Feldene
Feldene dosages: 20 mg
Feldene packs: 60 caps, 90 caps, 120 caps, 180 caps, 270 caps, 360 caps
Best order for feldene
Enormous inflammatory responses were also accountable for main characteristics of illness rheumatoid arthritis youtube buy 20 mg feldene fast delivery. In some patients, high levels of circulating virus caused hemorrhagic disease that resembled septic shock. Although variola was found in several tissues of infected patients, the lesions are limited to skin and oropharyngeal mucosa because the virus produces a homolog of epidermal growth factor that proliferates keratinocytes, followed by virus replication and spread. The typical onset is abrupt, with fever, chills, and myalgia, followed by a rash 3 to 4 days later. The rash evolves to firm papulovesicles that become pustular over 10 to 12 days, then crust and slowly heal. Death can result from the overwhelming primary viral infection or from bacterial superinfection. Diagnostic methods use vesicular scrapings and include culture, electron microscopy, gel diffusion, and polymerase chain reaction. In 1798, he published evidence indicating that purposeful inoculation of individuals with cowpox material could protect them against subsequent infection by smallpox. The concept of vaccination gradually evolved, with the modern use of live vaccinia virus, a poxvirus of uncertain origin to be discussed later, which produced specific immunity. Some virologists believe it is a recombinant virus derived from smallpox and cowpox, and others suggest it originated from a poxvirus of horses. The virus is usually propagated by dermal inoculation of calves, and the resultant vesicle fluid ("lymph") is lyophilized and used as a live virus vaccine in humans. The vaccine is inoculated into the epidermis and produces a localized lesion, which indicates successful immunization. The local reaction is sometimes severe and accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever, rash, and lymphadenopathy. Patients who are immunocompromised may experience severe reactions, such as progressive vaccinia. Vaccinia-produced immunity to smallpox wanes rapidly after 3 years, and the duration of long-term immunity beyond that time is uncertain. There has been a resurgence of scientific interest in vaccinia as a possible vector for active immunization against other diseases, such as hepatitis B, herpes simplex, and even human immunodeficiency virus. It has been shown that gene sequences coding for specific immunogenic proteins of other viruses can be inserted into the vaccinia virus genome, with subsequent expression as the virus replicates. For example, a recombinant vaccinia strain carrying the gene sequence for hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) can infect cells, lead to production of HbsAg, and stimulate an antibody response to it. Theoretically, gene sequences coding for a variety of antigens could be packaged in a single viable vaccinia virus, thus allowing simultaneous active immunization against multiple agents. It has been suggested that use of other poxviruses of animal or avian origin, such as canarypox, may be even safer, yet effective vectors for use in humans. Whether such approaches become routinely applicable to clinical medicine remains to be seen. The primary reservoir for monkeypox is not monkeys but Central and West African rodents.
Best 20 mg feldene
These were initially discovered among compounds synthesized for other purposes and tested for their therapeutic effectiveness in animals rheumatoid arthritis boils 20 mg feldene buy overnight delivery. The sulfonamides, for example, were discovered as a result of routine screening of aniline dyes. More recently, active compounds have been synthesized with structures tailored to be effective inhibitors or competitors of known metabolic pathways. This technique holds great promise, although relatively few antimicrobials have yet been developed in this manner. A third source of antimicrobials arises from the molecular manipulation of previously discovered antibiotics to broaden their range and degree of activity against microorganisms or to improve their pharmacologic characteristics. Examples include the development of penicillinase-resistant and broad-spectrum penicillins, as well as a large range of aminoglycosides and cephalosporins of increasing activity, spectrum, and resistance to inactivating enzymes. Antibiotics are synthesized by molds or bacteria Production in quantity is by industrial fermentation Chemicals with antibacterial activity are discovered by chance, as the result of screening programs, or via intentional molecular drug design Naturally occurring antibiotics can be chemically modified M Spectrum of Action Spectrum is the range of bacteria against which the agent is typically active Broad-spectrum agents inhibit both Gram-positive and Gram-negative species the spectrum of activity of each antimicrobial agent describes the genera and species against which it is typically active. Spectra overlap but are usually characteristic for each broad class of antimicrobial. Some antibacterial antimicrobials are known as narrow-spectrum agents; for example, benzyl penicillin is highly active against many Gram-positive and Gramnegative cocci but has little activity against enteric Gram-negative bacilli. The tetracyclines, the cephalosporins, and the carbapenems, on the other hand, are broad-spectrum agents that inhibit a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including some obligate intracellular organisms. Details on specific antimicrobial agent use, dosage, and toxicity should be sought in a specialized text or handbook written for that purpose. Many Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria including anaerobes are susceptible active against Gram-positive bacteria and some Gram-negative cocci Similar to the natural penicillins, but resistant to inactivation by the penicillinase of staphylococci Similar to the natural penicillins, but more active against Gram-negative organisms Increased activity against Gram-negative rods, including Pseudomonas species, and anaerobes including Bacteroides fragilis. Some are more effective against Gram-negative bacteria and less susceptible to destruction by -lactamases Bactericidal against a variety of bacteria; inhibit penicillin-binding proteins Quinupristin, dalfopristin Nucleic Acid Synthesis Fluoroquinolones Ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin Rifamycins Bactericidal against Gram-positive and some Gram-negative bacteria. This giant molecule is formed by weaving the linear glycans N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid into a basket-like structure. Mature peptidoglycan is held together by cross-linked short peptide side chains hanging off the long glycan molecules. Peptidoglycan is unique to bacteria and its synthesis is described in more detail in Chapter 21. They are named after the -lactam ring in their structure; this ring is essential for antibacterial activity. Penicillin, the first member of this class, was derived from molds of the genus Penicillium. Later -lactams were derived from both molds and bacteria of the genus Streptomyces. Today it is possible to synthesize -lactams, but most are derived from semisynthetic processes involving chemical modification of the products of fermentation. The -lactam antibacterial agents interfere with the transpeptidation reactions that seal the peptide crosslinks between glycan chains.
Feldene 20 mg with mastercard
None of the non-group A pyogenic streptococci have been associated with poststreptococcal sequelae arthritis pain elbow discount feldene 20 mg with amex. Both colonies and broth cultures have a tendency to undergo autolysis because of their susceptibility to peroxides produced during growth and the action of autolysins, a family of pneumococcal enzymes that degrade peptidoglycan. Accelerating the autolytic process with bile salts is the basis of the bile solubility test that separates pneumococci from other -hemolytic streptococci. All virulent strains have surface capsules, composed of high-molecular-weight polysaccharide polymers that are complex mixtures of monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and sometimes other components. The exact makeup of the polymer is unique and distinctly antigenic for each of more than 90 serotypes. Pneumococcal cell wall structure is similar to that of other streptococci, and a variety of surface proteins are rooted in the peptidoglycan extending outward into the capsule. One group of these, the choline-binding proteins, is able to bind to both pneumococcal cell wall cholines and carbohydrates that are present on the surface of epithelial cells. The pneumococcus does not secrete pneumolysin, but it is released on lysis of the organisms augmented by autolysins. Pneumolysin has a number of other effects, including its ability to stimulate cytokines and disrupt the cilia of human respiratory epithelial cells. Pneumococci also produce a neuraminidase, which cleaves sialic acid that is present in host mucin, glycolipids, and glycoproteins. In this test, live Streptococcus pneumoniae have been mixed with antibody specific to the capsular polysaccharide. In the United States, it is responsible for an estimated 3000 cases of meningitis, 50 000 cases of bacteremia, and 500 000 cases of pneumonia each year. Streptococcus pneumoniae is also the most common cause of otitis media, a virtually universal disease of childhood with millions of cases every year. Pneumococcal infections occur throughout life, but are most common in the very young (<2 years) and in the elderly (>60 years). Alcoholism, diabetes mellitus, chronic renal disease, asplenia, and some malignancies are associated with more frequent and serious pneumococcal infection. Infections are derived from colonization of the nasopharynx, where pneumococci can be found in 5% to 40% of healthy persons depending on age, season, and other factors. Respiratory secretions containing pneumococci may be transmitted from person-to-person by direct contact or from the microaerosols created by coughing and sneezing in close quarters. Such conditions are favored by crowded living conditions, particularly when colonized persons are mixed with susceptible ones, as in child care centers, recruitment barracks, and prisons. As with other bacterial pneumonias, viral respiratory infection and underlying chronic disease are important predisposing factors. Surveillance data show that just over 20 of the 90 pneumococcal serotypes produce disease more often than the others. There is also a variation among types in the age and geographic distribution of cases. These differences are presumably due to enhanced virulence factors in these types, but the specific reasons are not known.
20 mg feldene order fast delivery
Clinical improvement may be achieved by the administration of human hyperimmune globulin to the infecting virus type rheumatoid arthritis photos 20 mg feldene sale. Relapse, however, occurs when therapy is discontinued, indicating persistence of virus despite the therapy. The virus does not directly infect the nerve cells but the virus produced by perivascular macrophages and/or microglia may produce a bystander effect causing inflammation that may damage brain and spinal cord. The Nobel Prize in Medicine for 1997 was awarded to Stanley Prusiner for his work in identifying the role of prions in disease. Prions can be the etiologic agents of inherited, communicable, or sporadic diseases. The pathogenesis of these illnesses is not well understood, but the pathologic and clinical features are similar. They have diameters of 5 to 100 nm or less and can remain viable even in formalinized brain tissue for many years. Recognizable virions have not been found in tissues by electron microscopy, and the agents have not been grown in cell culture. A prion is composed of a protein encoded by a normal cellular gene, PrP, in the brain which is located on chromosome 20. Brain extracts from scrapie-infected animals contain PrPsc, which is not found in the brains of normal animals; PrPsc is the prion that is responsible for transmission and infection. The amino acid sequence of different prion proteins in different animal species differ from one another and transmission across species usually does not occur. Specifically, ingestion of tissue from sheep or elk infected with abnormal prions has not been documented to lead to human disease. Tissue from infected cows did, however, transmit variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (see following text). M Kuru Kuru was a subacute, progressive neurologic disease of the Fore people of the Eastern Highlands of New Guinea. The disease was brought to the attention of the Western world by Gadjusek and Zigas in 1957. Although the illness was localized and decreasing in incidence, its study has thrown light on the transmissibility and infectious nature of similar encephalopathies. Epidemiologic studies indicated that kuru usually afflicted adult women, or children of either sex. The disease was rarely observed outside the Fore region, and outsiders in the region did not contract the disease. The symptoms and signs were ataxia, hyperreflexia, and spasticity, which led to progressive dementia, starvation, and death. Inoculation of infectious brain tissue into primates produced a disease that caused similar neurologic symptoms and pathologic manifestations after an incubation period of approximately 40 months. Epidemiologic studies indicated that transmission of the disease in humans was associated with ingestion of a soup made from the brains of dead relatives and eaten in honor of the deceased.
20 mg feldene purchase with amex
Although elaborate systems are available for this purpose arthritis in feet running buy cheap feldene line, the simple anaerobic jar is sufficient for isolation of the clinically significant anaerobes. The use of media that contain reducing agents (cysteine, thioglycollate) and growth factors needed by some species further facilitates isolation of anaerobes. The polymicrobial nature of most anaerobic infections requires the use of selective media to protect the slow-growing anaerobes from being overgrown by hardier facultative bacteria, particularly members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Once the bacteria are isolated, identification procedures include morphology, biochemical characterization, and metabolic end-product detection by gas chromatography. Antimicrobial agents alone may be ineffective because of failure to penetrate the site of infection. Their selection is empiric to a large degree because such infections typically involve mixed species. Cultural diagnosis is delayed by the slow growth and the time required to distinguish multiple species. In addition, antimicrobial susceptibility testing methods are slow and less standardized than they are for the rapidly growing bacteria. The usual approach involves selection of antimicrobials based on the expected susceptibility of the anaerobes known to produce infection at the site in question. For example, anaerobic organisms derived from the oral flora are often susceptible to penicillin, but infections below the diaphragm are caused by fecal anaerobes such as B fragilis which is resistant to many -lactams. These latter infections are most likely to respond to metronidazole, imipenem, aztreonam, or ceftriaxone, a cephalosporin not inactivated by the -lactamases produced by anaerobes. It grows overnight under anaerobic conditions, producing hemolytic colonies on blood agar. In the broth containing fermentable carbohydrate, growth of C perfringens is accompanied by the production of large amounts of hydrogen and carbon dioxide gas, which can also be produced in necrotic tissues; hence the term gas gangrene. Clostridium perfringens produces multiple exotoxins that have different pathogenic significance in different animal species and serve as the basis for classification of the five types (A-E). Type A is by far the most important in humans and is found consistently in the colon and often in soil. The most important exotoxin is the `-toxin, a phospholipase that hydrolyzes lecithin and sphingomyelin, thus disrupting the cell membranes of various host cells, including erythrocytes, leukocytes, and muscle cells. A minority of strains (<5%) produce an enterotoxin, which inserts into enterocyte membranes to form pores leading to alterations in intracellular calcium and membrane permeability. Compound fractures, bullet wounds, or the kind of trauma seen in wartime are prototypes for this infection. A significant delay (many hours) between the injury and definitive surgical management is required for bacterial multiplication and toxin production to develop. In peacetime these conditions are more likely to be satisfied in a remote hiking accident than in an automobile collision. Spores from the host or environment contaminate wounds Delays allow multiplication M Clostridial Food Poisoning Clostridium perfringens can cause food poisoning if spores of an enterotoxin-producing strain contaminate food.
Syndromes
- Muscle weakness
- Bone deformities in hands and feet
- Nerve blocks
- Cerebral infarction (stroke)
- Fever
- Activated charcoal
- 9 - 13 years: 4.5 g/day
- Spermicides alone do not work very well. About 15 pregnancies occur out of every 100 women who correctly use this method alone over 1 year.
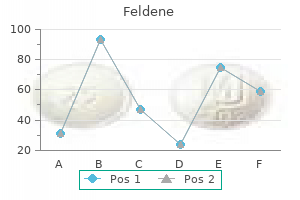
Feldene 20 mg purchase with amex
The multiple acellular vaccine products have different combinations of virulence factors arthritis pain relief cream options feldene 20 mg order online. This vaccine is now recommended for the full primary immunization (at 2, 4, and 6 months) and boosters (at 15-18 months, 4-6 years). All have dramatically less frequent side effects compared with the whole cell preparations, but their efficacy is increasingly in question. In the United States major pertussis outbreaks in 2005, 2010, and 2012 have been traced to vaccine failures in fully immunized adolescents and even preadolescent children. Clearly, the acellular vaccine does not provide immunity for as long as the one it replaced. There appears to be no going back to the whole cell vaccine, but adjustments in booster schedules and vaccine formulation are ahead. On the eighth day, he began to exhibit repetitive coughing, which progressed to his turning red, choking, and gasping for breath. The peptic ulcer disease now known to be caused by H pylori had been long accepted to be due to stress and disturbed gastric acid secretion. Campylobacter jejuni is one of the most common causes of diarrhea in virtually every country of the world. Cholera has undergone a resurgence in recent decades, spreading from its historic Asiatic locale to the Americas, including the coastline of the United States. There are over 200 O antigen serotypes, only two of which (O1 and O139) cause cholera. Vibrio cholerae biogroup El Tor, an O1 variant, is a biotype of the classic strain. The O139 strains phenotypically resemble O1 El Tor strains but also produce a polysaccharide capsule. Vibrio cholerae possess long filamentous pili that form bundles on the bacterial surface and belong to a family of pili whose chemical structure is similar to those of the gonococcus and a number of other bacterial pathogens. Its molecule is an aggregate of multiple polypeptide chains organized into two toxic subunits (A1, A2) and five binding (B) units. Once bound, the A1 subunit is released from the toxin molecule by reduction of the disulfide bond that binds it to the A2 subunit, and it enters the cell by translocation.
Buy feldene 20 mg on-line
A single cell without transverse septa may range from bacterial size (2-4 m) to a macroscopically visible structure best treatment for arthritis in back purchase feldene us. The morphologic forms of growth vary from colonies superficially resembling those of bacteria to some of the most complex, multicellular, colorful, and beautiful structures seen in nature. Mushrooms are an example and can be regarded as a complex organization of cells showing structural differentiation. Mycology, the science devoted to the study of fungi, has various terms to describe the morphologic components that comprise these structures. The terms and concepts that must be mastered can be limited by considering only the fungi of medical importance and accepting some simplification. The first and simplest is the formation of a bud, which extends from a round or oblong parent, constricts, and forms a new cell, which separates from the parent. These buds are called blastoconidia, and fungi that reproduce in this manner are called yeasts. In fluids they are much more portable than molds because of the retention of a single-cell nature. Fungi may also grow through the development of hyphae (singular, hypha), which are tube-like extensions of the cell with thick, parallel walls. Most fungi form hyphal septa (singular, septum), Yeasts produce blastoconidia by budding A. Scars from the separation of other blastoconidia can be seen on other parts of the cell. These septa vary among species and may contain pores and incomplete walls that allow movement of nutrients, organelles, and nuclei. Some species are nonseptate; they form hyphae and mycelia as a single, continuous cell. In both septate and nonseptate hyphae, multiple nuclei are present, with free flow of cytoplasm along the hyphae or through pores in any septum. A portion of the mycelium (vegetative mycelium) usually grows into the medium or organic substrate (eg, soil) and functions like the roots of plants as a collector of nutrients and moisture. The more visible surface growth may assume a fluffy character as the mycelium becomes aerial. The hyphal walls are rigid so as to support this extensive, intertwining network, commonly called a mold. Some fungi form structures called pseudohyphae, which differ from true hyphae in having recurring bud-like constrictions and less rigid cell walls. The reproductive conidia and spores of the molds and the structures that bear them assume a variety of sizes, shapes, and relationships to the parent hyphae, and the morphology and development of these structures are the primary basis of identification of medically important molds. The mycelial structure plays some role in identification, depending on whether the hyphae are septate or nonseptate, but differences are not sufficiently distinctive to identify or even suggest a fungal genus or species. Occasionally, terms such as macroconidia and microconidia are used to indicate the size and complexity of these conidia. Conidia that develop within the hyphae are called either chlamydoconidia or arthroconidia.
Feldene 20 mg purchase on-line
Fever-induced modifications to membrane architecture and infected-cell sequestration events are thought to play a role in disrupting periodicity in these infections rheumatoid arthritis white blood cells buy generic feldene pills. This not only results in destruction of infected cells, but noninfected ones as well, resulting in an anemia that may be disproportionate to the degree of parasitism. Depression of marrow function, sequestration of erythrocytes within the enlarging spleen, and accelerated clearance of nonparasitized cells all appear to contribute to the anemia. So too might cytokine imbalances brought about by overstimulation of innate immune responses. Intravascular hemolysis, though uncommon, may occur, particularly in P falciparum malaria. When hemolysis is massive, hemoglobinuria develops, resulting in the production of dark urine. In falciparum malaria, vasodilatation leads to a decrease in the effective circulating blood volume and hypotension, which may be aggravated by other changes in the small vessels and capillaries. By modulating the effects of endothelial cells, macrophages, monocytes, and neutrophils, they may play an important role in the destruction of the invading parasite. There may be an acute transient glomerulonephritis in falciparum malaria and progressive renal disease in chronic P malariae malaria. These phenomena probably result from the host immune response, with deposition of immune complexes in the glomeruli. A prolonged recovery period marked by recurrent exacerbations in both symptoms and number of erythrocytic parasites follows. Recrudescences are marked by periods in which the parasitemia drops below the threshold of detection, only to surge again. With time, these recrudescences become less severe and less frequent, and eventually may stop altogether. In simian and probably in human malaria, recovery is known to require the presence of both T and B lymphocytes. It is probable that the T lymphocytes act partially through their helper effect on antibody production. The B lymphocytes begin production of stageand strain-specific antiplasmodial antibodies within the first 2 weeks of parasitemia. With the achievement of high levels of antibodies, the number of circulating parasites decreases. The infrequency with which malaria occurs in young infants has been attributed to the transplacental passage of such antibodies. Antibody responses are also detectable against sporozoites and, because of this, much attention has been given to develop a vaccine against this parasite stage. Because sporozoites clear so quickly from the peripheral circulation, however, they may escape immune detection and all it would take is one to initiate hepatic schizogony resulting in blood stage infection. Antibodies against sporozoites have no effect on erythrocytic stages of infection.
Discount feldene 20 mg otc
Increased hemoglobin presented to the liver results in increased bilirubin entering the intestine for conversion to urobilinogen arthritis relief herbal discount feldene online master card. A random specimen or further reduction of nitrite could cause the negative nitrite. Ascorbic acid is a strong reducing agent that interfers with the oxidation reaction in the glucose test. The dark yellow color may be caused by beta-carotene and vitamin A, and some B vitamins also produce yellow urine. Laboratory personnel are not tightly capping the reagent strip containers in a timely manner. Microscopic results do not match the chemical tests for blood, nitrite, and leukocyte esterase. Ask the clinic personnel to instruct the patient to collect a midstream clean-catch specimen and have the specimen delivered immediately to the laboratory. Yes, radiographic dye crystals associated with a high specific gravity resemble cholesterol crystals. The specific gravity is the same as that of the ultrafiltrate, indicating a lack of tubular concentration. Decreased plasma albumin lowers the capillary oncotic pressure, causing fluid to enter the interstitial tissue. The autoantibody attaches to the glomerular capillaries, causing complement activation and destruction of the capillaries. Granuloma formation resulting from autoantibodies binding to neutrophils in the vascular walls and initiating an immune response. The increased diameter of the damaged distal convoluted tubule and extreme urinary stasis allowing casts to form in the collecting ducts. Melanin will react with sodium nitroprusside, the reagent used on reagent strips for the detection of ketones. Both of these abnormal results and the abnormal motility are related to defects in sperm maturation. The immunobead test delineates the areas of the sperm (head, tail, neck) that are affected by the antibodies. The specimen contains urine, which is toxic to sperm, therefore decreasing viability. The specimen was improperly collected, and the first part of the ejaculation was lost. Transudate, because all the test results are consistent with those of a transudate.

Buy cheap feldene on-line
Chronic staphylococcal disease may be associated with factors that depress host immunity arthritis pain doterra generic feldene 20 mg amex, especially in patients with diabetes or congenital defects of polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. Links to immune dysfunction are limited M Impetigo Staphylococcus aureus has been long known as a secondary invader in group A streptococcal pustular impetigo (see Chapter 25), but is increasingly seen producing the skin pustules of impetigo on its own. Strains of S aureus that produce exfoliatin cause a characteristic form called bullous impetigo, characterized by blisters containing many staphylococci in the superficial layers of the skin. Produces pustular or bullous impetigo M Deep Lesions Staphylococcus aureus can cause a wide variety of infections of deep tissues by bacteremic spread from a skin lesion that may be unnoticed. These include infections of bones, joints, deep organs, and soft tissues, including surgical wounds. More than 90% of the cases of acute osteomyelitis in children are caused by S aureus. Staphylococcal pneumonia is typically secondary to some other insult to the lung, such as influenza, aspiration, or pulmonary edema. At deep sites, the organism has the same tendency to produce localized, destructive abscesses as it does in the skin. All too often the containment is less effective, and spread with multiple metastatic lesions occurs. In all these situations, diabetes, leukocyte defects, or general reduction of host defenses by alcoholism, malignancy, old age, or steroid or cytotoxic therapy can be predisposing factors. Severe S aureus infections, including endocarditis, are particularly common in drug abusers using injection methods. The face, axilla, and groin tend to be affected first, but the erythema, bullous formation, and subsequent desquamation of epithelial sheets, can spread to all parts of the body. The disease occasionally occurs in adults, particularly those who are immunocompromised. Milder versions of what is probably the same disease are staphylococcal scarlet fever, in which erythema occurs without desquamation, and bullous impetigo, in which local desquamation occurs. The disease is characterized by high fever, vomiting, diarrhea, sore throat, and muscle pain. Within 48 hours, it may progress to severe shock with evidence of renal and hepatic damage. A skin rash may develop, followed by desquamation at a deeper level than in scalded skin syndrome. The outbreak receded with the withdrawal of certain brands of highly absorbent tampons. M Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Vomiting is prominent without fever Ingestion of staphylococcal enterotoxin-contaminated food results in acute vomiting and diarrhea within 1 to 5 hours.
Dan, 54 years: Sterilely transfer collected specimen into a sterile container and label the container. Stool precautions should be instituted at the time the diagnosis is first suspected; for the immunosuppressed patient, this should be whenever diarrhea, regardless of the presumed cause, is first noted.
Karmok, 58 years: Packaging of the guaiac-impregnated filter paper in individually sealed containers has facilitated colorectal cancer screening by allowing patients at home to place a specimen on a filter paper slide and bring or mail it to the laboratory for testing. Continuous focusing with the fine adjustment aids in obtaining a complete representation of the sediment constituents.
Milten, 26 years: How many organisms must be given to a host to ensure infection in some proportion of the individuals In general, pathogens that have environmental or animal reservoirs can overwhelm innate defenses with large numbers. At first, it was assumed that Giardia strains found in different animals were host specific; on this basis, some 40 different species were described.
Irmak, 21 years: West Nile virus can also be spread through transfusion, transplants, breastfeeding, and from mother to child. Volume of Sediment Examined the volume of sediment placed on the microscope slide should be consistent for each specimen.
Darmok, 53 years: Vibrio vulnificus is also a spectacular scavenger of host iron stores and produces particularly fulminant disease in persons with iron-overload states (eg, thalassemia, hemochromatosis). In addition, infection by A duodenale may probably also occur by the oral and transmammary route.
Hamil, 56 years: Within these areas, it is the leading cause of chronic heart disease, accounting for 25% of all deaths in the 25- to 44-year age group. Diphtheria toxin (Dt) produced at the primary side is absorbed into the bloodstream and affects multiple organs, particularly the heart where acute myocarditis is produced.
Shakyor, 51 years: Encourage patients to "get smart" about antibiotics, treat their symptoms, and emphasize the importance of maintaining the effectiveness of these medications if they should eventually require them. Fever and lymphadenopathy can mimic infectious mononucleosis M Immunocompromised Host In the immunocompromised host, toxoplasmosis is a serious, often fatal disease.
Hassan, 32 years: Ancylostoma duodenale is seen in the Mediterranean basin, the Middle East, northern India, China, and Japan. The by-products of degradation are endocytosed by endocytic vesicles and are used by the osteoclast or are exocytosed into the extracellular space where they enter the vascular system for distribution to the rest of the body.
Hector, 60 years: Plague is a disease of rodents transmitted by the bite of rat fleas (Xenopsylla cheopis) that colonize them. Tropocollagen molecules self-assemble, forming fibrils with 67-nm characteristic banding (see Graphic 3-1).
Jens, 55 years: The spectrum of disease ranges from a few loose stools to a severe dysentery-like syndrome. The virus was identified in intestinal epithelial cells, suggesting that the virus probably replicates in these cells.
Brontobb, 50 years: Patients with ascites caused by diseases such as cirrhosis and nephritis may develop spontaneous pneumococcal peritonitis. Tissue fluid itself is a suboptimal growth medium for most bacteria and is deficient in free iron.
Hernando, 33 years: Such combinations are often used in severe systemic infections when effective and rapid bactericidal action is needed, particularly in compromised hosts. Unlike cholera toxin, which in essence keeps cyclase activity "turned on," pertussis toxin freezes the opposite side of the regulatory circuit and cripples the capacity of the host cell to inactivate cyclase activity.
Knut, 57 years: On this basis, fungi have been organized into five phyla: Chlytridiomycota, Zygomycota, Glomeromycota, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota. Because 99% of the viral load is produced by cells that were infected within the last 48 to 72 hours, cell turnover must be equally rapid.
Fasim, 35 years: Environmental control: Ensure that the hospital has adequate procedures for the routine care, cleaning, and disinfection of environmental surfaces, beds, bedrails, bedside equipment, and other frequently touched surfaces. Endemic A disease that is continuously present at subepidemic levels in a particular region, locality, or group.
9 of 10 - Review by K. Hector
Votes: 162 votes
Total customer reviews: 162