Cialis Soft
Cialis Soft dosages: 40 mg, 20 mg
Cialis Soft packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Purchase cheap cialis soft on line
Muscles of the eye movement are innervated by the oculomotor erectile dysfunction las vegas generic cialis soft 40 mg without prescription, trochlear, and abducens nerves. Inferior oblique Nerves of Orbit and Ciliary Ganglion Ophthalmic nerve is the first division of trigeminal nerve, provides sensory innervation to the eyeball, tip of the nose, and It is given by the trigeminal ganglion at the floor of the middle cranial fossa. It is a pure sensory nerve, passes in the lateral wall of cavernous sinus and gives three branches, which pass through the skin of the face above the eye and mediates the afferent limb of the corneal reflex. Lacrimal nerve enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and reach the lacrimal gland, giving branches to the lacrimal gland, conjunctiva, and the skin of the upper eyelid. Frontal nerve enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure, runs superior to the levator palpebrae superioris. It divides into the supraorbital nerve, which passes through the supraorbital foramen (supplies the scalp, forehead, frontal sinus, and upper eyelid) and the supratrochlear nerve, which passes through the trochlea (supplies the scalp, forehead, and upper eyelid). Branches: Anterior and posterior ethmoidal nerves, infratrochlear nerve, long and short ciliary nerves, meningeal branch to supply dura in the anterior cranial fossa and a communicating branch is given to the ciliary ganglion. Anterior ethmoidal nerve is given in the orbit, passes out of orbit into the anterior cranial fossa (through anterior ethmoidal foramen) and supplies the duramater there. It runs in proximity to the cribriform plate of ethmoid bone and supplies the ethmoidal air cells. The nerve then enters the nasal cavity (passing a foramen close to crista galli), gives external and internal nasal branches to supply internal nasal cavity, nasal septum as well as the skin on the exterior of nose. Posterior ethmoidal nerve passes through the posterior ethmoidal foramen to the sphenoidal and posterior ethmoidal sinuses. Infratrochlear nerve innervates the eyelids, conjunctiva, skin of the nose, and lacrimal sac. The parasympathetic fibres arise from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus and synapse in the ciliary ganglion via the oculomotor nerve, the postganglionic fibres leave the ciliary ganglion in the short ciliary nerve and supply the ciliary muscle and sphincter pupillae. Sympathetic fibres are provided by the superior cervical ganglion and they reach the ganglion either as branches of the nasociliary nerve or directly from the extension of the plexus on the ophthalmic artery (sympathetic branch to ciliary ganglion). Long ciliary nerves provide sensory innervation to the eyeball, including the cornea (reflex). In addition, they carry sympathetic fibers from the superior cervical ganglion to the dilator pupillae muscle. Note: the sympathetic fibers to the dilator pupillae muscle mainly travel in the nasociliary nerve but there are also sympathetic fibers in the short ciliary nerves that pass through the ciliary ganglion without forming synapses. Ciliary ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion situated behind the eyeball, between the optic nerve and the lateral rectus muscle. They travel via a branch of the oculomotor nerve (nerve to the inferior oblique) to the ciliary ganglion, where they synapse.
Buy cialis soft without a prescription
Choice of instrumentation erectile dysfunction tips buy generic cialis soft 40 mg on line, approach or approaches, and fusion levels should be planned. Early revision strategies often involved explantation of the device, at times for migration of the interbody device. The general principle of revision spine surgery should be kept in mind-if you want to change the outcome, you must do something different than you did the first time. Barrier of fibrin glue or hydrogel sealant posterior to interbody device to seal annulotomy. Spurred on by consistently excellent fusion rates despite early reports of complications, larger series were reported including one in which a polyethylene glycol hydrogel sealant (Duraseal, Confluent Surgical Inc. Furthermore, "bone resorption within the vertebral body led to graft subsidence and lack of radiographic evidence of progression toward fusion in multiple cases. The question raised was whether osteolysis may be important in the early postoperative period in patients with new or continued pain. Histopathology of one of the patients revised for symptomatic posterior instrumentation showed granulation tissue next to trabecular bone with suggestion of inflammation at the site of osteolysis. In addition, Balseiro and Nottheimer36 reported two cases of postoperative pain that showed evidence of osteolysis seemingly originating from their preexisting subchondral endplate cysts, citing their preoperative existence as a possible risk factor for subsequent osteolysis. These early reports seemed to suggest association of osteolysis with early unfavorable results with variable longer term implications. They reported minimal associated cage migration or subsidence, although not quantified, and suggested the posterior instrumentation stabilized and negated any potential resultant instability. The resultant loss of intrinsic strength of the graft and endplates was followed by subsidence of the graft and loss of intervertebral height. Eight of the nine (88%) patients with cage migration required revision secondary to neurological symptoms. Later revisions found the cages fused in their posteriorly migrated position with both cage and heterotopic bone impingement on neural structures. Placement of cages/spacers at peripheral locations of interbody space is possibly less susceptible to subsidence if osteolysis occurs. Preexistence of subchondral endplate cysts may be a risk factor for developing adjacent osteolysis. Osteolysis with associated cage migration can be evident at or before 6 weeks postoperative on plain radiographs. Maintaining an increased awareness of these potential complications when osteolysis is present is necessary.
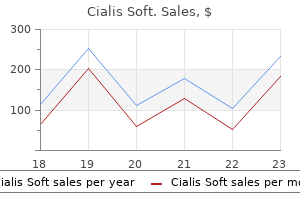
Order cialis soft cheap
Consequently erectile dysfunction doctor in bangalore cialis soft 40 mg purchase without a prescription, some authors have argued that asymptomatic cement leakage should not be considered a complication. An important point of this series is that though rare, institutions performing these procedures should have a plan to deal with potential complications that will require open surgical intervention. Cement leakage into the basivertebral vein and anterior internal venous plexus leads to the epidural space. Key technical considerations include using higher viscosity cement and minimizing injection pressure. Although these procedures are minimally invasive and often performed by specialists other an spinal Kim et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty immediately relieves pain of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures and prevents prolonged immobilization of patients. Baseline pain and disability in the Investigational Vertebroplasty Efficacy and Safety Trial. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures. North American Spine Society: newly released vertebroplasty randomized controlled trials: a tale of two trials. Evaluation of calcium phosphate and calcium sulfate as injectable bone cements in sheep vertebrae. Prevalent vertebral deformities predict mortality and hospitalization in older women with low bone mass. Effect of alendronate on limited-activity days and bed-disability days caused by back pain in postmenopausal women with existing vertebral fractures. Comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of the literature. Balloon kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a prospective, comparative, and randomized clinical study. Major neurological complications following percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate: a case report. Percutaneous treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of complications. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical follow-up. Leakage of cement in percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures with or without intravertebral clefts. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for vertebral compression fractures with and without intravertebral clefts.
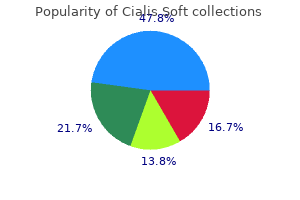
Cheap cialis soft 20 mg with mastercard
The anterolateral bundle tightens in flexion while the posteromedial bundle is tight in extension of the knee erectile dysfunction lubricant discount 40 mg cialis soft free shipping. Medial (tibial) collateral ligament is one of the four major ligaments of the knee. It resists forces pushing the knee medially (towards the body), which would otherwise produce valgus deformity. It is attached proximally to the medial condyle of femur immediately below the adductor tubercle; below to the medial condyle of the tibia and medial surface of its body. Morphologically, the medial collateral ligament represents the degenerated tendon of insertion of the ischial head of the adductor magnus, & fibular ligament represents the degenerated tendon of the peroneus longus. Oblique popliteal ligament is an expansion from the tendon of semimembranosus muscle, runs upward and laterally superficial to the capsule to be attached to the intercondylar line of the femur. It blends with capsule of knee joint and is pierced by: middle genicular vessels, middle genicular nerve, posterior division of the obturator nerve. Full extension results in the close-packed position, with maximal spiralization and tightening of the ligaments. Locking of knee joint involves lateral rotation of tibia, if the foot is not fixed to the ground and is free in the air. During walking locking and unlocking of the knee takes place alternatively and rhythmically. There is an anserine bursa at their tibial attachment separating each other near their insertion and also from the tibial collateral ligament. This occurs due to a repetitive posture of kneeling down and bending forward in activities like mopping up the floor. Anserine bursa is at their tibial attachment separating each other near their insertion and also from the tibial collateral ligament. Neurovascular Supply Arterial Supply Arterial anastomosis around the knee contributed by: Five genicular branches of popliteal artery, descending genicular branch of femoral artery, descending branch of the lateral circumflex femoral artery, two recurrent branches of the anterior tibial artery, and circumflex fibular branch of the posterior tibial artery. It is characterized by the (a) rupture of the tibial collateral ligament, as a result of excessive abduction; (b) tearing of the anterior cruciate ligament, as a result of forward displacement of the tibia; and (c) injury to the medial meniscus, as a result of the tibial collateral ligament attachment. A boy playing football received a blow to the lateral aspect of the knee and suffered a twisting fall. His medial meniscus is damaged; which other structure is most likely to be injured
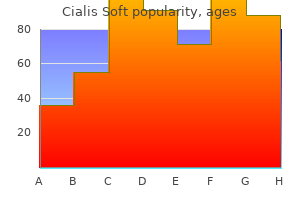
Order cialis soft with a visa
Variations in these techniques differ largely on how the lamina is secured into its new position or how the exposure in made erectile dysfunction drugs not working discount cialis soft uk. Initially, the hinges were sutured or tethered with wire to surrounding tissue or propped open with bone or synthetic grafts. Recent innovations have adapted plates and screws to securely fix the lamina in place and are favored among many high-volume laminoplasty surgeons. This increases the spinal canal diameter and the hinged lamina is held open with a cortical bone graft spacer or specific laminoplasty plates. The sagittal spinous process splitting approach involves splitting the spinous processes with a high-speed burr to create two hemilaminas. Furthermore, by avoiding a bicortical trough laminectomy laterally, the risk of injury to the lateral epidural venous elements is significantly reduced. The shoulders are often taped down to allow for lateral fluoroscopic imaging of the lower cervical spine. A reverse Trendelenburg position is used to decrease venous pressure and thus blood loss. Neuromonitoring of somatosensoryevoked potentials is generally recommended and employed for cervical laminoplasty, while the routine use of motor-evoked potentials is less common. Neuromonitoring allows for immediate detection and early intervention in cases of decreased spinal cord perfusion or severe hypotension. For this reason, anesthesia providers typically use an arterial catheter for continuous blood pressure monitoring. Complications of Laminoplasty undergoing cervical spine surgery with somatosensory-evoked potential monitoring and found degradation in evoked potentials in 17 (2. Intraoperative fluoroscopy can be used to localize the landmarks for skin incision and operative dissection and is especially useful in patients whose body habitus makes palpation of physical landmarks more challenging. In both cases, the laminoplasty is opened sequentially at each level with an understanding that adequate opening and subsequent decompression often require multiple levels to be opened. The fascial closure should be watertight and the skin closed meticulously, especially in patients with redundant soft tissue. Postoperative care involves typical wound care and most importantly limited use of brace immobilization. The evidence strongly suggests that postoperative immobilization following laminoplasty increases the risk of lost motion and axial neck pain. In general, neurologic recovery is expected in the majority of patients treated with laminoplasty, with studies suggesting that approximately 80% of patients will experience some type of improvement. A mean recovery rate of 55% with a range of 20 to 80% has been reported based on Japanese Orthopaedic Association Scale used to assess for myelopathy. Yonenobu et al compared laminoplasty with multilevel anterior corpectomy and found the complication rates to be four times higher in the corpectomy group, 29 versus 7%.
Swine Snout (Dandelion). Cialis Soft.
- Preventing urinary tract infection (UTI), loss of appetite, upset stomach, gas (flatulence), constipation, arthritis-like pain, and other conditions.
- How does Dandelion work?
- What is Dandelion?
- Dosing considerations for Dandelion.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96692
Discount generic cialis soft uk
The sternum (manubrium) forms synchondrosis with the first costal cartilage how does the erectile dysfunction pump work buy cialis soft 40 mg, whereas the second to seventh costal cartilages form synovial plane joints with the sternum. The sternocostal articulations (costosternal articulations), articulations of the cartilages of the true ribs with the sternum are arthrodial joints, with the exception of the first, in which the cartilage is directly united with the sternum, and which is, therefore, a synarthrodial articulation. It interlocks with the corresponding inferior articular facet making a strong articulation rendering dislocation in the thoracic region uncommon. Costosternal joint Ribs directly articulate with vertebral body by costovertebral joint, with transverse process by costotransverse joint and with costal cartilage by costochondral joint. Intercostal nerves are the anterior primary rami of the first 11 thoracic spinal nerves (12th is the subcostal nerve, which these nerves run between the internal and innermost layers of muscles, with the intercostal veins and arteries. They are lodged in the costal grooves on the inferior surface of the ribs and give muscular branches and lateral and anterior cutaneous branches. Classification the intercostal nerves are classified into the following two groups: Typical intercostal nerves (3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th). The atypical spinal nerves extend beyond the thoracic wall and partly or entirely supply the other regions. The typical intercostal nerves are those which remain confined to their own intercostal spaces. T1-T2: Also supply upper limb via brachial plexus (T1) and intercostabrachial nerve (T2). It carries sensation from the central portion of diaphragm, peritoneum, pleura and pericardium along the course. It descends on the anterior surface of the scalene anterior muscle under cover of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, passes between the subclavian artery and vein at the root of the neck and enters the thorax by crossing in front of the origin of the internal thoracic artery, where it is joined by the pericardiophrenic branch of this artery. It then passes anterior to the root of the lung (hilum) lying between the mediastinal pleura and fibrous pericardium and supplying them. Eventually it reaches and supply the diaphragm, alongwith the associated pleura and peritoneum. Pain from an inflammation of the pericardium (pericarditis) is carried in the phrenic nerve. The ganglionated sympathetic trunks lie anterior to the heads of the ribs and the posterior intercostal vessels. At the upper end sympathetic chain includes the cervicothoracic (or stellate) ganglion, which is formed by fusion of the At the lower end it enters the abdomen through the crus of the diaphragm or behind the medial lumbocostal arch. Greater Splanchnic Nerve arises usually from T5-9 sympathetic ganglia, perforates the crus of the diaphragm (or occasionally pass through the aortic hiatus), and ends in the celiac ganglion. Lesser Splanchnic Nerve is derived usually from the 10th and 11th thoracic ganglia, pierces the crus of the diaphragm, and ends in the aorticorenal ganglion.
Syndromes
- If you have type A blood, you can only receive types A and O blood.
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
- Diphenatol
- Fluids through a vein (by IV)
- Infections of heart valves
- Temperature control
- Eat 4 servings a day: one serving equals 1 cup milk or yogurt, 1 1/2 oz. natural cheese, or 2 oz. processed cheese.
- Burns
- Heart attack or stroke
- Next, your surgeon will separate your breastbone in order to see your heart.
Cialis soft 40 mg buy amex
The cerebellopontine angle cistern is the most common location erectile dysfunction young age causes buy discount cialis soft on line, followed by the parasellar and middle cranial fossa (Sylvian fissure) locations. They usually present in adulthood owing to slow growth causing compression of neural or vascular structures. Intracranial dermoid cysts are at least four times less common than epidermoid cysts and are most often midline in Treatment the general paradigm for treatment of clival chordomas is maximally safe aggressive resection on presentation with an emphasis on neurological preservation, followed by radiation therapy. Adjuvant radiation therapy is generally advocated for chordomas because of the poor prognosis in those who recur. It is difficult to administer adequately high doses of radiation with conventional two- or three-dimensional techniques; however, newer high-dose focused radiation delivery techniques with particles (primarily protons) or photons (stereotactic radiosurgery, stereotactic radiation therapy, and image-guided intensity-modulated radiation therapy) have allowed for administration of a higher dose to the tumor while sparing the surrounding structures. The most common site is the suprasellar cistern, followed by the posterior fossa and frontonasal region. They present at significantly younger ages (peaking in the second to third decades) compared to epidermoid cysts. Treatment Treatment for symptomatic epidermoid and dermoid cysts is surgical resection. The insinuating growth pattern for epidermoid cysts can make gross total resection impossible. Imaging Epidermoid cysts characteristically have irregular frondlike excrescences and an insinuating growth pattern, wrapping around vessels and cranial nerves in cisterns. Lesions do not enhance centrally, although mild marginal enhancement can be present. Also note small T1 hyperintense areas with the lesion, which is likely due to high triglycerides and unsaturated fatty acids that can sometimes be seen in epidermoids. For symptomatic arachnoid cysts, treatment options include endoscopic or open resection or fenestration, or cystoperitoneal shunting. It has the same signal as cerebrospinal fluid (hyperintense on T2-weighted images and suppresses in signal on fluid attenuation inversion recovery). Ecchordosis physaliphora Characteristic imaging features: Small T2 hyperintense mass in the prepontine cistern connected to the clivus by an osseous stalk. It differs from other head and neck squamous cell carcinomas in epidemiology, histology, natural history, and response to treatment. The incidence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in endemic areas in Southeast Asia is at least 10 times that in North America and Western Europe. It is two to three times more common in males than in females, with a peak incidence between 40 and 60 years of age. Clinical presentation includes headaches, conductive hearing loss secondary to middle ear obstruction, epistaxis, cranial nerve neuropathies, and neck mass due to cervical node metastases. They can also be found elsewhere along the craniospinal axis, reflecting the course of the embryonic notochord. They are similar to chordoma on histology, but are more hypocellular with absent mitoses. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma usually appears as a poorly marginated mucosal mass with epicenter in the fossa of Rosenmuller at the superolateral aspect of the nasopharynx.

Buy generic cialis soft 40 mg on-line
It consists of a medial lamella (red solid line) and a lateral lamella (red dotted line) that are separated by the vertical lamella of the middle turbinate (arrowheads) erectile dysfunction cpt code cheap cialis soft uk. It should be noted that in addition to the lateral lamella of the cribriform plate, the anterior part of the ethmoid roof, in the area just behind the frontal recess, also represents a site of potential inadvertent breach during endoscopic surgery. In addition to variations in the olfactory fossa depth, there is asymmetry of the ethmoid roof as well as a flat sloping shape of ethmoid roof on the right (c; arrow), with an increase in the angle between the fovea ethmoidalis and the lateral lamina of the cribriform plate approaching 180 degrees. Both of these variants can be associated with an increased risk of iatrogenic injury and complications during endoscopic surgery. It may also have bony projections or nasal septal spurs, as demonstrated on the coronal reformatted image (d). On the sagittal image (b), the superior turbinate is not seen because it is medial to the plane of the section. The middle turbinates have a particularly complex anatomy and understanding this anatomy is key for understanding the functional units and drainage pathways in the paranasal sinuses. There is variation in the terminology used which can cause confusion, but according to some descriptions, the basal lamella of the middle turbinate can be divided into three portions. As discussed earlier, there is variation in the terminology used for different parts of the middle turbinate, and some consider the anterior vertical part attaching to the cribriform plate the vertical lamella and the more posterior parts the basal lamella. In one study, 53% of patients examined had some degree of middle turbinate pneumatization. There is variation in terminology used, some referring to all parts as the basal lamella of the middle turbinate and others referring to the anterior part as the vertical lamella and the middle and posterior parts as the basal lamella. Regardless, there is an anterior vertical portion in a near sagittal plane that attaches to the cribriform plate between the medial and lateral lamella of the cribriform plate (a,b). It should also be noted that the basal lamella of the middle turbinate is the landmark used for separating anterior (white asterisks) from posterior (blue asterisks) ethmoid air cells (d,e). However, some believe that concha bullosa may become clinically significant when they are large and result in obstruction of drainage pathways and air cells. This refers to cases where the middle turbinate has a convex curvature on its lateral side rather than the more common medial side.
Cialis soft 40 mg without a prescription
Development of Atrium and Interatrial Septum Atrial Development Atrial development is dependent upon expansion of the original atrial region and incorporation of additional structures erectile dysfunction psychological causes treatment purchase cialis soft 20 mg. On the right, the sinus venosus is incorporated and forms the smooth-walled portion of the right atrium, which is separated from the trabeculated portion by the crista terminalis. On the left, the pulmonary vein, which forms in the dorsal mesocardium, is positioned into the posterior wall of the left atrium when cells in the dorsal mesenchyme proliferate and accompany the septum primum as this structure grows toward the floor of the atrium. Development of the pulmonary vein begins in the midline and then shifts to the left. At birth, when pressure in the left atrium increases, the two septa press against each other and close the communication between the two atria, completed at around 3 months after birth. As the septum primum and septum secundum get fused with each other, foramen ovale in septum secundum is apposed and closed by septum primum. The arrows in 6 indicate the direction of blood flow from the right atrium to the left atrium across the fully developed atrial septum. Fossa ovalis is an oval depression on the interatrial portion consisting of the valve of the fossa ovalis (a central sheet of thin fibrous tissue) which is a remnant of septum primum. Limbus fossa ovalis is the prominent horseshoe-shaped margin of the fossa ovalis; it represents the edge of the fetal septum secundum. If septum secundum is too short to cover foramen secundum, it allows shunting of blood from left to right atrium, through foramen (ostium) secundum. It is caused by either an excessive resorption of the Septum primum (large foramen secundum) or an underdevelopment and reduced size of the Septum secundum (large foramen ovale). Some authorities believe that the pulmonary vein develops as an outgrowth of the dorsal atrial wall, just to the left of the septum primum. Septum Formation in the Bulbus the bulbus is divided into the smooth-walled portion of the right ventricle and the conus and truncus arteriosus. The truncus region is divided by the spiral aorticopulmonary septum into the proximal segments of the aorta and pulmonary artery. Conus cushions divide the outflow tract regions of the aortic and pulmonary channels from the left and right ventricles, respectively and also, together with tissue from the inferior endocardial cushion, close the inter-ventricular foramen. There is absence of ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk, and the primitive truncus arteriosus is present with mixing of blood, resulting in cyanosis. Pericardium and Cavities (Embryology) the pericardial cavity is derived from the part of intraembryonic celom that lies in the midline cranial to prochordal plate and caudal to septum transversum. The heart tube invaginates the pericardial cavity from the dorsal aspect; hence it gets completely covered by myoepicardial mantle and a layer of the pericardial cavity. The myoepicardial mantle contributes to the wall of the heart and layer of the pericardial cavity applied to it forms the visceral layer of the pericardium (also called epicardium). Visceral layer of pericardium continues peripherally as parietal layer of pericardium, both enclosing the pericardial cavity. Visceral layer of serous pericardium is derived from splanchnopleuric mesoderm, whereas parietal layer of serous pericardium (and fibrous pericardium) is derived from somatopleuric mesoderm.
Enzo, 54 years: Cutaneous innervation of dorsum of the foot is mostly provided by the superficial peroneal nerves.
Yugul, 36 years: Extrinsic and intrinsic membranes and ligaments of the larynx Extrinsic Membranes Intrinsic · Thyrohyoid · Cricotracheal · Median and lateral thyroid · Cricotracheal · Cricovocal (conus elasticus) · Quadrate/Quadrangular · Vocal · Vestibular · Cricothyroid Ligaments Vocal Ligament extends from the posterior surface of the thyroid cartilage to the vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage, and is considered the upper border of the conus elasticus.
Copper, 53 years: Cervical lymph node metastases were seen in an average of 5% at presentation, and less than one-third of these patients were successfully treated.
8 of 10 - Review by K. Stejnar
Votes: 80 votes
Total customer reviews: 80