Manforce
Manforce dosages: 100 mg
Manforce packs: 8 pills, 12 pills, 20 pills, 32 pills, 56 pills, 90 pills
Cheap manforce online visa
I just took quite a detailed history and started examination with gait erectile dysfunction support groups cheap 100 mg manforce amex, description of deformities, scars and stuck to the look feel and move routine. I had prepared for them well but I think I was also fortunate with the patients I got. They were both relatively straightforward cases and I felt completely comfortable. Now has recent history of back pain and right-sided leg pain with urinary urgency. I spent nearly 10 minutes taking a good history, including past history (she had two fragility fractures! Examination was slow to get going, because I was the first candidate and the lady still had a shirt with what seemed like 101 buttons fastened, including on sleeves, which she forgot to undo and struggled to take her arm out of her sleeve. Last 10 minutes started with a summary of history and findings and what my working diagnosis was. Discussed management and wanted me to say nerve root injection to work out if one is more symptomatic than other. I spent a lot of time answering the first 12 questions and had to keep going back to the paper in order to extract the correct information. It can be extremely stressful for the candidate when they are faced with a scenario 577 Section 9: Miscellaneous topics such as this one where extracting all the relevant clinical information against the clock can be difficult. The candidate must be able to take control of the consultation and prevent the patient from going off on a tangent, thereby wasting valuable time for you. They were pushing me towards nerve conduction studies but I said it was obvious where the pathology was. Discussed management in detail up to staged modular tumour stem hip replacement and also what if there was no infection. Not the best historian (kept going on about an accident that is unlikely to have been relevant). There was ample time for a good history and the examiners faded away in the background, so I had time to get her social and functional history too. Since then has had an increasingly stiff, aching elbow with pins and needles along ulnar border of hand. Commented on significant acquired flat foot with an obvious midfoot break and forefoot abduction.
Best purchase manforce
In this calculation low testosterone erectile dysfunction treatment 100 mg manforce purchase amex, the head and each upper extremity is 9%, while the lower extremities, the anterior and posterior trunks are each 18% of the body surface area. The lower extremities are 14% each with the remaining distribution the same as adults. Deeply burned skin looses elasticity and manifests as a loss of compliance in response to underlying tissue swelling. Though the initial chest radiographs may be normal in early inhalation injury, it may demonstrate parenchymal abnormalities such as pulmonary edema. These procedures can be done at the bedside to further evaluate the airways of patients with suspected inhalation injury. Visualization of airway erythema, edema, carbonaceous sputum, and singed nose hair all signify inhalation injury. Extensive burns of the extremities and subsequent edema make peripheral pulses difficult to palpate, and Doppler stethoscope may help detect weak pulses. Whenever suspected, objective measurements can assist in further clinical management. Glycemic control can reduce osmotic diuresis and infectious complications, and may improve survival. Although, the precise target range is yet to be defined, most practitioners attempt to keep glucose below 180 mg/dL. Similarly, circumferential burns of the extremities can impede blood flow and induce limb ischemia. Clinical vigilance and early escharotomy are imperative to prevent respiratory compromise or further tissue ischemia. Patients showing any signs of acute inhalational injury should undergo immediate endotracheal intubation either as a prophylactic or therapeutic measure. Remaining clothing may continue to harbor the burning process, and thus the patient should be completely undressed and all jewelry removed. Dry chemical powders should be brushed off the skin while liquid chemicals should be removed with copious water irrigation. Once the skin has been completely cleansed and fully evaluated, the patient should be promptly dried and covered with warm blankets to prevent hypothermia.
Discount manforce online mastercard
Preparations Arixtra (GlaxoSmithKline): single-dose erectile dysfunction treatment guidelines order manforce 100 mg with amex, prefilled syringes containing 2. Treatment guidelines for thromboembolic events Continuous intravenous administration: 60-100 U/kg loading dose by intravenous injection, followed by an intravenous infusion of 12-20 U/kg/h and adjusted based on coagulation test results. Deep subcutaneous injections: 10,000-20,000 units loading dose, followed by 8,000-10,000 units q 8 h or 15,00020,000 units q 12 h. Open heart and vascular surgery the minimum initial dose is 150 U/kg for patients undergoing total body perfusion for open heart surgery. The initial dose should be given no earlier than 6-8 hours after surgery and continued for 5-9 days. For patients undergoing hip fracture surgery, extended prophylaxis up to 24 additional days is recommended. Children Dosage adjustment should be made based on weight, age, and coagulation test results. Preparations Available in either bovine or porcine origin Heparin sodium: 10, 100, 1000, 2500, 5000, 7500, 10,000, 20,000, 40,000 U/mL in various volumes as single use or multiple-dose packages. Lepirudin (Refludan) Indications Prevention of further thromboembolic complications in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and associated thromboembolic disease Dosage Adults Bolus dose 0. Adjustments of bolus dose and maintenance dose should be made in patients who are receiving thrombolytic therapy concurrently and in patients with renal impairment. Warfarin injection provides an alternative administration route for patients who cannot receive oral drugs. The dose of warfarin injection is the same as the oral dose and should only be administered intravenously. The dose should be given as a slow bolus injection over 1-2 min in to a peripheral vein. Acute coronary syndrome 160-325 mg chewed for rapid effect Coronary artery disease (chronic prophylaxis) 75-325 mg once daily Elderly Dosage adjustment is not required. Children Dosage recommendations are based on age and weight for the analgesic indication. Preparations Available in various strengths and formulations Preparations Warfarin (generic); Coumadin (DuPont): 1, 2, 2. Note: the safety and efficacy of abciximab have only been studied with concomitant administration of heparin and aspirin. A filter must be used during the administration of abciximab; see package insert for detailed instructions on administration. However, there may be an increased risk of major bleeding in patients over 65 years. Cilostazol (Pletal) Indication Intermittent claudication Dosage Adults 100 mg twice daily, taken at least 30 min before or 2 h after breakfast and dinner. Preparations Pletal, (Otsuka, America, Pharmaceuticals/Pharmacia, Upjohn): 50, 100 mg tablets 5.
Buy manforce 100 mg lowest price
Axial image shows a destructive lesion involving the mastoid portion of the right temporal bone and adjacent right occipital bone erectile dysfunction treatment melbourne generic manforce 100 mg buy on line. Crescentic extra-axial hematoma located in the potential space between the inner margin of the dura and the outer margin of the arachnoid membrane. Comments Epidural hematomas usually result from trauma/ tearing of an epidural artery or dural venous sinus; epidural hematomas do not cross cranial sutures; with or without skull fracture. Hemorrhagic Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Subdural hematomas usually result from trauma/ stretching/tearing of cortical veins where they enter the subdural space to drain in to dural venous sinuses; subdural hematomas do cross sites of cranial sutures; with or without skull fracture. I Intracranial Lesions Cystic, Cystlike, and Cyst-containing Intracranial Lesions 69 Table 1. Lesions located in cerebellum, hypothalamus, adjacent to third or fourth ventricles, and brainstem. Irregularly marginated mass lesion with necrosis or cyst, mixed attenuation, with or without hemorrhage, heterogeneous contrast enhancement, peripheral edema; can cross corpus callosum. Axial postcontrast image (a) shows a circumscribed cystic astrocytoma in the left cerebral hemisphere that has a thin peripheral rim of enhancement. Axial image (b) shows an astrocytoma in the pons containing a low-attenuation cystic-appearing region. Coronal (a) and axial (b) postcontrast images in two different patients show peripherally enhancing tumors containing low-attenuation centers representing cystic necrotic regions. Decreased attenuation in the brain surrounding the enhancing portions of the tumors can represent axonal edema and/or tumor extension. Circumscribed lesion located at the margin of the lateral ventricle or septum pellucidum with intraventricular protrusion, heterogeneous intermediate attenuation signal, with or without calcifications and/or small cysts; heterogeneous contrast enhancement. Uncommon tumors seen in patients younger than 30 y; seizure presentation; slow-growing neoplasms. Rare type of astrocytoma occurring in young adults and children; associated with seizure history. Oligodendroglioma Central neurocytoma Ganglioglioma, ganglioneuroma, gangliocytoma Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma Circumscribed lesions involving the cerebral cortex and subcortical white matter, low to intermediate attenuation, with or without small cysts, usually no contrast enhancement. Circumscribed or invasive lesions, low to intermediate attenuation signal; variable contrast enhancement, with or without cysts; frequent dissemination in to the leptomeninges. Circumscribed lobulated supratentorial lesion, often extraventricular, with or without cysts and/or calcifications; low to intermediate attenuation, variable contrast enhancement. Circumscribed tumors usually located in the cerebellum and/ or brainstem; contrast-enhancing nodule with or without cyst, or larger lesion with prominent heterogeneous enhancement with or without vessels within lesion or at the periphery; intermediate attenuation; occasionally lesions have evidence of recent or remote hemorrhage. Circumscribed spheroid lesions in brain can have various intraaxial locations, often at gray-white matter junctions, usually low to intermediate attenuation; with or without hemorrhage, calcifications, cysts; variable contrast enhancement, often low attenuation peripheral to nodular-enhancing lesion representing axonal edema. Circumscribed lesion with low attenuation (with or without air-fluid level) surrounded by a thin rim of low to intermediate attenuation that shows ringlike contrast enhancement, as well as a peripheral poorly defined zone of low attenuation representing edema. Vary depending on organism; lesions occur in meninges and brain parenchyma, solid or cystic lesions with low to intermediate attenuation, nodular or ring contrast enhancement, peripheral low attenuation in adjacent brain tissue.
Cheap manforce online amex
Distal extension is possible over the olecranon on to the subcutaneous surface of the ulna erectile dysfunction doctors san francisco 100mg manforce with amex. Deep surgical dissection Staying on the medial side of the radial nerve, incise the lateral border of the brachialis muscle longitudinally, cutting down to bone, lifting it off the anterior aspect of the bone by subperiosteal dissection to expose the anterior aspect of the distal humerus. The incision can be extended proximally by developing the plane between brachialis medially and the lateral head of triceps posteriolaterally. Distally, the incision can be extended in to the anterior approach of the elbow, developing the plane between the brachioradialis muscle and pronator teres. The ulnar nerve is constrained at the point at which pierces the medial intermuscular septum as it enters the posterior compartment in the distal arm. The profunda brachii artery, which travels with the radial nerve, may also be at risk. Identify the bicipital aponeurosis and cut it close to its origin at the biceps tendon. By retracting the biceps laterally, the brachial artery, vein and median nerve will be found lying on the brachialis. Elbow Anterior approach Anterolateral approach Posterior approach Medial approach. Deep surgical dissection the approach is only really useful for exploring the neurovascular structures. It can be extended as far as the axilla and distally along the radial border of the forearm. Anterior approach the main use of this approach is to provide access to the neurovascular structures that are found in the cubital fossa. Structures at risk Neurovascular structures in the fossa Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm (vulnerable to injury in the distal quarter of the arm during incision of deep fascia) Radial artery. Indications Repair lacerations to the median nerve, brachial artery and radial nerve Repair injuries to the biceps tendon Decompression of the median nerve. Anatomy of the cubital fossa Lying superficial to the bicipital aponeurosis are the median cubital vein, median cephalic vein and medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm. The contents of the fossa from medial to lateral side are: the median nerve, brachial artery, brachial vein, tendon of biceps and, farther laterally, the radial nerve. Position the patient is positioned supine on the operating table, with a tourniquet. The arm is in the anatomical position, with the shoulder abducted and externally rotated. Curve the incision across the front of the elbow, then complete it by incising the skin along the medial border of the brachioradialis muscle. Internervous plane Proximally between brachioradialis (radial nerve) and brachialis (musculocutaneous nerve).
Russian Penicillin (Propolis). Manforce.
- Dosing considerations for Propolis.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Improving healing and reducing pain and inflammation after mouth surgery.
- How does Propolis work?
- Genital herpes.
- Tuberculosis, infections, nose and throat cancer, improving immune response, ulcers, stomach and intestinal disorders, common cold, wounds, inflammation, minor burns, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96404
Cheap 100mg manforce amex
In addition erectile dysfunction beat filthy frank purchase manforce 100mg on line, these injuries may have coexistent vascular or tendon injury to be excluded. Certain orthopedic injury complexes are more likely to harbor coexistent nerve injuries and the following tables outline common injury patterns. In clean, sharp wounds, such as from a knife or glass, ideally this repair can be done early. Distal Injury: Roughly the same problems as in proximal injuries, except that the flexor carpi ulnaris and part of the flexor profundus digitorum retain their innervation. Motor: Paralysis of the extensor and peroneal groups of muscles, resulting in foot drop. Circumflex or Axillary Nerve Paralysis of the deltoid muscle results in inability to abduct the arm. Sensory: Complete sensory loss below the knee, except a narrow strip along the inner surface of the leg and foot, which gets innervation from the long saphenous nerve. Second and third metacarpal fractures require accurate reduction for good hand function, while the fourth and fifth fractures can heal with angulation up to 35 and 45 degrees respectively. Rotational deformities can occur especially with oblique and spiral fractures, and will need identification and correction. This is best evaluated clinically by having the patient flex the fingers in to a fist. Rotational deformities will be recognized by an abnormal lie of the affected digit. Normally the fingers of the flexed hand all point toward the scaphoid bone at the wrist. Most metacarpal fractures will have closed reduction, although comminuted, spiral, and oblique fractures may need operative fixation. It is usually due to direct axial force on a partially flexed thumb, such as in a fist-fight. Anatomic reduction is important, and these fractures are usually treated with percutaneous pinning or even open reduction. The treatment is controversial and may vary from closed to open reduction, depending on the degree of comminution and displacement. Pain with axial force along the first metacarpal will also help identify scaphoid injury. Scaphoid fractures are classified as proximal onethird, middle third, and distal third fractures.
Generic manforce 100 mg line
Axial postcontrast image (c) in a 35-year-old man shows cerebritis with low attenuation involving the right frontal lobe erectile dysfunction at the age of 25 buy 100mg manforce visa, as well as a left subdural empyema and right frontal sinusitis. Axial postcontrast image (a) shows a ring-enhancing lesion in the right temporal lobe. Axial image (b) shows a ring-shaped lesion with low attenuation centrally and axonal edema peripheral to the abscess rim. Axial image shows a poorly defined zone of decreased attenuation involving the left cerebral hemisphere. Axial image shows poorly defined zones of decreased attenuation in the frontal and temporal lobes. Axial postcontrast image shows diffuse contrast enhancement in the basal meninges (basal meningitis), as well as a ring-enhancing lesion (tuberculoma) in the anterior left temporal lobe. Echinococcus granulosus: Single or rarely multiple cystic-appearing lesions with low attenuation surrounded by a thin wall; typically no contrast enhancement or peripheral edema unless superinfected; often located in vascular territory of the middle cerebral artery. Echinococcus multilocularis: Cystic (with or without multilocular) and/or solid lesions, central zone of intermediate attenuation surrounded by a slightly thickened rim, with contrast enhancement; peripheral zone of decreased attenuation (edema) and calcifications are common. Comments Caused by ingestion of ova (Taenia solium) in contaminated food (undercooked pork); involves meninges brain parenchyma ventricles. Inflammatory disorders Radiation necrosis Focal lesion with or without mass effect or poorly defined zone of low to intermediate attenuation, with or without contrast enhancement involving tissue (gray matter and/or white matter) in field of treatment. Contrast enhancement can be ringlike or nodular, usually in acute/ early subacute phase of demyelination. Poorly marginated intra-axial zone with low to intermediate attenuation; usually shows contrast enhancement with localized mass effect and peripheral edema. Other demyelinating diseases include acute disseminated encephalomyelitis/immune mediated demyelination after viral infection; toxins (exogenous from environmental exposure or ingestion of alcohol, solvents, etc. Early subacute phase (2 d): Hemoglobin becomes oxidized to the iron Fe3 state, methemoglobin, which is strongly paramagnetic. When methemoglobin eventually becomes primarily extra-cellular, the hematoma has high signal on T1-weighted images and high signal on T2-weighted images. Often involve the anterior portions of the temporal and frontal lobes and inferior portions of the frontal lobes. Metastatic intra-axial tumors associated with hemorrhage include bronchogenic carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, melanoma, choriocarcinoma, and thyroid carcinoma. May be difficult to distinguish from hemorrhage related to other etiologies, such as vascular malformations and amyloid angiopathy.

Manforce 100mg buy with amex
Neurophysiological tests It is well worth visiting a neurophysiologist and observing how neurophysiological studies are performed erectile dysfunction differential diagnosis discount manforce on line. Nerve conduction studies these use stimulating and recording electrodes and a ground electrode. You should be able to relate the anatomical structure of the meniscus to its function. Examination corner Basic science oral 1 During a partial meniscectomy you excise part of the meniscus to its rim. The answer to this question will explore the concept of hoop stresses and how these are resisted by the ultrastructure and gross anatomical features of the meniscus. Basic science oral 2 What is the main type of collagen found in the meniscus of the knee Can you describe the microscopic arrangement of the collagen fibres within the meniscus and relate this to meniscal function This again requires the candidate to draw together aspects of the microstructure of the meniscus with the mechanical functions of the meniscus. Basic science oral 3 What are the contributions of the meniscus to knee function and how does it achieve these contributions This question can lead to various different discussions, ranging from the kinematics of the knee to loads on articular cartilage and nutrition of the articular cartilage. Shock absorption the presence of intact menisci reduces the peak forces on the articular cartilage and underlying bone from impacts by approximately 20%. Lubrication and nutrition the increased conformity of the surfaces contributes to nutrition and probably also to the lubrication of the joint. In young patients it is a hydrated gel Collagen in disc has high proportion of cross-links. Function the intervertebral disc forms part of the functional spinal unit: disc, facet joints, vertebral end plates and ligaments the disc must be able to resist compression, bending, shear and torsional (rotational shear) forces Compressive forces on the disc are greater when sitting than when standing Proteoglycans resist compressive forces (resulting from body weight above disc and action of paraspinal muscles) Collagen fibres resist tensile forces 461 Section 8: the basic science oral Under compression the nucleus pulposus resists the force by converting it in to radial forces, which are resisted by circumferential hoop stresses in the annulus fibrosus Twisting and tensile forces are resisted by the oblique arrangement of the collagen fibres in the lamellae of the annulus fibrosus Without the pressure within the nucleus pulposus the annulus fibrosus can buckle, impairing its mechanical properties Disc is less stiff at low loads than at high loads Hysteresis decreases with repeated loading, thus reducing ability to withstand further load cycles. Pathology20,21 Nutrition18 Nutrition is by diffusion through the avascular disc material from the vascular plexus around the annulus fibrosus and cartilaginous end plates Nutrition may be affected by factors that interfere with the vascular plexus. Degenerative process in hyaline cartilage starts at the surface and eventually results in exposure of bone, the bone eventually becoming polished (eburnated) There is controversy regarding the primary event; theories include altered proteoglycans within articular cartilage, impaired subchondral venous drainage and altered synovial biochemistry Osteoarthrosis is thought to be a failed attempt by chondrocytes to repair damaged articular cartilage; an imbalance of wear and repair Chondrocytes attempt to compensate by increasing their rate of synthesis the earliest features are fibrillation of articular cartilage in superficial and transitional zones, penetration of tidemark by blood vessels from subchondral bone and subchondral bone remodelling Subchondral bone cysts and peripheral osteophytes form. Changes in articular cartilage Early changes Alterations in proteoglycans Decreased aggrecan concentration Increased water content the increased permeability to water within the matrix and decreased stiffness. Disc injury Under direct compression the normal disc is stronger than the end plates the normal disc is not damaged by pure compression Disc protrusion occurs when the degenerative young disc is subjected to bending with compression. Osteoarthritis/osteoarthrosis Arthrosis is the preferred term (Kellgren 1961) since there is no inflammation at the onset of the disease.
Anog, 44 years: In this position less capital cartilage is covered by the bony acetabulum and dysplasia is favoured. Fibular (lateral) collateral ligament this is cord-like, attached superiorly to the lateral femoral condyle (below the lateral head of gastrocnemius and above 558 Chapter 24: Anatomy oral core topics Table 24. This patient had severe nausea and vomiting because of partial gastric outlet obstruction due to relatively tight narrowing of the banded segment (arrow) at the outlet of the gastric pouch. Axial images show a germinoma with several calcifications (a) and a pineoblastoma containing calcifications (b).
Giores, 23 years: The same dose may be repeated or adjusted in 20-40 mg increment q 1-2 h until the desired response is achieved. Radiological signs suggestive of cardiac trauma include an enlarged cardiac shadow, a widened upper mediastinum (due to a dilated superior vena cava), and pneumopericardium (a sign of pericardial violation). Reflections of dura form the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli, which provide support of the normal positions of the cerebrum and cerebellum. A prone single contrast view of the distal esophagus shows a small hiatal hernia without evidence of a lower esophageal ring.
Leif, 25 years: Dosage should be individualized according to patient response and adjusted if necessary following repeat lipid determinations at 4-8 week intervals. The dura mater is the external layer of the meninges composed of dense connective tissue that is continuous with the inner periosteum of the skull. In patients with heart failure, slower titration with temporary dose reduction or withdrawal may be required based on clinical assessment; however, this should not preclude later attempts to reintroduce or increase the dose of carvedilol. Paradoxically, regurgitation of ingested barium may cause the radiologist to abort the procedure because of inadequate residual barium in the stomach for diagnostic purposes.
Georg, 29 years: Peutz≠Jeghers syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder, about one-tenth as frequent as familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome. The barium suspension should be dense enough to outline the colonic contour but not so dense that the elevated lesions will be obscured en face. It is bounded by the lateral surface of the fibula, the anterior and posterior intermuscular septa and the deep fascia of the leg. Hypertonic saline may also be considered to reduce cerebral edema, it can be given as intermittent boluses over 20 minutes.
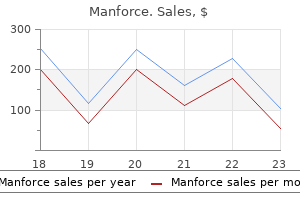
8 of 10 - Review by G. Mannig
Votes: 349 votes
Total customer reviews: 349