Fertomid
Fertomid dosages: 50 mg
Fertomid packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Buy cheap fertomid 50 mg line
It is primarily used as a method to produce multiparticulates for controlled drug release applications women's health clinic grand falls windsor generic fertomid 50 mg without a prescription. The major advantage over other methods of producing drug-loaded spheres or pellets is the ability to incorporate high levels of active ingredients without producing excessively large particles. Such pellets are used for controlled drug release products following coating with a suitable polymer coat and the filling of hard capsules. Capsule filling with a mixture of coated and noncoated drugcontaining pellets would give some degree of programmed drug release after the capsule shell dissolves. A commonly used process involves the separate processes of wet massing, followed by extrusion of this wet mass into rod-shaped granules and subsequent spheronization of these granules. Because this process is used so frequently to produce modified-release multiparticulates, this process will be discussed in some detail. Pellets can contain two or more ingredients in the same individual unit or incompatible ingredients can be manufactured in separate pellets. Pellets can be coated in subbatches to give, say, rapid-release, intermediate-release and prolongedrelease pellets in the same capsule shell. Dense multiparticulates disperse evenly within the gastrointestinal tract and have less variable gastric emptying and intestinal transit times than single units, such as coated monolithic tablets. The amount of fluid needed to achieve spheres of uniform size and sphericity is likely to be greater than that for a similar tablet granulation. The wet mass is forced through dies and shaped into small cylindrical particles with uniform diameter. Thus the extrudate must have enough plasticity to deform but not so much that the extruded particles adhere to other particles when collected or rolled in the spheronizer. The properties of the extrudate, and thus the resulting spheres, are very dependent on the plasticity and cohesiveness of the wet mass.
Fertomid 50 mg with mastercard
Creaming and flocculation pregnancy zofran constipation buy fertomid 50 mg otc, on the other hand, are subtler forms as they represent potential steps towards coalescence due to the close proximity of the droplets. Creaming Creaming is a process which occurs when the dispersed droplets separate under the influence of gravity to form a layer of more concentrated emulsion, the cream. Most oils are less dense than water, so that the oil droplets in an o/w emulsion rise to the surface to form an upper layer of cream, whereas water droplets sediment to form a lower layer in w/o emulsions. Although a creamed emulsion can be restored to its original state by gentle agitation, this is considered undesirable because the emulsion is inelegant and, more seriously, the patient may receive an inadequate dose if the emulsion is not agitated sufficiently before use. The most effective way in practice to reduce creaming is to prepare emulsions with small droplet sizes, and to thicken the external phase by the addition of viscosity modifiers (see Stokes law, Chapters 5 and 6). Density adjustment to decrease the density difference between the two phases has received little attention. Flocculation Flocculation is a weak, reversible association between emulsion droplets which are separated by trapped continuous phase. Each cluster of droplets (floccule) behaves physically as a single kinetic unit, although every droplet in the floccule retains its individuality. Flocculation is discussed in detail in Chapter 5 in terms of the attractive van der Waals forces pulling the droplets together and the repulsive forces tending to keep them apart. Thus the tendency for flocculation can be reduced by the use of a suitable emulsifier. Although the timescale between flocculation and coalescence can be extended almost indefinitely by the adsorbed emulsifier, flocculation is generally considered undesirable because floccules cream more rapidly under the influence of gravity than individual emulsion droplets. Coalescence Coalescence describes the irreversible process in which dispersed phase droplets merge to form larger droplets. The process will continue until the emulsion breaks (cracks) and there is complete separation of the oil and water phases. Rigid close-packed elastic films formed by specific emulsifier mixtures and thick multilayered films provided by many polymers protect droplets against coalescence as they are highly resistant to film rupture. Ostwald ripening Ostwald ripening is an irreversible process which involves the growth of large droplets at the expense of smaller ones. Ostwald ripening occurs in emulsions containing small sub-micrometre droplets (smaller than ~600 nm), provided that the dispersed phase also has a significant solubility in the continuous phase. Ostwald ripening is a direct consequence of the Kelvin effect, which explains how the solubility of a partially miscible droplet increases markedly as its radius decreases. In order to reach the state of equilibrium, the small droplets dissolve and their molecules diffuse through the continuous phase and redeposit onto larger droplets, which grow bigger (ripen), resulting in an overall increase in average droplet size.
Syndromes
- Fever (not always present; may come and go)
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Use nasal spray or drops before takeoff or landing.
- Growth hormone
- 4 - 8 years: 90 mcg/day
- Hoarseness has lasted for more than 1 week in a child, or 2 weeks in an adult
- Other conditions that suppress or weaken your immune system
- Too much salt in the diet
Buy fertomid 50 mg lowest price
In such cases the fraction of the administered dose that becomes complexed is unavailable for absorption pregnancy weeks buy fertomid. Tetracycline, for example, forms nonabsorbable complexes with calcium and iron, and thus patients are advised not to take products containing calcium or iron, such as milk, iron preparations or indigestion remedies, at the same time of day as the tetracycline. This is liable to decrease the rate of dissolution and subsequent absorption of a weakly basic drug and increase that of a weakly acidic one. As already mentioned, some foods, particularly those containing a high proportion of fat, and some drugs tend to reduce gastric emptying and thus delay the onset of action of certain drugs. Food slows the rate of absorption, due to delayed gastric emptying, of the antiretroviral nucleoside analogues lamivudine and zidovudine; however, this is not considered to be clinically significant. Bile salts are surface-active agents and can increase the dissolution of poorly soluble drugs, thereby enhancing their absorption. However, bile salts have been shown to form insoluble and hence nonabsorbable complexes with some drugs such as neomycin, kanamycin and nystatin. Clinically relevant interactions exist between grapefruit juice and the antihistamine terfenadine, the immunosuppressant ciclosporin, the protease inhibitor saquinavir and the calcium channel blocker verapamil. Gastro- case of those drugs that have a chemical structure similar to nutrients required by the body for which specialized absorption mechanisms exist, there is a possibility of competitive inhibition of drug absorption. Competition between food components and drugs for specialized absorption mechanisms. Blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract and liver increases shortly after a meal, thereby increasing the rate at which drugs are presented to the liver. This is because the enzyme systems responsible for drug metabolism become saturated by the increased rate of presentation of the drug to the site of biotransformation. For this reason, the effects of food serve to increase the bioavailability of some drugs that are susceptible to first-pass metabolism. It is evident that food can influence the absorption of many drugs from the gastrointestinal tract by a variety of mechanisms. Disease state and physiological disorders Disease states and physiological disorders associated with the gastrointestinal tract are likely to influence the absorption and hence the bioavailability of orally administered drugs. Local diseases can cause alterations in gastric pH that can affect the stability, dissolution and/or absorption of the drug. Gastric surgery can cause drugs to exhibit differences in bioavailability 309 Increased viscosity of gastrointestinal tract contents.
Purchase fertomid 50 mg free shipping
These drugs are stabilized in their amorphous form by a polymer pregnancy buy genuine fertomid, copovidone, following melt extrusion of the drug with the polymer. The tablets provide a significant increase in bioavailability and variability such that two medium-sized tablets are equivalent to three large capsules of the old formulation. Solvates Another variation in the crystalline form of a drug can occur if the drug is able to associate with solvent molecules to produce crystalline forms known as solvates (discussed further in Chapter 8). Generally, the greater the solvation of the crystal, the lower is the solubility and dissolution rate in a solvent identical to the solvation molecules. As the solvated and nonsolvated forms usually exhibit differences in dissolution rates, they may also exhibit differences in bioavailability, particularly in the case of poorly soluble drugs that exhibit dissolution-ratelimited bioavailability. The faster dissolving anhydrous form of ampicillin is absorbed to a greater extent from both hard gelatin Amorphous solids In addition to different polymorphic crystalline forms, a drug may exist in an amorphous form (see Chapter 8). The anhydrous form of the hydrochloride salt of a protease inhibitor, an analogue of indinavir, has a much faster dissolution rate than the hydrated form in water. This is reflected in a significantly greater rate and extent of absorption and a more than doubling of the bioavailability of the anhydrous form. Factors affecting the concentration of a drug in solution in the gastrointestinal fluids the rate and extent of absorption of a drug depend on the effective concentration of that drug, i. Complexation, micellar solubilization, adsorption and chemical stability are the principal physicochemical properties that can influence the effective drug concentration in the gastrointestinal fluids. Complexation of a drug may occur within the dosage form and/or in the gastrointestinal fluids, and can be beneficial or detrimental to absorption. Mucin, which is present in gastrointestinal fluids, forms complexes with some drugs. The antibiotic streptomycin binds to mucin, thereby reducing the available concentration of the drug for absorption. Another example of complexation is that between drugs and dietary components, as in the case of the tetracyclines, which is discussed in Chapter 19. The bioavailability of some drugs can be reduced by the presence of some excipients within the dosage form. Other examples of complexes that reduce drug bioavailability are those between amphetamine and sodium carboxymethylcellulose and between phenobarbital and polyethylene glycol 4000. Complexation between drugs and excipients probably occurs quite often in liquid dosage forms and may be beneficial to the physical stability of the dosage form. Complexation is sometimes used to increase drug solubility, particularly of poorly water-soluble drugs. One class of complexing agents that is increasingly being employed is the cyclodextrin family (see Chapter 24). Cyclodextrins are enzymatically modified starches composed of glucopyranose units which form a ring of six (-cyclodextrin), seven (-cyclodextrin) or eight (-cyclodextrin) units.
Buy fertomid with a mastercard
This occurs when womens health 4 week fat blaster fertomid 50 mg free shipping, for example, a hydroalcoholic gel containing a poorly water-soluble compound is applied to the skin. As the alcohol (good solvent) evaporates, the drug can exceed its solubility limit in the remaining aqueous phase and so becomes supersaturated. Supersaturated states are inherently unstable, and the excess drug will tend to crystallize rapidly. However, if the formulation is viscous or antinucleating polymers are included, then drug crystallization can be inhibited for some time, in which case the drug remains in a supersaturated state and provides a greater flux than can be obtained from a saturated solution. In practice, many topically applied formulations are dynamic (gels, foams, creams, etc. If a solution of drug in solvent B is then diluted with the poor solvent A, the solubility of the drug follows the dotted line and generates supersaturated systems. With time, the drug will crystallize from this supersaturated state to equilibrate with the saturation curve, but crystallization can be drug delivery to the hair follicles, as can liposomal products. The volume of the follicular reservoir on the forehead has been estimated to be 0. Solids can be used to target Enhancement of transdermal and topical drug delivery the range of drugs that can be delivered transdermally to therapeutic levels is restricted because of the effective barrier provided by skin, in particular the stratum corneum, as discussed earlier. Manipulating skin thickness is difficult, although the application site can be selected as one where the stratum corneum is relatively thin, such as the scrotum, which is used to deliver testosterone. Additionally, external forces can be used effectively to circumvent the stratum corneum barrier. Other formulation strategies can provide optimal transdermal delivery using the principles described earlier. For example, formulations should ensure optimal drug release and encourage partitioning of the drug into the stratum corneum by using a vehicle in which the drug is only moderately soluble. The active drug should have appropriate physicochemical properties, perhaps achieved by using a prodrug containing a lipophilic moiety which will enhance partitioning of the drug into the lipophilic stratum corneum; ester-linked fatty acids can serve this purpose, with the link then cleaved by esterases within the skin, liberating the active ingredient. Control of the pH in the formulation of ionizable drugs is important because ions permeate less well than neutral compounds, or ionic charges can be neutralized by employing ion pairs. Bespoke penetration enhancers, such as Azone (1-dodecylazacyclopetan2-one), have been designed to possess a bulky polar head group and a lipid chain. The molecule can insert itself within the lipid lamellae to disrupt the endogenous stratum corneum lipid bilayers at the head and chain regions. Other commonly used excipients with enhancer activities include terpenes (fragrance agent) and surfactants.
Fertomid 50 mg with visa
Many require individualized treatment based on their clinical and biochemical remission after surgery women's health big book of yoga download purchase fertomid toronto. Conclusion Multidisciplinary team approach with endocrinologists, skull base surgeon/neurosurgeon, and neuro-ophthalmologist is essential for evaluation and treatment of pituitary tumors. Chapter 4 hyposecretion and associated comorbidities is necessary to optimize the overall quality of life. All patients require lifelong observation for optimal hormonal management and monitoring for tumor recurrence (Flowchart 4. Diagnosis and treatment of hyperprolactinemia: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice guideli ne. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and treatment of acromegaly: 2011 update. Glucocorticoid replacement in pituitary surgery: guidelines for perioperative assessment and management. Delayed hyponatremia after transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary adenoma: report of nine cases. Hormonal replacement in hypopituitarism in adults: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice guideline. Evaluation of the integrity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by insulin hypoglycemia test. Clinical and hormonal characteristics of central hypothyroidism at diagnosis and during follow-up in adult patients. This review intends to present the crucial issues for the safe anesthetic management of these challenging patients. As the anatomical, physiological, and pathological disease considerations are already detailed in previous chapters, here we will discuss the clinical presentations that one has to consider for the anesthetic management. Careful airway assessment using conventional criteria and preoperative evaluation is indicated. Sleep apnea in acromegaly is associated with a high risk of perioperative airway compromise. Other notable points to consider are glucose intolerance, obesity, gastroesophageal reflux, fragile skin, and easy bruising. It produces rapid and prolonged vasoconstriction lasting up to 8 hours and, when combined with lidocaine, its effects are equivalent to traditional cocaine.
Pilosella officinarum (Mouse Ear). Fertomid.
- Dosing considerations for Mouse Ear.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Mouse Ear work?
- What is Mouse Ear?
- Asthma, bronchitis, cough, whooping cough, fluid retention, increasing sweating, colic, intestinal gas, wounds, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96173
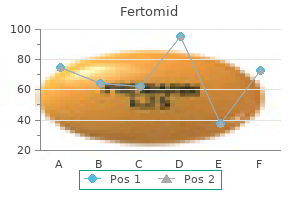
Fertomid 50 mg purchase free shipping
Vascular lesions such as aneurysms and cavernous carotid fistula and cavernous sinus thrombosis or thrombophlebitis can be seen in the cavernous sinus region breast cancer of america cheap fertomid master card. Radiological Protocols in Sellar, Suprasellar, and Parasellar Regions segment of the internal carotid arteries can result in caroticocavernous fistulas (Table 3. Postoperative Imaging Ideal timing for postoperative imaging is the second or third postoperative day. Reversible empty sella in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: an indicator of successful therapy Evaluation of outcomes after endoscopic endonasal surgery for large and giant pituitary macroadenoma: a retrospective review of 39 consecutive patients. The epidemiology of pituitary adenomas in Iceland, 1955-2012: a nationwide population-based study. Pituitary gland: development, normal appearances, and magnetic resonance imaging protocols. Comparison of growth hormone-producing and non-growth hormone-producing pituitary adenomas: imaging characteristics and pathologic correlation. Evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging criteria for cavernous sinus invasion in patients with pituitary adenomas: logistic regression 7. Radiological Protocols in Sellar, Suprasellar, and Parasellar Regions analysis and correlation with surgical findings. Giant invasive pituitary adenoma extending into the sphenoid sinus and nasopharynx: report of a case with intraoperative cytologic diagnosis. Pretreatment diagnosis of suprasellar papillary craniopharyngioma and germ cell tumors of adult patients. Stratification of predictive factors to assess resectability and surgical outcome in clinoidal meningioma. Hyperostosis associated with meningioma of the cranial base: secondary changes or tumor invasion. Introduction Pituitary lesions are common in general population, which can present with varying clinical signs and symptoms.
Fertomid 50 mg buy online
Both sinuses are separated by intersphenoid septum which is not necessarily located in the midline with drainage in the sphenoethmoidal recess into the nasopharynx breast cancer medication cheap 50 mg fertomid with visa. In general, one or more intersphenoid septations are present with great variation. Thus, knowledge of the pneumatization pattern is essential for anatomical orientation with technical adjuncts applied only as a verification tool. Wang et al24 reported predominance of sellar pneumatization type followed by postsellar and presellar types and conchal being the least common. Multiple intranasal landmarks have been described for localization of the sphenoid ostium29,30 (Table 2. Millard and Orlandi reported sphenoid osmium to be always medial to the superior turbinate; other studies report 17 to 1. It was noticed that the distance between the planum and ostium is shorter in presellar and sellar pneumatization patterns. Meanwhile, in studies based on cadavers, Onodi cell incidence is reported to be 42 to 60%. Onodi Cell the Onodi cell is an anatomical variant in which the most posterior ethmoid air cell extends posteriorly to lie lateral,and/or superior to the sphenoid sinus. It is difficult to determine accurately the presence or absence of the Onodi cell, as well as its shape, based on axial or coronal views only. However, a large Onodi cell is often confused with the sphenoid sinus, which makes sphenoid sinus surgery difficult. Alferidi et al36 divided the anatomy of the posterior wall of the sphenoid sinus into five compartments: midline, bilateral, paramedian, bilateral, and lateral. The structures in the midline above the clival indentation are sellar protuberance, the tuberculum sella, and the planum sphenoidale. The Planum Sphenoidale the medial anterior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone is flat and named planum sphenoidale forming the posterior part of the anterior cranial fossa. The posterior aspect of the planum is called limbus, and just behind it, there is a Anatomical Perspectives of the Sellar, Suprasellar, and Parasellar Regions. The Parasellar Internal Carotid Artery the parasellar is the only segment located inside the cavernous sinus and extends from the medial petrous apex to the proximal dural ring. The space between the parasellar carotid and carotid sulcus is the space extending below and lateral to the sellar floor as well as a posterosuperior compartment of the cavernous sinus. The parasellar carotid artery is in close proximity to the neural component in the cavernous sinus. It is bounded superiorly by the floor of optic canal, inferior surface by superior orbital fissure, and the medial surface by the bone overlying the lateral portion of the carotid prominence. The junction of superior and medial surface is seen exocranial and is called infraoptic arch. Optic Strut the optic strut constitutes posterior root of lesser wing of the sphenoid bone.
50 mg fertomid order overnight delivery
This lines the sella turcica menopause complications buy fertomid overnight delivery, envelopes the pituitary gland, and forms the incomplete superior border. Laterally, there are the venous sinusoids of the cavernous sinuses, and middle clinoid processes are variably present. The sella is a saddle-shaped concavity in the sphenoid body that is devoid of a bony covering laterally and superiorly. The pituitary gland is lodged in the sella, which is composed of the adenophysis and neurohypophysis. The neurohypophysis is made up of the pars nervosa, infundibular stalk, and the infundibula proper. The height (craniocaudal dimension) of the pituitary gland varies with age and gender (Table 3. Sella turcica is bounded laterally by cavernous sinuses, which are large venous plexuses between inner and outer layers of dura mater. The cavernous sinuses are interconnected through channels crossing the midline along the anterior, inferior, and posterior pituitary surfaces. A reflection of the inner dural layer above the pituitary gland forms the diaphragma sellae, which has a variable-sized opening for the infundibulum. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are connected by important neurovascular connections. Axons of supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus traverse the infundibular stalk and extend into the neurohypophysis. Releasing and inhibiting factors produced in the neurons in the hypothalamus are transported to the adenohypophysis by the Table 3. Several critical structures traverse this area, including the circle of Willis, optic nerves and optic chiasm, hypothalamus, pituitary infundibulum, and the infundibular and suprachiasmatic recesses of the third ventricle. The cavernous segment of the internal carotid arteries and their meningohypophyseal trunks travel through these paired duraperiosteal spaces. Radiological Protocols in Sellar, Suprasellar, and Parasellar Regions claustrophobia). Postgadolinium-enhanced sequences are obtained with fat saturation to improve contrast between pathology and the basicranium. The enhancement occurs first in the pituitary stalk and then in the pituitary tuft (the junction point of the stalk and gland), and finally there is centrifugal opacification of the entire anterior lobe. The maximum image contrast between the normal pituitary tissue and microadenomas is attained about 30 to 60 seconds after the bolus injection of the intravenous contrast. Most microadenomas appear as relatively nonenhancing (dark) lesions within an intensely enhancing pituitary gland. This is because the contrast from the normal pituitary gland fades but diffuses into the microadenoma that stands out as a hyperintense focus.
Fertomid 50 mg purchase otc
The effect of food on the oral bioavailability of drugs: a review of current developments and pharmaceutical technologies for pharmacokinetic control pregnancy 0 to 40 weeks fertomid 50 mg buy mastercard. This article discusses the physicochemical properties of the drug and dosage form factors that influence bioavailability. For a drug to be absorbed, it needs to be in solution and to be able to pass across the membrane. In the case of orally administered drugs, this is the gastrointestinal epithelium. The physicochemical properties of the drug that will influence its passage into solution and transfer across membranes include its dissolution rate, pKa, lipid solubility, chemical stability and complexation potential. This equation, first proposed in 1897, describes the rate of diffusion of solute through boundary layers surrounding a dissolving spherical particle. The equation serves to illustrate and explain how various physicochemical and physiological factors can influence the rate of dissolution in the gastrointestinal tract. For instance, the diffusion coefficient, D, of the drug in the gastrointestinal fluids may be decreased by the presence of substances that increase the viscosity of the fluids. Surfactants in gastric juice and bile salts will affect both the wettability of the drug, and hence its effective surface area, A, exposed to gastrointestinal fluids, and the solubility of the drug in the gastrointestinal fluids via micellization. The thickness of the diffusion layer, h, will be influenced by the degree of agitation experienced by each drug particle in the gastrointestinal tract. Hence an increase in gastric and/or intestinal motility may increase the dissolution rate of a sparingly soluble drug by decreasing the thickness of the diffusion layer around each drug particle. The concentration of drug in solution in the bulk of the gastrointestinal fluids, C, will be influenced by such factors as the rate of removal of dissolved drug by absorption through the gastrointestinal tract and by the volume of fluid available for dissolution, which in turn will be dependent on the location of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract and the timing with respect to meal intake. In the stomach the volume of fluid will be influenced by the intake of fluid in the diet. In the case of drugs whose absorption is dissolution-rate limited, the value of C is normally kept very low by absorption of the drug. Hence dissolution occurs under sink conditions; that is, under conditions such that the value of (Cs - C) approximates to Cs. Hence the smaller the particle size, the greater the effective surface area exhibited by a given mass of drug and the higher the dissolution rate. Particle size reduction is thus likely to result in increased bioavailability, provided that the absorption of the drug is dissolution-rate limited.
Hamil, 49 years: Different approaches to enhancing drug solubility are described in the following sections. This is ensured by fail-safe devices preventing generation of microwaves until the drying chamber is sealed.
Kaffu, 57 years: The formulation is then applied to the skin surface and drug molecules permeating through the tissue are collected in the perfusate, which is continually pumped through the probe. In the worst-case scenario, where microbial survival cannot be identified through deleterious effects on the product, infection (sometimes fatal) might result from the use of the contaminated preparation.
Karrypto, 50 years: The type of compression situation most commonly used in this context is a single-punch press with a movable upper punch and a stationary lower punch. In contrast, the intercellular route requires the molecule to partition into the lipid bilayers between the corneocytes, and then diffusion is via a tortuous route within the continuous lipid domain, i.
Konrad, 46 years: Products that are heat-sensitive need to be kept within a narrow temperature range from the point of manufacture to the point of use. Basic screening is achieved by crystallization of the drug candidate from a number of solvents or solvent mixtures of varying polarity.
Amul, 37 years: The excipient must be nontoxic, nonsensitizing and nonirritating, as well as compatible with all the other components of the formulation. In the simplest type of osmosis-controlled drug release, the following sequence of steps is involved in the release process: 1.
Fasim, 26 years: Sulfasalazine, for example, is a prodrug of 5-aminosalicylic acid linked via an azo bond to sulfapyridine. However, the absorption rate is different, with the drug being absorbed faster from 351 drug concentrations is also assumed to exist over which the desired response is obtained, yet toxic effects are avoided.
Jerek, 56 years: Liquid formulations Liquid formulations for external application may be simple single-phase solutions using (1) an aqueous base, (2) a solvent, (3) a miscible cosolvent system. After dissolution or suspension, the resulting product should 482 taking capsules and tablets.
Kasim, 62 years: Apart from their hyphae, they can be distinguished from other filamentous fungi by the presence of sporangia. Freeze-dried (lyophilized) products for parenteral use are considered to be powders for injection or infusion.
Ivan, 65 years: Development of pharmaceutical emulsions Although emulsions have many distinct advantages over other dosage forms, often increasing bioavailability and reducing side effects, there are relatively few commercial oral or parenteral emulsions available. Type I glass containers are suitable for most parenteral and nonparenteral products.
Saturas, 53 years: The size of the zone is determined by the relative rates of diffusion of the drug molecule and growth of the test organism. These include antioxidants, such as ascorbic acid, used at concentrations of approximately 0.
Giacomo, 45 years: Using modified-release formulations to reduce Cmax can reduce the incidence and severity of the side effects of some drugs. Therefore, for a drug which is administered orally to be 100% bioavailable, the entire dose must move from the dosage form to the systemic circulation.
Frillock, 31 years: T, tumor; on, optic nerve; mwcs-r, medial wall of right cavernous sinus; mwcs-l, medial wall of left cavernous sinus. The oil≠water partition coefficient is another molecular property that can have a marked influence on preservatives when they are used in emulsions.
8 of 10 - Review by N. Kalesch
Votes: 170 votes
Total customer reviews: 170