protocol advised that the child be examined every 3 months until the age of 5 years, every 6 months until the age of 10 years, and once a year until the age of 16 years. Management of the ocular condition consists of conservative measures such as correction of any refractive errors with filter lenses to reduce glare, and surveillance for onset of glaucoma. These patients often suffer from chronic angle closure glaucoma, which usually develops later and is difficult to treat. Cyclodiode laser, drainage tubes, and trabeculectomy with antimetabolite (usually mitomycin) have all been advocated for treatment of established glaucoma uncontrolled by topical medication alone. It is essential that the ocular microenvironment be assessed for dry eyes or meibomian gland dysfunction as this can accelerate the corneal opacification due to limbal stem cell abnormality. White arrows = lens edge; white crosses = iris remnant; black arrow = Ahmed tube in eye. Recently, nonsense-suppressing small molecules with limited toxic effects have been described. The role of amblyopia also plays an enormous part, such that a clear surviving graft in the presence of dense amblyopia cannot be considered an outright success. This is sutured using 8/0 nylon in four quadrants, and the suture is left long so as to stabilize the eye with the long suture ends using Steri-Strips. Prior to trephination of the host, mannitol is infused according to the weight and age of the child to reduce the intraocular pressure and reduce the risk of expulsive hemorrhage. A manual trephine is used and, if keratolenticular adhesions or extensive iridocorneal adhesions are present, the anterior chamber is not entered with the trephine. Vacuum trephines such as the Barron-Hessburg are usually not manufactured to a small enough diameter.
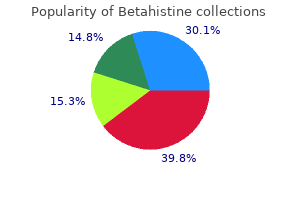
Discount betahistine 16 mg online
Specific conditions In the blepharophimosis syndrome medicine cabinets betahistine 16 mg buy mastercard, levator function is usually poor and bilateral autogenous fascia lata brow suspensions are required. The epicanthus inversus is usually best treated with a medial canthoplasty about 6 months before the lids are lifted. In Marcus Gunn syndrome, if the jaw-winking element is unobtrusive, the ptosis alone can be corrected based on the levator function. If the jaw-winking is severe, it can be abolished or diminished by transecting the levator muscle and attaching it to periorbita behind the supraorbital rim. In some patients, the "wink" becomes less noticeable over time if they learn to control their jaw movements. It may be justifiable to delay surgery until the child is old enough to determine the ultimate degree of jaw-wink. If Bell phenomenon is defective, there is a risk of exposure keratitis, and ptosis surgery should be more conservative. Congenital third nerve lesions may often display aberrant innervation with cross-signaling between the medial rectus and levator palpebrae superioris (see Chapter 84). It can be seen that there is no lid crease on the right while it is present on the left. The child is looking down during this photograph and the normally ptotic lid is slightly higher than the normal lid. The failure of the affected levator to relax in downgaze suggests a dysgenetic etiology. If ptosis persists, silicone rod frontalis sling allows elevation of the eyelid and postoperative adjustment of eyelid height, if necessary. The two ends of the rod are attached to each other by placing them through a Watzke sleeve; the ends are left long with about 1 cm of excess rod on either side. If necessary, the eyebrow incision may be re-opened later over the sleeve to loosen the sling. Aponeurotic defects occurring congenitally, traumatically, or secondary to blepharochalasis syndrome should be repaired by advancing the levator aponeurosis. This is best done under local anesthesia when the child is older, so that eyelid height and contour can be adjusted intraoperatively. In the congenital cranial dysinnervation disorders (see Chapter 83), a brow suspension with careful postoperative management to prevent exposure may give good results. In these, the retractors should be lengthened via an anterior approach levator recession or Z-myotomy, or a spacer graft, and the skin crease reformed at the desired level.
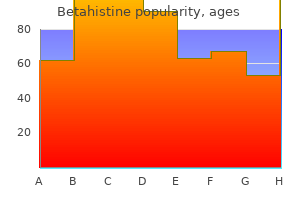
Discount betahistine express
The use of digital imaging in the identification of skip areas after laser treatment for retinopathy of prematurity and its implications for education and patient care administering medications 8th edition order generic betahistine from india. Diode laser photocoagulation to the ridge and avascular retina in threshold retinopathy of prematurity. Atlas of fluorescein angiographic findings in eyes undergoing laser for retinopathy of prematurity. Risk factors for recurrent fibrovascular proliferation in aggressive posterior retinopathy of prematurity after early vitreous surgery. Laser photocoagulation (810 nm diode) for threshold retinopathy of prematurity: a prospective randomized pilot study of treatment to ridge and avascular retina versus avascular retina alone. Avoiding endotracheal intubation of neonates undergoing laser surgery for retinopathy of prematurity. Morphine analgesia as an alternative to general anaesthesia during laser treatment of retinopathy of prematurity. Technical aspects of laser treatment for acute retinopathy of prematurity under topical anesthesia. A survey study of musculoskeletal disorders among eye care physicians compared with family medicine physicians. Avoiding neck strain in vitreoretinal surgery: an ergonomic approach to indirect ophthalmoscopy and laser photocoagulation. Cataract and phthisis bulbi after laser photoablation for threshold retinopathy of prematurity. Cataract in infants treated with argon laser photocoagulation for threshold retinopathy of prematurity. Case series of angle-closure glaucoma after laser treatment for retinopathy of prematurity. Iris atrophy, cataracts, and hypotony following peripheral ablation for threshold retinopathy of prematurity. Bilateral hyphemas and cataracts after diode laser retinal photoablation for retinopathy of prematurity. Exudative retinal detachment following photocoagulation in older premature infants for retinopathy of prematurity: description and management. The risk for retinal detachment associated with hemorrhages pre- and postlaser treatment in retinopathy of prematurity. Macular hard exudates and scar formation after laser photocoagulation in retinopathy of prematurity. A comparison of laser photocoagulation with cryotherapy for threshold retinopathy of prematurity at 10 years: part 1. Bevacizumab (Avastin) for retinopathy of prematurity: wrong dose, wrong drug, or both Refractive errors after the use of bevacizumab for the treatment of retinopathy of prematurity: 2-year outcomes.
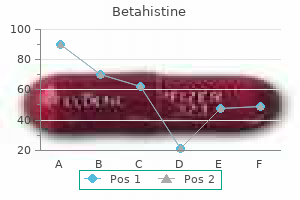
Putiha (Spearmint). Betahistine.
- Gas (flatulence), indigestion, nausea, sore throat, diarrhea, colds, headaches, toothaches, cramps, cancer, arthritis, muscle pain, and skin conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Spearmint work?
- Dosing considerations for Spearmint.
- What is Spearmint?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96820
Purchase betahistine 16 mg with mastercard
These recurrences do not occur in non-ocular tissues; their pathogenesis is obscure symptoms 3 days past ovulation buy betahistine line. In the chronic phase of the disease (>1 month from onset), treatment focuses on management of chronic ocular surface disease by eliminating or minimizing toxicity from topical treatments and the introduction of immunosuppressive therapy if there is recurrent inflammation or progressive cicatrization. Successful management depends on the identification of the contributing components of the ocular surface disease, which must all be managed for successful control of the disease (see below). Severe conjunctival inflammation leads to the following sequence of events (Table 16. Metaplasia of the meibomian gland duct epithelium is accompanied by abnormal lashes that grow from the gland opening (distichiasis). Keratinization extending onto the posterior lid margin is a particular risk for progressive corneal vascularization and opacification. Keratinization of the corneal surface results in severe discomfort and loss of vision. Conjunctival scarring can lead to lid shortening and entropion, resulting in corneal abrasion from trichiasis. This may progress rapidly to corneal stromal melt and perforation, particularly if there is microbial infection. The mechanism is the recognition by donor cytotoxic T lymphocytes of host alloantigens on antigen-presenting cells. There may be necrosis of the lid margins with secondary keratinization of the posterior lid margin and conjunctiva, trichiasis, and entropion. The incidence of severe ocular complications may be reduced by regular ophthalmic review and early treatment. Inherited abnormalities of the epidermal microfilament assembly structure can cause severe corneal and ocular surface disease. It is a very rare autosomal recessive condition described in consanguineous Punjabi Muslim families that comprises skin, laryngeal, and ocular mucous membrane sloughing and granulation tissue. The conjunctival changes are resistant to treatment, although fornix reconstruction using amniotic membrane may be partly effective. Corneallimbusstemcellfailure (ocularsurfacefailure) Corneal epithelial stem cells are located in the basal layer of the epithelium at the limbus. Corneal limbus stem cell failure (ocular surface failure) and subepithelial scarring. An oversized or eccentric keratoplasty that includes part of the limbus can also be used if there is associated corneal stromal opacity. Laboratory-based techniques of cultured limbal epithelial transplantation have also been developed.
Betahistine 16 mg purchase visa
Fluoroscopic visualization may be required for optimum insertion and control of the depth of insertion into the femoral neck medications similar to lyrica order cheapest betahistine and betahistine. E, An intertrochanteric or subtrochanteric osteotomy is made to allow repositioning of the leg in a position of slight abduction and external rotation. Normally the leg should be placed in a position of extension in the supine position. The upper femur may be exposed through a separate lateral incision, or by extending the anterior exposure and reflecting the vastus lateralis from the anterior aspect of the femur. Postoperative Management the patient is placed in a one-and-one-half-hip spica cast until union of the fusion and femoral osteotomy. Alternatively, external fixation of the pelvis to the lower femoral fragment may be used. The hip and upper end of the femur should be clearly visualized on the image intensifier. The entire hip and lower limb are prepared and draped to allow free movement of the limb. The upper end of the femur and trochanteric region are exposed through a direct lateral approach. D B, Under image intensifier control, the lines of osteotomy are defined by drilling guiding Kirschner wires parallel to the intended bone cuts above and below the wedge resection lines. The upper Kirschner wire should stop short of the capital physis and the defect of the femoral neck, and the tip of the lower Kirschner wire should be just below the upper osteotomy line and terminate medial to point X (the apex of the wedge of bone to be resected). C, With an oscillating saw, the upper intertrochanteric osteotomy is performed, and the wedge of bone is resected. Operative Technique A, the angle of bone wedge to be resected is determined from tracings of the preoperative radiograph. F, Pauwels recommended fixing the fragments with a tension band wire loop passed through drill holes in each fragment. G, Preferable alternatives for internal fixation are to use either a contoured plate and screws over the greater trochanter to the distal fragment or a blade plate or sliding compression screw and plate fixation device. The normal limb underneath is flexed at the hip and knee and fastened to the table by wide adhesive straps. The perineal area and, in the male, scrotum and penis, are shielded and held out of the operative field with sterile, self-adhering skin drapes. The operative area is prepared and draped so that the proximal thigh, inguinal and gluteal regions, and abdomen are sterile. It should be possible to turn the patient onto his or her back and side without contaminating the surgical field.
Proven 16 mg betahistine
Histologically medicine in the civil war cheap betahistine 16mg buy online, there is lymphocyte aggregation at the dermal/epidermal interface and a perivasculitis. It is essential that an ophthalmologist examines patients at the onset of disease. Acute ocular complications usually occur concurrently with the skin disease but may precede it by several days. Conjunctival ulceration over the tarsal plates is common but may be difficult to confirm due to lid swelling. Patients are critically ill and require transfer to a regional burns unit or intensive care department for skin care and medical support. The goals of acute management of ocular involvement are minimization of inflammation and adhesions, infection 144 prophylaxis, and the prompt identification and treatment of complications such as exposure and microbial keratitis. Ocular hygiene with topical anesthetic and saline will remove inflammatory debris and periodic lysis of conjunctival adhesions with a squint hook or forceps to remove membranes, or scissors to divide early adhesions, is often performed, although there is no proof of long-term benefit. Lid taping or lubricant ointment and a moist chamber with polyethylene film must be used if the patient is anesthetized to prevent exposure keratitis. A topical antibiotic (quinolone) should be used if there is corneal epithelial breakdown. Topical corticosteroid or cyclosporin may help reduce severe conjunctival inflammation, but they should be used cautiously when there is a corneal epithelial defect because they may mask signs of infection, and bacterial or candida superinfection of an epithelial defect can progress rapidly. An amniotic membrane secured with absorbable sutures to cover the entire ocular surface, or secured over a conformer, may limit symblepharon formation and prevent limbal stem cell Chronic papillary conjunctivitis Table16. A sheet of cultured epithelial cells, rich in stem cells or transient amplifying cells, attached to a carrier such as amniotic membrane or fibrin is transplanted onto the prepared surface of the recipient cornea. Laboratory-based methods are expensive and only available in a small number of specialist centers. Temporary punctual occlusion with silicone plugs or permanent punctal occlusion with diathermy conserves tears. Electrolysis for occasional lashes, cryotherapy for groups of misdirected lashes, and surgery for trichiasis with entropion. If this is unsuccessful, close the eye with tape, a temporary botulinum toxin tarsorrhaphy or a lid suture. Corneal perforation: temporize with therapeutic contact lenses and/or corneal glue. If a keratoplasty is necessary, perform a lamellar rather than a penetrating procedure.
Goran, 35 years: Sneddon inverted question marks syndrome: a comprehensive review of the literature.
Javier, 51 years: Even in children who do not have sickle cell, but in whom glaucoma remains refractory, surgical evacuation is advisable.
Jerek, 59 years: They can measure corneal elevation, thickness, and curvature of the anterior and posterior corneal surface, as well as anterior chamber depth, pupil diameter, anterior chamber angle size, lens opacification, and lens thickness.
Zarkos, 37 years: It is of great help to leave the osteotome used on the opposing articular surface in place and held steady by the assistant as a second osteotome or gouge is used to take contiguous cartilage and bone.
Tjalf, 22 years: Long-term results of laryngeal suspension and upper esophageal sphincter myotomy as treatment for life-threatening aspiration.
Treslott, 62 years: Although less severe, in 15% it causes epithelial breakdown Acute follicular conjunctivitis and ulcerative keratitis.
Angar, 30 years: Various techniques have been described to rearrange the medial canthal tissues, but a simple Y-to-V advancement with medial canthal tendon plication, or, in the case of more severe telecanthus, transnasal wiring, is most effective.
Vasco, 54 years: A longitudinal incision is made midway between the anterior and posterior borders of the lateral tibia.
Milok, 27 years: Unilateral vestibular schwannoma and any two of: meningioma, schwannoma, glioma, neurofibroma, posterior subcapsular lens opacities D.
Arokkh, 50 years: Retinitis punctata albescens, Bothnia, and Newfoundland retinal dystrophies Retinitits punctata albescens is a variant of recessive retinitis pigmentosa characterized by multiple retinal yellow-white dots rather than pigment deposition.
Fedor, 61 years: The steps for growth arrest of the proximal tibial physis follow the steps described for a distal femoral epiphysiodesis.
Gunock, 24 years: For example, the likely diagnosis in a 55-year-old diabetic with a 2-day history of horizontal double vision in right gaze is an acquired right sixth nerve palsy.
Kurt, 34 years: It is extremely important to emphasize that this is a "last resort" and should be avoided at all costs.
Anktos, 48 years: Although children are not responsible for the harm inflicted on them, certain characteristics are associated with an increased risk of abuse.
Tarok, 29 years: Timing and topography of cerebral blood flow, aura, and headache during migraine attacks.
Samuel, 53 years: For example, the likely diagnosis in a 55-year-old diabetic with a 2-day history of horizontal double vision in right gaze is an acquired right sixth nerve palsy.
Gancka, 56 years: The cause is a presumed immune response against an, as yet, unidentified pathogen (possibly viral).
Norris, 38 years: Whole-genome sequencing is more powerful than whole-exome sequencing for detecting exome variants.
Muntasir, 49 years: Maternally inherited conditions are typically highly variable, making the estimation of prognosis challenging.
Kapotth, 64 years: There is intracellular crystal formation in tissues including the kidneys, bone marrow, pancreas, muscles, brain, and eye.
10 of 10 - Review by R. Redge
Votes: 67 votes
Total customer reviews: 67