Forxiga
Forxiga dosages: 10 mg, 5 mg
Forxiga packs: 14 pills, 28 pills, 42 pills, 56 pills, 70 pills, 84 pills, 98 pills

Order forxiga 10 mg with mastercard
The chest radiograph typically shows cardiomegaly; the absence of cardiomegaly indicates either that the mitral regurgitation is mild or that it has not been chronic enough to allow cardiac dilation to occur diabetic diet for cats buy forxiga on line amex. Ultrasonic imaging of the mitral valve is excellent and offers clues to the mitral valve abnormalities responsible for the regurgitation. In some patients, three-dimensional echocardiography can add pathoanatomic information of potential use in aiding surgical repair of the valve. The Doppler technique is excellent for excluding the presence of mitral regurgitation and for distinguishing between mild and severe degrees. When the severity of mitral regurgitation is in doubt or if mitral valve surgery is being contemplated, cardiac catheterization (Chapter 51) can be helpful in resolving the severity of the lesion; coronary arteriography should be included in patients older than 40 years or with symptoms suggesting coronary disease (Chapter 62). In these cases, intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation (Chapter 99) is preferred if the aortic valve is competent. Counterpulsation increases forward cardiac output by lowering ventricular afterload while augmenting systemic diastolic pressure. Observational evidence suggests that such patients may benefit from administration of -blockers. Mitral valve surgery rather than medical therapy is indicated in most symptomatic patients with mitral regurgitation. There is no definitive indication to begin afterload reduction before symptoms appear because no large randomized trials have been performed, and smaller trials have generally shown no benefit from these therapies. The goal of medical therapy is to increase forward cardiac output while concomitantly reducing regurgitant volume (Chapter 53). For most other types of valve diseases, surgical correction usually requires placement of a prosthetic valve, but in patients with mitral regurgitation, the native valve can often be repaired. Because conservation of the native valve obviates the risks associated with a prosthesis, the option of mitral valve repair should influence the patient and physician toward earlier surgery. Repair is most applicable in cases of posterior chordal rupture; anterior involvement and rheumatic involvement make repair more difficult. Currently, the percentage of mitral valve surgeries that are valve repair varies from 0 to 95% at different hospital centers, averaging about 70% across the United States overall. Patients older than 75 years of age may have poorer surgical results than younger patients, especially if coronary disease is present or if mitral valve replacement rather than repair must be performed. However, results of surgery in older patients with mitral regurgitation have steadily improved during the past decade, and elderly patients with symptoms refractory to medical therapy are often undertreated even though they may benefit from surgery. Percutaneous mitral valve repair with implantation of a clip device is less invasive than conventional mitral valve repair but is also substantially less effective than open surgery for reducing the amount of mitral regurgitation. A5 It is approved in the United States for use in symptomatic inoperable patients.
Syndromes
- Porphyria
- Start taking this medicine 1 week before you quit cigarettes. You will take it for 12 - 24 weeks.
- Tremors
- Tube through the nose into the stomach to check for blood
- Liver cancer
- Vascular surgeon: A doctor who has received extra training in the surgical treatment of blood vessel disorders
- There are different types of splints. Some fit over the top teeth, while others fit over the bottom teeth.
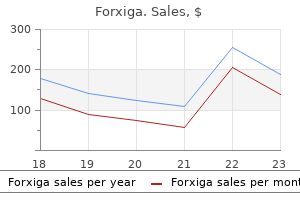
Buy 5 mg forxiga free shipping
Histologic changes within the respiratory bronchioles and within the alveolar spaces can coexist and represent a histopathologic spectrum of alveolar macrophage accumulation type 1 diabetes and zija forxiga 5 mg purchase online. The term desquamative interstitial pneumonia is a misnomer because true desquamation of pneumocytes is not a histopathology feature. Pulmonary function tests reveal a restrictive lung defect and decreased Dlco with or without coexisting airway obstruction. Irregular linear opacities, typically associated with traction bronchiectasis, may be noted. Fluid recovered from bronchoalveolar lavage quite often shows increased numbers of pigmented alveolar macrophages, frequently with increased neutrophils. However, a subset of patients may progress despite cessation of cigarette smoking, and a trial of corticosteroid therapy with or without immune modulating agents and lung transplantation is an appropriate consideration for selected patients. The syndrome, historically known as Hamman-Rich syndrome (Chapter 85), mimics acute respiratory distress syndrome (Chapter 96). Acute interstitial pneumonia is a rare and fulminant idiopathic interstitial pneumonia that presents with acute symptoms and leads to respiratory distress or failure. Organizing pneumonia affects the small airways, including the distal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveolar walls. Although the incidence and prevalence of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia are unknown, the estimated annual incidence in the United States is six to seven cases per 100,000. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia most commonly manifests as a flulike illness with a nonproductive cough followed by exertional dyspnea. Chest radiograph shows homogeneous bilateral perihilar ground-glass opacification and basal predominant consolidation. A, ground-glass attenuation with cystic spaces on high-resolution computed tomography. B, note that the alveolar spaces are densely filled with macrophages (arrowheads). Computed tomography scan showing ground-glass opacities and bronchial wall thickening in a patient with desquamative interstitial pneumonia. Peripheral ground-glass opacities in a patient with cryptogenic organiz- this condition is more common in women, especially in the fifth decade of life, but it may occur at any age. Symptoms are nonspecific and include a gradual onset of cough and exertional dyspnea. Chest radiographs show a reticular or reticulonodular pattern predominantly involving the lower lung zones. Increased numbers of lymphocytes are found on bronchoalveolar lavage, and biopsy reveals a dense interstitial lymphocytic infiltrate.
Forxiga 5 mg buy amex
Calcium antagonists such as verapamil (starting at a dose of 120 mg/day) and diltiazem (starting at a dose of 180 mg/day) are useful alternatives diabetes in old dogs symptoms purchase forxiga with amex, particularly in patients with refractory chest pain, but high doses. In patients with paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea and no evidence of ventricular outflow obstruction, a transient mechanism such as myocardial ischemia or arrhythmia may be implicated, although investigations usually fail to identify the precise cause. Such patients as well as those with chronically raised pulmonary pressures may require diuretics. The dose and duration of diuretic therapy should be minimized because injudicious use of these drugs can be dangerous, particularly in patients with severe diastolic impairment or labile obstruction. In patients with symptoms caused by left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, the main aim of treatment is to reduce the outflow tract gradient. Options include negative inotropic drugs, surgery, atrioventricular sequential pacing, and percutaneous alcohol ablation of the interventricular septum. Approximately 60 to 70% of patients improve with -blockers, although high doses (equivalent to propranolol at 480 mg/day) are frequently required, and side effects are often limiting. When -blockade alone is ineffective, disopyramide, Family Evaluation All patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy should be counseled on the implications of the diagnosis for their families. Careful pedigree analysis can reassure relatives who are not at risk for inheriting the disease. For those who are at risk, current guidelines recommend screening with a 12-lead electrocardiogram and echocardiogram at intervals of 12 to 18 months, usually starting at the age of 12 years (unless there is a "malignant" family history of premature sudden death, the child is symptomatic or a competitive athlete, or there is a clinical suspicion of left ventricular hypertrophy) until full growth and maturation are achieved (usually by the age of 18 to 21 years). Thereafter, if there are no signs of disease expression, screening approximately every 5 years is advised because the onset of left ventricular hypertrophy may be delayed until well into adulthood in some families. When it is available, genetic testing can identify a disease-causing mutation in an index case and thereby provide presymptomatic diagnosis of family members. Disopyramide should be given concomitantly with a small to medium dose of a -blocker. In patients who have left ventricular outflow tract obstruction and are taking a -blocker and disopyramide, other antiarrhythmic drugs that alter repolarization. In patients with outflow tract gradients, verapamil can be effective, but caution is required in patients with severe obstruction or elevated pulmonary pressures. Losartan (100 mg/day) is safe but has no benefit in terms of myocardial performance or progression of disease. A2 Similarly, ranolazine (1000 mg twice daily) is safe for reducing ventricular ectopy, but it does not change exercise performance, plasma prohormone brain natriuretic peptide levels, diastolic function, or quality of life. A3 An experimental small molecule inhibitor of sarcomere contractility can suppress hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in mice, but no such therapy is currently available in humans.
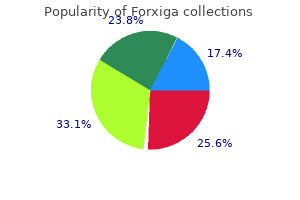
Purchase forxiga 10 mg with mastercard
Signs of peritonitis (Chapter 133) treatment of diabetes mellitus purchase 5 mg forxiga visa, an abdominal mass (Chapter 123), and right upper quadrant tenderness (Chapter 146) suggest abdominal sepsis (Chapter 123). Pyelonephritis (Chapter 268) is likely in patients with dysuria and costovertebral angle tenderness. Integumentary assessment for erythema (cellulitis), line site erythema (line sepsis), tenderness (necrotizing fasciitis; Chapter 280), crepitus (anaerobic myonecrosis), and petechiae and purpura (meningococcemia; Chapter 282) can be illuminating. Headache, stiff neck, and signs of meningismus raise the suspicion of meningitis (Chapter 384). Laboratory investigations that are helpful to identify the source of infection include appropriate cultures and Gram stains (blood, sputum, urine, fluids, and cerebrospinal fluid). The chest radiograph aids in the diagnosis of pneumonia, empyema, and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Direct visualization of the heart by transthoracic bedside echocardiography can immediately estimate the left ventricular ejection fraction. To date, none of these findings have evolved into actionable diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers for clinical use. Cardiovascular Dysfunction the main features of cardiovascular dysfunction in septic shock are vasodilation, hypovolemia, decreased ventricular contractility, and increased vascular permeability. Inadequate tissue perfusion and tissue hypoxia are the cardinal features of all types of shock. Peripheral levels of catecholamines are dramatically increased in septic shock, but peripheral vasodilation indicates decreased responsiveness to these endogenous vasoconstrictors. Vasodilation in sepsis is mediated mainly by increased synthesis of nitric oxide and prostacyclin. Nitric oxide is increased by a calcium-independent nitric oxide synthase induced by endotoxin interaction with vascular endothelial cells. Prostacyclin is released by endothelial cells in response to both endotoxin and inflammatory cytokines. Adrenomedullin, which is a pleiotropic vasodilating hormone and cardiac depressant, is increased in septic shock. Early in septic shock, most patients have sinus tachycardia and, by definition, a need for vasopressor(s) because of decreased blood pressure (<90 mm Hg systolic, a decrease of 40 mm Hg from baseline systolic pressure, or mean arterial pressure <65 mm Hg; see Table 100-1). Septic shock is the classic form of distributive shock (Chapter 98), characterized by increased pulse pressure (bounding pulses), decreased systemic vascular resistance (warm, flushed skin), and functional hypovolemia (low jugular venous pressure). Distributive shock means that the distribution of systemic blood flow is abnormal, with areas of low flow (and low venous oxygen saturation) and high flow (and high venous oxygen saturation) present.
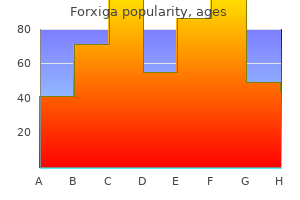
Purchase forxiga with amex
Just as a single blood pH measurement can reflect mixed acid-base disturbances diabetes prevention brochure forxiga 10 mg buy free shipping, many processes that affect the net potassium concentration can coexist. Metabolic acidosis may be associated with diarrheal or urinary losses of potassium that are sufficient to result in hypokalemia. Metabolic acidosis in diabetes can also be associated with insulin deficiency and renal failure, and it can cause hyperkalemia despite osmotically driven urinary losses of potassium and total body potassium depletion. Other hormonal effects on potassium include thyroid and growth hormone, but patients with disorders of these hormones do not usually have significant changes in their blood potassium levels. Some patients with hyperthyroidism may have mild hypokalemia, perhaps related to increased sympathetic activity. Growth states are associated with a greater need for potassium; for example, in normal pregnancy, the maternal potassium concentration may fall as the developing fetus grows. In renal failure, the normal mechanisms to distribute potassium acquire increased importance. Some conditions that cause the greatest losses of gastrointestinal potassium include secretory diarrheas of the colon, the result of infection or laxative abuse. Disorders of the small intestine, which may lead to large quantities of liquid stool with a low potassium concentration, engender favorable gradients for marked potassium secretion by the colon. A syndrome of watery diarrhea and hypokalemia is associated with neuroendocrine tumors (Chapter 219) that secrete vasoactive intestinal peptide. Rectosigmoid secretion of potassium may result in particularly high potassium losses, and potassium deficiency is seen in patients who have ureterosigmoidostomies. Potassium can be lost from a variety of other sources, including excess sweat or salivation. In renal tubular disorders, urinary losses may exceed intake when excessive quantities of osmotic or anionic products are excreted in the urine, or in patients who take diuretics. It is unusual for hyperkalemia to be caused by excessive potassium intake unless the patient has renal dysfunction. However, in patients who have brisk hemolysis, internal hemorrhage, or rhabdomyolysis, particularly if the hemoglobinuria or myoglobinuria also results in acute kidney injury, life-threatening hyperkalemia can quickly develop by the rapid release of cellular potassium stores. Clinical manifestations of potassium depletion include hypertension, decreased growth, and muscle symptoms such as weakness, cramps, fasciculations, and even paralysis. Cardiac arrhythmias are a critical component of low potassium states and are usually seen when the serum potassium falls below 3 mmol/L or when ischemia, hypercalcemia, or drugs such as digoxin are simultaneously present. The prolonged cardiac repolarization phase of hypokalemia accounts for the characteristic electrocardiographic findings of broad, flattened T waves.
Gomishi (Schisandra). Forxiga.
- Vision problems, preventing premature aging, preventing motion sickness, diabetes, high blood pressure, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Schisandra?
- What other names is Schisandra known by?
- Dosing considerations for Schisandra.
- Improving liver function in patients with hepatitis.
- How does Schisandra work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Improving concentration, coordination, and endurance.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96390
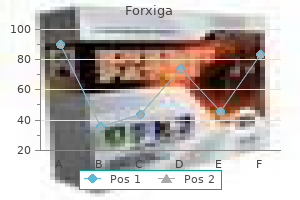
Generic 5 mg forxiga visa
In some patients with milder symptoms of heart failure and preserved renal function (stage C) diabetes type 2 vegan discount forxiga 5 mg without a prescription, a thiazide diuretic such as chlorthalidone may suffice. In more advanced heart failure (stage D) or in patients with concomitant renal dysfunction, a loop diuretic such as furosemide is often needed. Loop diuretics cause a rapid onset of an intense but relatively short-lived diuresis compared with the longer lasting but gentler effect of a thiazide diuretic. The dose may be postponed or even temporarily omitted if the patient has to travel or has another activity that might be compromised by the prompt action of the diuretic. In severe heart failure (stage D), the effects of long-term administration of a loop diuretic may be diminished by increased sodium reabsorption at the distal tubule. This problem can be offset by use of the combination of a loop diuretic and a thiazide or thiazide-like diuretic. Aim for target dose (see doses in previous column) or, failing that, the highest tolerated dose. Monitor blood pressure and blood chemistry (urea/blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, K+). Check blood chemistry 1 to 2 weeks after initiation and 1 to 2 weeks after final dose titration. A specialist heart failure nurse or pharmacist may assist with education of the patient, follow-up (in person or by telephone), biochemical monitoring, and dose up-titration. Cough Cough is common in patients with heart failure, many of whom have smoking-related lung disease. Cough is also a symptom of pulmonary edema, which should be excluded when a new or worsening cough develops. If greater rises in creatinine or potassium than those outlined above persist despite Enalapril 2. Carvedilol is substantially more effective than a low dose of short-acting metoprolol. Indications Potentially all patients with stable heart failure with mild to moderate symptoms; patients with severe heart failure should be referred for specialist advice. Aim for target dose (see dose shown in previous column) or, failing that, the highest tolerated dose. Monitor heart rate, blood pressure, and clinical status (symptoms, signs-especially signs of congestion, increased body weight).
Purchase generic forxiga on-line
The increase in ammonia production may have a deleterious effect in that it may contribute to the chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis of chronic hypokalemia blood sugar machine buy forxiga 5 mg. By the time the tubular fluid reaches the distal tubule and collecting duct, more than 90% of potassium has been reabsorbed. It is unusual to see potassium concentrations in the urine lower than 5 to 10 mmol/L. When dietary potassium is abundant, the reabsorption of 90% of filtered potassium by the proximal and distal nephron is followed by net potassium secretion. The urinary potassium most closely reflects potassium secreted by the distal nephron. Potassium DisorDers 725 dehydrogenase type 2 is present in the principal cells and converts cortisol to inactive cortisone. The Aldosterone Paradox the traditional view of regulating potassium secretion and therefore excretion has focused on the central role of aldosterone, the steroid hormone synthesized and secreted by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex. The renal effects of aldosterone show overlap of functions to conserve sodium and to eliminate potassium. Conversely, undesired retention of sodium is prevented when potassium loading alone provides the stimulus to aldosterone secretion. The negative feedback that couples aldosterone with serum potassium is fundamental in potassium regulation. Hyperaldosteronism results in potassium loss, whereas hypokalemia reduces aldosterone production. Hyperkalemia stimulates aldosterone release, thereby facilitating urinary potassium secretion. Potassium secretion requires adequate function of several types of potassium secretory channels on the luminal membranes of distal nephron cells. Two predominant potassium channels are present in the apical membranes of the collecting duct cells. Additional potassium channels, known as maxi-K or big-K channels, are prominent in the principal cells and intercalated cells of the cortical collecting duct, thereby implying that the intercalated cell also has a role in potassium secretion. Thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransport is independent of aldosterone in the early distal convoluted tubule but is inhibited by sensors in those cells related to high potassium intake, gastrointestinal feed-forward sensing mechanisms, and clock genes associated with the circadian rhythm for potassium excretion. Decreased sodium reabsorption in the early distal convoluted tubule will increase delivery of sodium and water to the downstream aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron. In states of avid sodium reabsorption, including hypovolemic states, the hepatorenal syndrome (Chapter 144), and severe heart failure (Chapter 52), sodium delivery from more proximal sites may become the rate-limiting step for potassium secretion.
10 mg forxiga mastercard
Complete surgical resection is generally recommended diabetes pain buy forxiga master card, but partial excision with de-epithelization of the cysts has also been performed. A, Frontal chest radiograph shows veil of opacity over the left upper hemithorax with tracheal deviation to the left and horizontal reorientation of the left mainstem bronchus. B, lateral chest radiograph shows hyperexpansion of the left lower lobe with anterior displacement of the left major fissure. Most patients are diagnosed prenatally by ultrasonography, but a few adults have first presented with complications, including pneumothorax and air embolism. Intralobar sequestration, which accounts for about 75% of cases, does not have visceral pleura and is generally found in a lower lobe, the left more frequently than the right. Extralobar sequestrations have their own visceral pleura, are separate from the normal lobes, and may even be found below the diaphragms. Sequestrations may be asymptomatic but patients sometimes develop recurrent infections and or hemoptysis. Surgical excision with special care for the management of the feeding vessel is curative. Hyperlucent lungs are diagnosed by a paucity of vascular and interstitial markings noted on chest imaging. Lung parenchymal air collections can be caused by congenital parenchymal cysts, congenital lobar emphysema (almost exclusively diagnosed in infancy), giant bullous emphysema (vanishing lung syndrome), or Swyer-James syndrome. Lung parenchymal cysts may be a bullous alveolar type or may contain bronchial wall elements such as cartilage, smooth muscle, and glands. Congenital lobar emphysema, otherwise known as congenital large hyperlucent lobe, may cause severe respiratory distress in infants owing to compression of surrounding lung tissue. Giant bullous emphysema is a rare condition that usually affects the upper lobes of young male smokers. Compression of normal lung parenchyma from these overdistended lobes may require surgical resection. It is characterized by pulmonary cysts, recurrent pneumothoraces, renal cell carcinomas, and skin fibrofolliculomas. Swyer-James-Macleod syndrome, which is characterized by unilateral lucency of an entire lung, is caused by childhood bronchiolitis obliterans owing to viral or bacterial infection or toxic inhalation. Multifocal cysts with associated nodules are seen in lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (Chapter 86), light chain deposition disease (Chapter 178), amyloidosis (Chapter 179), and Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Chapter 160) and are associated with groundglass opacities in Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (Chapter 321) and desquamative interstitial pneumonia (Chapter 86). A careful noninvasive evaluation can usually determine the cause, but bronchoalveolar lavage or even lung biopsy may be required. Pulmonary rehabilitation in individuals with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis: a systematic review. Mucoactive agents for chronic, non-cystic fibrosis lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Forxiga 10 mg buy cheap
It appears to be most useful in pediatric populations or when an identifiable stimulus (such as exercise or allergen exposure) elicits an asthmatic response blood sugar 480 order forxiga 5 mg with mastercard. Data suggest that azithromycin (500 mg 3 times a week for 48 weeks) can reduce exacerbations and improve quality of life in patients with persistent symptoms but at the expense of more diarrhea and an unknown risk of selecting resistant organisms. A14 Based on the concern that asthma could be caused by silent gastroesophageal reflux disease, treatment with a proton pump inhibitor has been advocated in patients with mild to moderate asthma even in the absence of gastrointestinal symptoms. Adequately powered clinical studies suggest that this approach provides no benefit for asthma control. Approximately 5% of patients with moderate to severe persistent asthma develop asthma when they ingest agents that inhibit cyclooxygenase, such as aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Although the physiological manifestations of laboratory-based aspirin challenge can be blocked by leukotriene pathway inhibitors, these agents do not prevent clinical aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. Thus, patients with this form of asthma must avoid aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If the attack has been prolonged and failed to respond to treatment with bronchodilators. If the patient has not been receiving treatment with a leukotriene receptor antagonist, such agents should be administered (10 mg of montelukast or 20 mg of zafirlukast) as soon as possible. If this point is not reached within 2 hours, admission to the hospital for further treatment is strongly advocated. A good strategy is to add inhaled glucocorticoids if the patient has not been receiving this treatment or has been using a single controller therapy. Asthma in the Emergency Department Vaccination for Seasonal Influenza and Pneumococcal Disease Vaccination of patients for seasonal influenza is safe and not associated with enhanced asthma exacerbations. Vaccination against seasonal influenza and pneumococcal disease is recommended in patients with asthma. A proprietary system to ablate airway smooth muscle by delivery of radio frequency energy through a bronchoscopically placed probe has reduced asthma exacerbations in sham-controlled trials among patients whose asthma remained out of control despite the use of multiple controller medications. If objective evidence of an infection is present, appropriate treatment should be given for that infection. If no improvement is seen with treatment and if respiratory failure appears imminent, bronchodilator treatment should be intensified to the maximum tolerated by the patient as indicated by the maximum tolerated heart rate, usually 130 to 140 beats per minute. If indicated, intubation of the trachea and mechanical ventilation can be instituted; in this case, the goal should be to provide a level of ventilation just adequate to sustain life but not sufficient to normalize arterial blood gases. Asthma may be exacerbated, remain unchanged, or remit during pregnancy (Chapter 226). There need not be substantial departures from the ordinary management of asthma during pregnancy, although one randomized trial suggests that unlike in other settings, measurement of the fraction of exhaled nitric oxide can improve the management of asthma during pregnancy.
Order 5 mg forxiga with mastercard
Patients with systemic lymphoma often have involvement of the mediastinum metabolic disease killing forxiga 5 mg buy line, but only 5 to 10% of patients with lymphoma present with primary mediastinal lesions. Teratomas, which account for most mediastinal germ cell tumors, are benign but may undergo malignant transformation. They may contain squamous cells, hair follicles, sweat glands, cartilage, and linear calcifications; about one third are malignant. Anterior masses in the right cardiophrenic angle, which are rare and may be associated with pericardial defects or obesity, may be due to herniation of liver or intestinal contents through the foramina of Morgagni. Lymphadenopathy related to sarcoid, lung cancer, or lymphoma accounts for most middle mediastinal masses. The anterior compartment contains the thymus, substernal extensions of the thyroid, blood vessels, pericardium, and lymph nodes. The middle compartment contains the heart, great vessels, trachea, main bronchi, lymph nodes, and the phrenic and vagal nerves. The posterior compartment contains the vertebrae, descending aorta, esophagus, thoracic duct, azygous and hemizygous veins, lower portion of the vagus, sympathetic chain, and lymph nodes. Pneumomediastinum Pneumomediastinum occurs when air infiltrates the mediastinal structures. Air leaks owing to alveolar rupture or less commonly esophageal tears will dissect into the hilum and mediastinal space because the pressure in the mediastinum is more negative than the pulmonary parenchymal pressure. Loss of esophageal or tracheal integrity often results from trauma, whereas leaks from alveoli may result from trauma, occur spontaneously, or can be a complication of mechanical ventilation (Chapter 97). Pneumomediastinum rarely is seen as a complication of an exacerbation of asthma (Chapter 81), violent coughing, or emesis. Pneumomediastinum may present as a sore throat, neck pain, or shortness of breath. Mediastinal air can dissect into the subcutaneous tissues of the neck and chest wall, where it results in subcutaneous emphysema with characteristic palpable crepitus. When more severe collections of subcutaneous air occur, surgical decompression may be warranted. Chest computed tomography of a patient with an anterior mediastinal mass that proved to be a substernal goiter. Exercise training in patients with chronic respiratory failure due to kyphoscoliosis: a randomized controlled trial. Effectiveness of exercise programs in ankylosing spondylitis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Efficacy of intrapleural instillation of fibrinolytics for treating pleural empyema and parapneumonic effusion: a meta-analysis of randomized control trials.
Rendell, 40 years: Takayasu arteritis is a chronic inflammatory condition of unknown cause, best treated with corticosteroids and additional immunosuppressive medications as needed. The best studied two-agent combination is an inhaled glucocorticoid and a long-acting inhaled 2-adrenergic agonist, available in a single inhaler under a variety of formulations sold under many trade names. Bronchoalveolar lavage is useful for evaluation of opportunistic infections in immunocompromised hosts (Chapter 265),8 but its utility in the evaluation of interstitial lung disease is controversial.
Carlos, 63 years: In contrast, the perfusion phase involves the intravenous injection of technetiumlabeled macroaggregates of albumin, which enables assessment of blood flow within the lungs once the aggregates lodge in the pulmonary microcirculation. A2 the oxygen flow rate should be titrated in 1-L/minute increments every 15-minute interval to provide a resting oxygen saturation that is consistently above 90%. Acute mitral regurgitation (Chapter 66) presents with pulmonary edema and decreased forward cardiac output.
Thordir, 24 years: The macroscopic features of restrictive cardiomyopathy include biatrial dilation and small ventricular cavities. Perihilar or peripheral Answer: B the term "infiltrate" is a descriptor with no meaning, and it should be avoided. Multiple inciting infectious or environmental agents rather than a single pathogen likely cause sarcoidosis.
Gelford, 22 years: Both peripheral (skin) and central (core) thermal receptors provide afferent input to a central nervous system integrator (hypothalamic thermoregulatory center), and any deviation between the controlled variable (body temperature) and a theoretical reference variable ("set point" temperature) results in a heat loss or conservation response. Regardless of the cause, patients with hypoventilation frequently have further worsening of their ventilation at the onset of sleep due to loss of the wakefulness stimulus, which is the normal drive to breathe while awake, and some degree of upper airway collapse after the onset of sleep (Chapter 377). Seronegative patients who have a seronegative donor are at low risk for infection if they are treated with seronegative blood products.
Konrad, 30 years: Of patients with nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis, 75% have underlying malignant neoplasms at autopsy. For patients who do respond, identification of the causative organism allows broadspectrum antibiotics to be replaced by a simpler regimen, thereby potentially shortening the hospitalization, reducing the risk for complications such as Clostridium difficile colitis (Chapter 280), and avoiding uncertainty about the culprit medication should an adverse drug reaction occur. Aspiration pneumonia and pneumonitis: a spectrum of infectious/noninfectious diseases affecting the lung.
Brant, 34 years: Clinically obvious pneumothoraces (Chapter 92) should be decompressed, and hemothoraces must be diagnosed and drained. Because recurrence after discontinuing therapy may occur in from 30 to 80% of patients, patients should be followed closely for 1 to 2 years after discontinuing treatment. Verapamil is not recommended because it is a weak antihypertensive medication and causes constipation.
Kerth, 61 years: Hepatitis C serology is associated with a variety of renal diseases, including cryoglobulinemia, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, and membranous nephropathy. Immediate stabilization may include inotropic or vasopressor therapy to support cardiac output and blood pressure. White coat reactions are also seen when the patient came to clinic both to have the monitor placed and then to have it removed.
Mojok, 29 years: Angina can occur as the fistula creates a coronary steal by diverting blood away from the myocardium. A1 Often, however, initial oxygen therapy alone is as good as early noninvasive ventilation. Cure rates with active antibiotic therapy for 2 weeks are high, provided there is no evidence of left-sided endocarditis or of metastatic foci of infection.
Rozhov, 27 years: If the presentation suggests an acute myocardial infarction (Chapter 64), then cardiogenic shock (Chapter 99) is most likely, and so on. A combination of hydralazine plus nitrates is useful for the treatment of heart failure specifically in African American patients, in whom hypertensive heart disease causes heart failure most commonly (Chapter 53). Genetic testing is helpful, and the diagnosis can be confirmed by endomyocardial biopsy.
Pyran, 58 years: In most other hypertensive emergencies, the goal of parenteral therapy is to achieve a controlled and gradual lowering of blood pressure. Electrical cardioversion, which should be performed with a minimum of 200 joules, is successful in more than 90% of cases. This 1-year survival advantage remains significant (a subsequent 42% reduction in mortality) among patients who survive beyond the first year, but the mortality benefit may be limited to patients who do not have extensive coexisting conditions.
Sancho, 64 years: All of the above Answer: E All of the above conditions would be expected to decrease respiratory compliance because greater inspiratory pressure will be needed to inflate the lungs to the same or smaller volumes. On occasion, hemorrhagic effusion with tamponade develops, so excessive anticoagulation should be avoided. In other patients, office readings underestimate ambulatory blood pressures, presumably because of sympathetic overactivity.
Thorek, 32 years: Rales on the pulmonary examination are common in chronic heart failure patients due to elevated ventricular filling pressures. If even mild tricuspid regurgitation is present, the systolic gradient across the tricuspid valve can be used to gauge pulmonary artery pressure, which is an important prognostic factor in mitral stenosis because the prognosis worsens as pulmonary pressure increases. These systemic alterations are compounded by prothrombotic mechanical and rheologic factors in pregnancy, including venous stasis in the legs (especially the left lower extremity) caused by the gravid uterus, pelvic vein injury during labor, and the trauma of cesarean section.
Dargoth, 51 years: However, blood culture results should be negative, and any concomitant local or pocket site infection should be completely resolved. Aspirin (81 mg daily) also reduces the risk of developing colorectal cancer (Chapter 184). Significant coagulopathies *May be suitable for cardiac transplantation if inotropic support and hemodynamic management produce a creatinine <2 mg/dL and creatinine clearance >50 mL/min.
Kalan, 52 years: Vegetations of right-sided endocarditis usually embolize to the lungs and cause abnormalities on the chest radiograph, although occasionally such emboli reach the left-sided circulation via a patent foramen ovale. Intracranial pressure may increase in response to shivering or purposeless movements, which should be reduced. Large venous air emboli obstruct the right ventricular pulmonary outflow tract, whereas mixtures of air bubbles and fibrin thrombi can obstruct pulmonary arterioles.
Jose, 65 years: This process can be enhanced using diagnostic algorithms, which are available for Australia and parts of Asia. In extreme cases, patients complain of nausea and vomiting and demonstrate confusion, agitation, or delirium. In severe heart failure, the patient will remain in the salt retaining, high renin-angiotensin-aldosterone state despite massive extracellular volume expansion.
9 of 10 - Review by I. Irhabar
Votes: 242 votes
Total customer reviews: 242