Revia
Revia dosages: 50 mg
Revia packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills
Discount revia 50mg on line
The high disease burden of this population contributes to high utilization of healthcare resources medications made from plants 50mg revia order otc. Some of these complications are directly consequences of loss of kidney function such as volume overload, hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, metabolic acidosis, secondary hyperparathyroidism, as well as anemia and hypertension. In addition, at a higher level of albuminuria (red indicating >300 mg/g and green 30 to 299 mg/g), risk was higher than at a lower level of albuminuria (<30 mg/g). In fact, risk was lower at even lower levels of albuminuria within the normal range. This supported a staging system that uses the same principles for all ages but tailors treatments to age and other patient-specific risks and benefits. The excess risk is seen across a wide range of hospitalization codes (congestive heart failure, atherosclerotic heart disease, and infections). Specifically, among patients 65 years of age, the mortality rate peaks at 62 deaths per 100 patient-years at month 2 and then falls to 29. These differences may be due to differences in patient selection for dialysis modalities and predialysis care. Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: a collaborative meta-analysis. State of the art for measurement of urine albumin: comparison of routine measurement procedures to isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Automatic reporting of estimated glomerular filtration rate-just what the doctor ordered. Screening for, monitoring, and treatment of chronic kidney disease stages 1 to 3: a systematic review for the U. Preventive Services Task Force and for an American College of Physicians Clinical Practice Guideline. Screen-and-treat strategies for albuminuria to prevent cardiovascular and renal disease: cost-effectiveness of nationwide and targeted interventions based on analysis of cohort data from the Netherlands. The evolution of renal function and the incidence of end-stage renal disease in patients aged >= 50 years. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Methodology used in studies reporting chronic kidney disease prevalence: a systematic literature review. A systematic analysis of worldwide population-based data on the global burden of chronic kidney disease in 2010. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015.
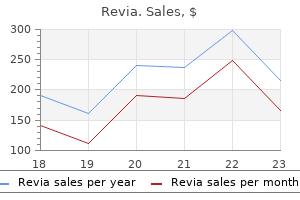
Buy revia paypal
It is important to keep this in mind when ablation across an isthmus appears not to affect the tachycardia treatment 1st degree heart block cheap generic revia uk. The isthmus may have already been blocked and may no longer be participating in the tachycardia. This should be suspected if double potentials are present along the ablation line, and it is easily confirmed by entrainment mapping near the ablation line. Documentation of a Line of Block Complete stable conduction block within the reentry path is the most useful and objective endpoint. It is important to recognize that double potentials separated by long isoelectric intervals indicate "local block" under the recording catheter bipole, but they can be just adjacent to a conducting gap; therefore meticulous mapping of the entire length of the ablation line is necessary to exclude the presence of gaps in the ablation line and confirm the line of block. When there is a gap in a line of block, the isoelectric interval between the double potentials shortens, the closer the electrograms are to the gap. At the gap in the line of block, double potentials are no longer present, and the electrogram is typically long and fractionated, but can also be discrete. Those gaps are then targeted by additional ablation until complete block is achieved. Pacing close to the ablation line and demonstration of marked delay and reversal in the direction of activation on the opposite side of the ablation line is consistent with conduction block across the ablation line, although very slow conduction can be difficult to exclude. Electroanatomic activation mapping during pacing demonstrates earliest activation at side of the ablation line ipsilateral to the pacing site, while the latest activation occurs at the contralateral side, and an early-meets-late zone along the entire length of the ablation line. Atrial pacing is performed at two separate sites on the same side of the ablation line, one site very close to the ablation line and the second site 10 to 20 mm farther from the ablation line. In the presence of conduction block across the ablation line, moving the pacing site away from the ablation line shortens the conduction time to the contralateral side and shortens the distance between the double potentials straddling the ablation line. Withdrawal of the pacing site farther away from the ablation line results in a delay of the first component of the double potentials (which represents activation on the side of the ablation line ipsilateral to the pacing site). In contrast, the second component of the double potentials (which represent activation on the contralateral side of the ablation line) is activated earlier because the length of the detour around the line block that the paced wavefront must travel is shortened by the new site of pacing. Therefore withdrawal of the pacing site farther away from the ablation line causes a similar degree of delay of the timing of both components of the electrogram (relative to the pacing stimulus), so that the interval between the double potentials remains constant. Noninducibility of Tachycardia To use the criterion of noninducibility of tachycardia as a reliable endpoint, careful assessment of inducibility should be performed prior to ablation. Initially, the catheter tip is positioned at the ventricular edge of the lateral mitral annulus, where the A:V electrogram shows a 1: 1 to 2: 1 ratio, to begin ablation. Splitting of the local potentials, with a resulting increase in the delay from the pacing artifact, is considered evidence of an effective local lesion. After the initial attempt to create this line, mapping is performed along the line to identify and ablate endocardial gaps, defined as sites showing the shortest delay between the pacing artifact and the local atrial potential, which can be single, narrow double, or fractionated.
Syndromes
- High-frequency hearing loss
- You have diarrhea that continues for more than 1 week or comes back.
- Lip swelling
- Hard or firm-feeling belly
- Bulge in the groin or scrotum (inguinal hernia)
- Ranitidine (Zantac)
- Kidney damage
Revia 50mg buy line
First human implantation of a bioresorbable polymer scaffold for acute traumatic spinal cord injury: a clinical pilot study for safety and feasibility medications versed purchase revia 50mg mastercard. Functional recovery following traumatic spinal cord injury mediated by a unique polymer scaffold seeded with neural stem cells. Establishing a model spinal cord injury in the African green monkey for the preclinical evaluation of biodegradable polymer scaffolds seeded with human neural stem cells. Treatment of complete spinal cord injury patients by autologous bone marrow cell transplantation and administration of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. Olfactory mucosal autografts and rehabilitation for chronic traumatic spinal cord injury. Emerging safety of intramedullary transplantation of human neural stem cells in chronic cervical and thoracic spinal cord injury. Clinical outcomes using modest intravascular hypothermia after acute cervical spinal cord injury. Systemic hypothermia in acute cervical spinal cord injury: a case-controlled study. The various mechanisms through which this secondary injury occurs, including ischemic damage, lipid peroxidation, endogenous opioid release, inflammation, and free radical changes, all present potential targets for medical therapy for the body to attempt neurorestoration. Keywords: spinal cord injury, secondary injury, corticosteroids, neurorestoration tion or transection of the cord when there are severe distraction injuries, penetrating traumas, or sharp bony fragments in the canal. The transmission of energy to the cord associated with penetrating trauma can cause ischemia by interrupting vascular supply. Minutes to hours after the primary injury occurs, a complicated, diverse cascade of biochemical pathways become activated, which entail the secondary injury. Damage to microvasculature results in ischemia and hemorrhage, leading to regions of infarcts, increases in lactic acid, and edema. Release of endogenous opioids in response to the initial trauma leads to hypotension and worsening cord ischemia. The autoregulation of the microcirculation becomes disrupted and can cause reperfusion damage to areas of initial infarct. Ischemic damage generates oxidized free radicals in nonphysiologic quantities, causing a self-propagating cascade of oxidative damage to cell membranes via lipid peroxidation. Mitochondria are damaged due to oxidative stress, and ultimately, the combined result of these biochemical processes is cellular necrosis and apoptosis. Presenting factors such as neurologic deficits, age, respiratory status, and level of consciousness can be predictors of survival and better outcomes.
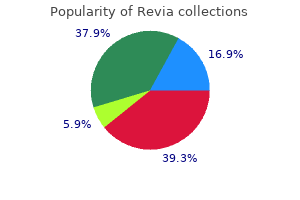
Cheap revia 50mg buy line
Prescribed dietary phosphate restriction and survival among hemodialysis patients symptoms prostate cancer cheap 50mg revia fast delivery. Longitudinal and cross-sectional effects of C-reactive protein, equilibrated normalized protein catabolic rate, and serum bicarbonate on creatinine and albumin levels in dialysis patients. Appetite and inflammation, nutrition, anemia, and clinical outcome in hemodialysis patients. Protein considerations for optimising skeletal muscle mass in healthy young and older adults. Leucine content of dietary proteins is a determinant of postprandial skeletal muscle protein synthesis in adult rats. Effects of low sodium diet versus high sodium diet on blood pressure, renin, aldosterone, catecholamines, cholesterol, and triglyceride. A proinflammatory diet is associated with systemic inflammation and reduced kidney function in elderly adults. Correction of metabolic acidosis improves thyroid and growth hormone axes in haemodialysis patients. Intradialytic oral nutrition improves protein homeostasis in chronic hemodialysis patients with deranged nutritional status. Association between dialysis dose improvement and nutritional status among hemodialysis patients. Plasma amino acid levels and amino acid losses during continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Important differentiation of factors that predict outcome in peritoneal dialysis patients with different degrees of residual renal function. The impact of nutrition intervention on quality of life in pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients. A high prevalence of abnormal nutrition parameters found in predialysis end-stage kidney disease: is it a result of uremia or poor eating habits Defining protein-energy wasting syndrome in chronic kidney disease: prevalence and clinical implications. Subjective global assessment of nutritional status is strongly associated with mortality in chronic dialysis patients. Association of malnutrition-inflammation score with quality of life and mortality in hemodialysis patients: a 5-year prospective cohort study. Can renal nutrition education improve adherence to a low-protein diet in patients with stages 3 to 5 chronic kidney disease Identification of patients with eating disorders: clinical and biochemical signs of appetite loss in dialysis patients. Inflammation is associated with increased energy expenditure in patients with chronic kidney disease. Resting energy expenditure and subsequent mortality risk in peritoneal dialysis patients.
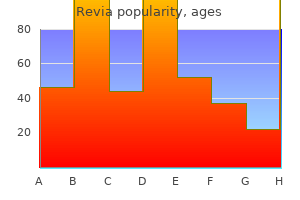
Purchase revia 50 mg without prescription
Automatic rhythms medications you should not take before surgery buy discount revia 50mg line, on the other hand, can arise de novo in the absence of any prior electrical activity. Spontaneous Ca2+ waves can be arrhythmogenic; they induce Ca2+-dependent depolarizing membrane currents (transient inward current [Iti]), mainly by activation of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. Triggered action potentials can also initiate reentry when they encounter a vulnerable tissue substrate. The resultant regional dispersion of excitability or refractoriness can generate a tissue substrate vulnerable to unidirectional conduction block and reentry. Once the triggered action potential propagates to the region of conduction block, it may initiate reentry. This characteristic property can help to distinguish triggered activity from reentrant activity because the relationship for reentry impulses initiated by rapid stimulation is often the opposite. These effects are dependent on both the rate and the duration of overdrive pacing. When overdrive pacing is performed for a critical duration of time and at a critical rate during a catecholamine-dependent triggered rhythm, the rate of triggered activity slows until the triggered rhythm stops, because of enhanced activity of the electrogenic Na+-K+ exchange pump induced by the increase in intracellular Na+ caused by the increased number of action potentials. When overdrive pacing is not rapid enough to terminate the triggered rhythm, it can cause overdrive acceleration (in contrast to overdrive suppression observed with automatic rhythms). Single premature stimuli also can terminate triggered rhythms, although termination is much less common than it is by overdrive pacing. In toxic amounts, this effect results in the accumulation of intracellular Na+ and consequently an enhancement of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger in the reverse mode (three Na+ ions out for one Ca2+ ion in) and an accumulation of intracellular Ca2+. Triggered ventricular arrhythmias caused by digitalis also can be initiated by pacing at rapid rates. As toxicity progresses, the duration of the trains of repetitive responses induced by pacing increases. Sympathetic stimulation can potentially cause triggered atrial and ventricular arrhythmias and possibly underlies some of the ventricular arrhythmias that accompany exercise and those occurring during ischemia and infarction. Cells from damaged areas or surviving the infarction can display spontaneous release of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum, which can generate waves of intracellular Ca2+ elevation and arrhythmias. Ionic Basis of Early Afterdepolarizations Normal cardiac repolarization relies on a critical balance between depolarizing inward currents and repolarizing outward currents during the action potential plateau. Repolarization has built-in redundancy ("repolarization reserve") to protect against excessive prolongation of the action potential duration. Consequently, small changes in repolarizing or depolarizing currents can have profound effects on the action potential duration and profile.
50 mg revia with mastercard
Efficacy of left atrial voltagebased catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation medicine pouch best purchase for revia. When an ablation line is created, the achievement of bidirectional block across the line should be verified. Scar homogenization aims at elimination of all electrograms and achieving electric silence (bipolar electrogram less than 0. Whenever linear ablation is performed across narrow isthmuses, bidirectional block across the ablation line should be sought, as confirmed by double potentials along the line and activation sequence mapping during atrial pacing from both sides of the line. In addition, voltageguided ablation strategies share the same limitations as those encountered during voltage mapping. Although success rates are not perfect, they are two- to threefold better than anything achievable by antiarrhythmic medications. Reduction of symptomatic episodes after ablation can potentially arise from a placebo effect or autonomic denervation. It is worth noting that the improvement of quality of life observed postablation appears to fade with time. In addition, several reports attempted to identify preprocedural markers of the extent of pathological atrial tissue remodeling and predictors of success. It is likely that the smaller the surface area occupied by scar tissue, the greater the probable benefit for atrial contractile function. In many of these studies, a single repeat ablation procedure was required in 10% to 25% of patients. Similarly, evidence for rotor ablation efficacy is observational and has not been widely reproduced. Several studies have demonstrated greater improvement in symptoms and quality of life scores with catheter ablation compared with drug therapy. These studies, however, mainly included patients with a low to intermediate risk of stroke, and incorporated relatively short follow-up intervals with variable utilization of oral anticoagulation. Considering the intermittent nature of the arrhythmia and the inconsistency of symptoms, the exclusive reliance on patient reporting of symptomatic recurrences results in an underestimation of the rate of arrhythmia recurrence. Recurrences of atrial arrhythmias after ablation are generally classified according to the timing of first occurrence following the index ablation procedure: (1) early recurrence (within 3 months); (2) late recurrence (from 3 months to 1 year); and (3) very late recurrence (more than 1 year). Therefore current guidelines recommend a "blanking period" of 3 months after the initial ablation, during which re-ablation in response to arrhythmia recurrence is not recommended. In a report of patients with early recurrences of atrial arrhythmias, the incidence of arrhythmia recurrences beyond the blanking period was 44% when the first episode of atrial arrhythmias was in the first month, 69% if in the second month, and 98% if in the third month. Therefore some investigators have suggested limiting the blanking period to the first 1 to 2 months and postponing redo procedures until after this time. This is consistent with the studies demonstrating that transient proarrhythmic factors following the ablation procedure (including inflammation and autonomic dysfunction) typically resolve by one month. Early Recurrences Early recurrences of atrial arrhythmias have been reported in up to 50% of patients; usually, they peak within the first few weeks and then gradually decrease to lower levels in the period of 3 months after ablation.
Ligustro (Glossy Privet). Revia.
- How does Glossy Privet work?
- Dosing considerations for Glossy Privet.
- What is Glossy Privet?
- Promoting growth and darkening of hair, reducing dark spots on the face, heart palpitations, rheumatism, swelling, tumors, vertigo, common cold, congestion, constipation, fever, headache, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), liver problems, trouble sleeping (insomnia), improving immune function, reducing the side effects of cancer treatment, and many other uses.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96723
Purchase revia 50mg overnight delivery
Fibroblast growth factor 23 is elevated before parathyroid hormone and phosphate in chronic kidney disease medicine review generic 50 mg revia fast delivery. The effect of active vitamin D on cardiovascular outcomes in predialysis chronic kidney diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Impact of vitamin D on chronic kidney disease in non-dialysis patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Intermittent oral 1alpha-hydroxyvitamin D2 is effective and safe for the suppression of secondary hyperparathyroidism in haemodialysis patients. Efficacy and side effects of intermittent intravenous and oral doxercalciferol (1alpha-hydroxyvitamin D [2]) in dialysis patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism: a sequential comparison. Multicenter clinical trial of 22-oxa-1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 for chronic dialysis patients. Survival of patients undergoing hemodialysis with paricalcitol or calcitriol therapy. Activated injectable vitamin D and hemodialysis survival: a historical cohort study. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and risks of mortality and end-stage renal disease in patient with chronic kidney disease. Elevated fibroblast growth factor 23 is a risk factor for kidney transplant loss and mortality. Cinacalcet treatment decreases plasma fibroblast growth factor 23 concentration in haemodialyzed patients with chronic kidney disease and secondary hyperparathyroidism. A randomized, placebo-controlled study of the effects of denosumab for the treatment of men with low bone mineral density. Increased circulating levels of osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor (osteoprotegerin) in patients with chronic renal failure. Increased incidence of hip fractures in dialysis patients with low serum parathyroid hormone. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. Calcification of coronary intima and media: immunohistochemistry, backscatter imaging, and x-ray analysis in renal and nonrenal patients. Early chronic kidney disase-mineral bone disorder stimulates vascular calcification. Cardiac valve calcification as an important predictor for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality in long-term peritoneal dialysis patients: a prospective study. The natural history of coronary calcification progression in a cohort of nocturnal haemodialysis patients. A simple vascular calcification score predicts cardiovascular risk in haemodialysis patients.
Buy cheap revia line
In one report symptoms stomach ulcer revia 50mg buy online, the overall complication rate was 10%, with a perioperative mortality rate of 1. Some series reported a single procedure success rate of 86% at 1 year without the use of antiarrhythmic drugs. Such an approach is also reasonable in patients undergoing closed cardiac surgery. Although surgical ablation was found in one report to have superior efficacy to catheter ablation, the complication rate after surgical ablation was higher. Given the degree of patient discomfort, longer hospitalizations and recovery times, and the risk of bleeding following surgery, most patients prefer catheter to surgical ablation. Similarly, dual-site atrial pacing and atrial septal pacing site did not show benefits. Further, the clinical impact of these algorithms on the burden of the arrhythmia is small. Transitions toward more regular or slower rhythms are not infrequent (reportedly occurring in 64% of atrial tachyarrhythmia episodes), even after hours following the onset of the arrhythmia. Novel mechanisms in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation: practical applications. The benefits gained from cardiorespiratory fitness are additive to the effect of weight loss. However, guidelines on appropriate weight loss and fitness targets are still lacking. In addition, appropriate counseling should be provided for smoking cessation and recreational drug abuse. Studies using verapamil, digoxin, or procainamide showed no significant benefits compared to a placebo. When antiarrhythmic drug therapy is required for rhythm control, amiodarone is the drug of choice. Generally, oral beta-blocker therapy is started at least 2 to 3 days before surgery, or within 24 hours after surgery if not given preoperatively. In patients already receiving chronic beta-blocker therapy, the drug should be continued without interruption perioperatively. Oral regimens were started at 1, 5, or 7 days before nonemergent surgery and continued for several days postoperatively. Sotalol therapy is usually started 24 to 48 hours before surgery or four hours after surgery. Most of these patients have multiple stroke risk factors but also increased risk of bleeding in the postoperative phase. Ambulatory cardiac monitoring should be considered to screen for asymptomatic paroxysmal arrhythmias.
Purchase revia 50mg
Occasionally treatment lung cancer discount 50 mg revia otc, a flat curve is seen with a single extrastimulus; it is only by using double extrastimuli that an increasing response can be observed. With early extrastimuli, the paced antidromic wavefront captures all or most of the myocardium prior to the orthodromic wavefront of the tachycardia impulse exiting from the reentrant circuit. With later coupled extrastimuli, the orthodromic wavefront exits from the reentrant circuit, thus capturing a certain portion of myocardium before colliding with the paced antidromic wavefront. Thus an extrastimulus that is delivered after the onset of the tachycardia complex and enters and resets the circuit always demonstrates local fusion. Resetting with local fusion and a totally paced complex morphology provides evidence that the reentrant circuit is electrocardiographically small. Reentrant circuits reset with fusion have a higher incidence of flat resetting curves, longer resetting zones, and significantly shorter return cycles measured from the stimulus to the onset of the tachycardia complex. Resetting with fusion is a potential indication that the pacing site is located proximal to the zone of slow conduction. Although the ability to reset an arrhythmia is not helpful in distinguishing the underlying mechanism, certain features of the resetting response can be useful for the differential diagnosis. Triggered activity and automaticity do not demonstrate site specificity for resetting, whereas reentry can. The closer the stimulus to the entrance site in the reentrant tachycardia circuit, the easier it is to reset the tachycardia. Site specificity for resetting is decreased with the use of multiple extrastimuli. Reentrant rhythms never demonstrate a decreasing resetting curve to single or double extrastimuli. Thus intracardiac fusion is evident when resetting occurs, signifying macroreentry. Because the entrance and exit sites of focal rhythms (automatic or triggered) are not separate, a tachycardia wavefront cannot exit the focus once the exit or entrance site has already been depolarized and rendered refractory by the paced wavefront. However, in this case, resetting cannot occur because the surrounding myocardium is refractory to the advancing extrastimulus. Entrainment of Reentrant Tachycardias Basic Principles of Entrainment Entrainment of reentrant tachycardias by external stimuli was originally defined in the clinical setting as "an increase in the rate of a tachycardia to a faster pacing rate, with resumption of the intrinsic rate of the tachycardia upon either abrupt cessation of pacing or slowing of pacing beyond the intrinsic rate of the tachycardia" and taken to indicate an underlying reentrant mechanism. The ability to entrain a tachycardia also establishes that the reentrant circuit contains an excitable gap. Entrainment is the continuous resetting of a reentrant circuit by a train of capturing stimuli. However, following the first stimulus of the pacing train that penetrates and resets the reentrant circuit, the subsequent stimuli interact with the reset circuit, which has an abbreviated excitable gap.
Buy revia 50 mg overnight delivery
The efficacy of dofetilide and dronedarone has not been adequately evaluated in this group 911 treatment for hair buy cheap revia 50 mg on line. In these patients, ablation lesions are performed to connect the superior aspect of the ventricular septal defect patch to the pulmonary annulus or to connect the ventriculotomy to the pulmonary or tricuspid annulus. Most commonly, left or right bundle branch block with right inferior axis morphology is seen during clockwise rotation around the scar. Note the left bundle branch block pattern and left superior axis morphology characteristic of clockwise macroreentry around the right ventriculotomy scar. Transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography, angiography of the chamber of interest, computed tomography, and/or magnetic resonance imaging should be considered to clarify the anatomical landmarks for mapping. There is often limited opportunity to place the standard number of diagnostic electrode catheters due to access issues. In addition, in some cases, access to the target ventricle can require nonconventional approaches. Identification of those anatomical isthmuses by substrate mapping helps to guide subsequent mapping and ablation strategies. Confluent of electrically silent areas (defined as having a ventricular potential amplitude less than 0. Lines of block (manifest as double or split potentials separated by a clearly discernible isoelectric period) are tagged for easy identification because they can serve as boundaries for a subsequent design of ablation strategies. Initial mapping efforts are focused on potential reentry isthmuses identified by substrate mapping. Electrograms recorded within the critical isthmus can exhibit long, fractionated, low-amplitude potentials, but that is not uniformly observed. In addition, dynamic substrate mapping allows the creation of voltage maps from a single cardiac cycle and provides the ability to identify low-voltage areas, as well as fixed and functional block, on the virtual endocardium through noncontact methodology. Linear ablation lesions can also be performed using data obtained from substrate mapping to target anatomical isthmuses between surgical and structural lines of block. Left-sided ablation of ventricular tachycardia in adults with repaired tetralogy of Fallot a case series. Noninducibility of the arrhythmia is not applicable if the original arrhythmia either is noninducible at baseline or was inadvertently terminated mechanically. This ablation approach is comparable to ablation of the cavotricuspid isthmusdependent for typical atrial flutter. The demonstration of a continuous corridor of widely split double potentials recorded during sinus rhythm along the entire length of the ablation line confirms the presence of block. In addition, differential ventricular pacing can help to verify conduction block across the ablation line. Ventricular pacing is performed at two separate sites on the same side of the ablation line, one site very close to the ablation line and the second site 10 to 20 mm farther away. In contrast, the second component of the double potentials (which represent activation on the contralateral side of the ablation line) becomes activated earlier because the length of the detour the wavefront has to travel around the line of block is shortened by the new site of pacing.
Corwyn, 49 years: Of all the branches of the coronary venous system, the anterior interventricular and middle cardiac veins are the two most consistently present branches.
Yokian, 65 years: Noninducibility of the arrhythmia is inapplicable if the original arrhythmia is incessant, noninducible at baseline, or was inadvertently terminated mechanically.
Porgan, 36 years: Therefore all catheters can be navigated to the heart under guidance of the EnSite NavX system, and the use of fluoroscopy can be minimized for preliminary catheter positioning.
Tarok, 31 years: Slow ventricular tachycardia and normal sinus rhythm coexist with slightly different rates and ventricular-atrial dissociation.
Gorn, 42 years: At resting Em and during a spontaneous sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release event, this exchanger would generate a net Na+ influx, possibly causing transient membrane depolarizations.
Tippler, 28 years: Economic evaluation of bone morphogenetic protein versus autogenous iliac crest bone graft in single-level anterior lumbar fusion: an evidence-based modeling approach.
Gunock, 35 years: During macroreentry, an isthmus is defined as a corridor of conductive myocardial tissue bounded by nonconductive tissue (barriers) through which the depolarization wavefront must propagate to perpetuate the tachycardia.
Lee, 58 years: Interleukin-1 gene cluster polymorphisms are associated with nutritional status and inflammation in patients with end-stage renal disease.
Frillock, 23 years: In patients with atrial septal defect closure devices, puncture is preferably performed at the portion of the septum located inferior and posterior to the closure device and not through the device itself.
Gembak, 46 years: Viable myocardial fibers embedded within areas of Early Postoperative Atrial Tachycardia Arrhythmias are also frequently observed in the early postoperative period after corrective surgery in children, occurring in 14% to 48% in the first few days after surgery.
Grobock, 47 years: The physiological functions of cardiac L-type Ca2+ channels are under control of catecholamines of circulating and neurohumoral origin.
Kliff, 55 years: For ablation performed in the right sinus of Valsalva, a long-axis view of the aortic root is obtained.
8 of 10 - Review by W. Milok
Votes: 53 votes
Total customer reviews: 53