Zyprexa
Zyprexa dosages: 20 mg, 10 mg, 7.5 mg, 5 mg, 2.5 mg
Zyprexa packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Discount zyprexa 7.5 mg with amex
Proximal carpal bone situated between the hamate and lunate bones medicine organizer safe 7.5 mg zyprexa, dorsal to the pisiform bone. Proximal carpal bone residing on the palmar aspect of the triquetrum with which it articulates. Roughened expansions at the distal flexor side of each terminal phalanx for attachment of the tactile pads. Elevation on the palmar side of the trapezium distal to the scaphoid tubercle and radial to the groove for the flexor carpi radialis. Distal carpal bone positioned between the 2nd metacarpal and the scaphoid and between the trapezium and capitate bones. Distal carpal bone located between the 4th and 5th metacarpals, capitate and triquetrum. Hook-shaped process on the palmar aspect of the hamate distal to the pisiform bone. Palmar concavity between the tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium on the radial side, and the hamulus and pisiform bone on the ulnar side. A transverse ligament converts it into a closed canal (carpal tunnel) for the flexor tendons of the fingers. Notch in the lunate surface of the acetabulum facing the obturator foramen and continuous with the acetabular fossa. A flat ridge situated somewhat in the middle of the ala of the ilium between the fields of origin of the gluteus medius and minimus muscles. Bony ridge between the fields of origin of the gluteus medius and maximus muscles. Bony ridge above the acetabulum between the fields of origin of the gluteus minimus and rectus femoris muscles. Surface of the dorsal segment of the ilium facing the sacrum and consisting of the following two parts. Palpable projection on the external lip of the iliac crest about 5 cm behind the anterior iliac spine at the junction of the anterior gluteal line with the iliac crest. Bony ridge on the inner margin of the iliac crest for attachment of the transversus abdominis muscle. The portion of the pubis located anteroinferior the obturator foramen between the symphysis and the suture line with the ischium. Line extending along the arcuate line from the promontory to the upper margin of the symphysis.
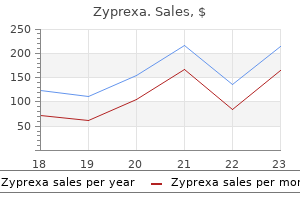
10 mg zyprexa buy with amex
Osteoblasts are responsible for forming new bone and are found in the growing portions of bone medications similar to abilify generic 7.5 mg zyprexa otc, including the periosteum and endosteum. Osteoblasts, which do not divide, synthesize and secrete the collagen matrix and calcium salts. As the secreted matrix surrounding the osteoblast calcifies, the osteoblast become trapped within it; as a result, it changes in structure and becomes an osteocyte, the primary cell of mature bone and the most common type of bone cell. Each osteocyte is located in a space called a lacuna and is surrounded by bone tissue. Osteocytes maintain the mineral concentration of the matrix via the secretion of enzymes. They can communicate with each other and receive nutrients via long cytoplasmic processes that extend through canaliculi (singular = canaliculus), channels within the bone matrix. The dynamic nature of bone means that new tissue is constantly formed, and old, injured, or unnecessary bone is dissolved for repair or for calcium release. They are found on bone surfaces, are multinucleated, and originate from monocytes and macrophages, two types of white blood cells, not from osteogenic cells. Osteoclasts are continually breaking down old bone while osteoblasts are continually forming new bone. The ongoing balance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts is responsible for the constant but subtle reshaping of bone. Spongy Bone the differences between compact and spongy bone are best explored via their histology. Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces, while spongy bone has open spaces and supports shifts in weight distribution. It can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphysis of long bones, where it provides support and protection. The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon, or Haversian system. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae (singular = lamella). Running down the center of each osteon is the central canal which contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels. These vessels and nerves branch off at right angles through a perforating canal to extend to the periosteum and endosteum. Osteocytes are located inside spaces called lacunae (singular = lacuna), found at the borders of adjacent lamellae. As described above, canaliculi connect with the canaliculi of other lacunae and eventually with the central canal. This system allows nutrients to be transported to osteocytes and wastes to be removed from them.
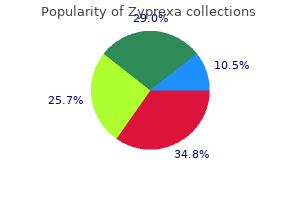
Generic zyprexa 10 mg buy on-line
The hormones released from each lobe are Adenohypophysis the adenohypophysis is served by an elaborate vascular system symptoms 3 days dpo cheap zyprexa express, including the hypothalamohypophyseal portal system, 207 Human Anatomy and Physiology which transports hypothalamic the regulating of cells hormones in the (hypophyseotropic hormones) to the glandular cells of the adenohypophysis. Some hypophyseotropic hormones influence the secretion of more than one adenohypophyseal hormone. In addition to growth hormone, the thyroid hormones, insulin, androgens, and estrogens play important roles in normal human growth and development at various times of the life cycle. However, in cartilage, bone, and other body tissues, the protein anabolic and growth-promoting actions are mediated by insulinlike growth factors (somatomedins). The elevation of plasma levels of free fatty acids resulting from the hydrolysis of triglycerides (stored neutral fats) is potentially ketogenic. Prolactin facilitates the secretion of dopamine in the hypothalamus, thereby regulating its own secretion by a negative feedback mechanism. Actions Prolactin initiates and maintains milk secretion from breasts primed for lactation by other hormones such as estrogens, progesterone, and insulin. It also appears to inhibit the effects of the gonadotropins and may prevent ovulation in lactating women. Actions Follicle-stimulating hormone directly stimulates the sertoli cells in testicular seminiferous tubles, there by promoting spermatogenesis in the male. Elevated plasma levels of free thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) inhibit thyrotropin secretion. Actions Thyroid-stimulating hormone maintains the structural integrity of the thyroid gland and promotes the synthesis and release of thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The enhanced reabsorption of water from the renal tubules results in the production a concentrated urine that is reduced in volume. The early observations that posterior pitutary extracts produce a marked elevation of arterial blood pressure led to the initial naming of this hormone as vasopressin. Oxytocin Control of Secretion and Actions the two major physiologic actions of oxytocin are exerted on the female breast and uterus. Oxytocin binds to a G-protein coupled receptor that ultimately brings about elevated intracellular calcium levels. The ejection of milk from a primed, lactating mammary gland follows a neuroendocrine reflex in which oxytocin serves as the efferent limb. The reflex is normally initiated by sucking, which stimulates cutaneous receptors in the areola of the breast. Afferent nerve impulses travel to the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus to effect the release of oxytocin from the neurohypophysis.
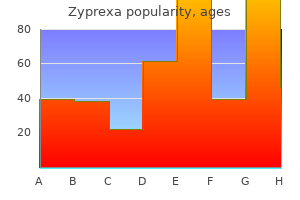
Discount 5 mg zyprexa with mastercard
Abdominal muscles are contracted to increase intra-abdominal pressure during forced expiration symptoms 8dpiui purchase zyprexa 2.5 mg fast delivery, micturition, defecation, and parturition. The superior and inferior epigastric veins run alongside their arterial counterparts. Interestingly, the paraumbilical veins drain to the portal vein via the falciform ligament. Superficially, the anterior abdominal wall superior to the umbilicus drains to anterior axillary nodes. The deep lymphatic drainage of the anterior abdominal wall follows the deep arteries. The inguinal region (groin) is the area where the anterior abdominal wall and thighs meet. During development, the initial position of the testes/ovaries is high in the posterior abdominal wall. The processus vaginalis continues to push outward through several layers: transversalis fascia, internal oblique musculature, and the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. As the processus vaginalis continues to push through the abdominal wall, the inguinal canal is formed. The layer of transversalis fascia becomes the deepest layer, while the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle remains the most superficial layer. The gubernaculum (directly posterior to the processus vaginalis) pulls the testes through the inguinal canal and into the scrotum, while ovaries remain in the pelvic cavity. As the testes move through the inguinal canal, their complement of vessels, nerves, and ducts acquire the same complement of layers as the inguinal canal. In females, the remnant of the gubernaculum (round ligament of the uterus) remains in the inguinal canal. Descent of the gonads is complete upon the obliteration of the processus vaginalis. If it remains patent, a weakening of the abdominal wall can occur, possibly resulting in a hernia. The canal is a tube formed during gonad development which spans the region between the deep and superficial inguinal rings. As previously described, this ring of the inguinal canal results from an evagination of the transversalis fascia, a contributor to the formation of the internal spermatic fascia in males. The superficial ring of the inguinal canal is found at the lower end of the canal. The lateral and medial crura (attaching to the pubic symphysis and pelvic tubercle, respectively) form the sides of the arch. These tendinous crura are joined at the apex of the arch by the intercrural fibers. In males it also contains the spermatic cord, whereas in females it contains the round ligament of the uterus.
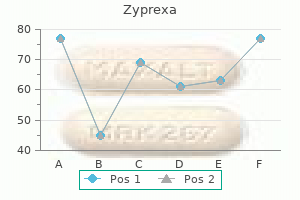
Buy zyprexa 5 mg with mastercard
Treatment Most patients medications you can take when pregnant buy 2.5 mg zyprexa with amex, regardless of the cause, respond to a general programme that includes analgesia, education, back exercises, aerobic conditioning and weight control. Specific treatment is available only for the small number of patients with major neurologic compression or underlying systemic disease. Imaging studies Diagnostic testing is rarely indicated unless symptoms persist beyond 4 weeks, as 90% of patients will have recovered within this time, thus avoiding unnecessary testing. A major problem with all imaging studies is that many of the anatomical abnormalities (often the result of age-related degenerative changes) are common in asymptomatic people. Flexion exercises strengthen the abdominal muscles and extension exercises the paraspinal muscles. Educational booklets that include back exercises and safe lifting techniques are helpful. There is no evidence that spinal manipulative therapy is superior to standard treatment for back pain. Ultrasound, shortwave diathermy, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and other treatments such as lumbar braces, traction, acupuncture and biofeedback are ineffective. Chiropractic focuses on the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of mechanical disorders of the musculoskeletal system, and on the effects of these disorders on the nervous system and on general health. Chiropractors may specialize in low back pain problems, or they may combine chiropractic with manipulation of the extremities, physiotherapy, nutrition or exercise to improve the strength of the spine. A multidisciplinary approach focusing on functional restoration through an intensive rehabilitation programme based on cognitive behavioural therapy is often helpful. The results of back surgery are disappointing when the goal is relief of back pain (such as by spinal fusion or artificial discs) rather than relief of radicular symptoms from neurologic compression. Osteopathy is a manual therapy that is primarily focused on the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions. He concluded that manipulating bones back into place would restore the interrupted flow of nerve impulses and cure disease. Osteopaths will commonly treat back pain by manipulation, but may also use soft, tissue massage or advise exercise. Elective surgery may be considered in a few patients among those who have a significant persistent neurologic deficit or severe sciatica after 6 weeks of conservative care. Surgical treatment, aimed at decompression of the neural elements, is offered to patients with either disabling pseudoclaudication or significant neurologic deficit. There is limited evidence supporting the use of epidural glucocorticoid injections for short-term relief of radicular pain. Nerveroot blocks and injection of anaesthetic agents or glucocorticoid into trigger points, ligaments, sacroiliac joints and facet joints are of unproven efficacy. Unexplained thigh or knee pain should also raise the suspicion of hip abnormality.
Zyprexa 5 mg cheap
Application of the Bobath Concept seeks to enable the patient to interact within their environment treatment rosacea buy 20 mg zyprexa, producing an effective, desirable and appropriate response to their surroundings. Motor recovery and control is developed via the successful execution of an intended task within the environment, through the processes of neuroplasticity. Rehabilitation on a stroke unit has been shown to reduce mortality significantly (by approximately 28%) compared to general medical wards (Langhorne et al. Consistent team input, providing expert 24-hour management, and therefore carry-over in an organised stroke unit, is the vital ingredient for better survival, recovery and regaining independence to return home (Langhorne et al. Task-specific training and repetition have demonstrated cortical functional reorganisation (Nelles et al. Studies show training, or rehabilitation, increases cortical representation with subsequent functional recovery, whereas a lack of rehabilitation or training decreases cortical representation and delays recovery (Teasell et al. The relevance and appropriateness of the task makes all the difference to the sensory guidance required and motor patterns that are produced, therefore enhancing motor recovery. For the individual involved in rehabilitation, reaching into the air for an imaginary meaningless object will not produce the same movement patterns, and therefore learning, as reaching to take a tissue from a box or to put an arm in a sleeve. Motor learning theories inform therapists about what makes an effective learning environment and how to design a rehabilitation programme to meet the needs 183 Bobath Concept: Theory and Clinical Practice in Neurological Rehabilitation of the individual. A passive recipient will never be an active learner and will never get the most out of rehabilitation (Bobath 1990). The active learner needs to be engaged, challenged and involved in meaningful task training. Practising an activity of relevance is probably the most effective therapeutic technique available for successful rehabilitation (Trombly & Wu 1999). The early days the patient who has neurological dysfunction enters a period of initial cerebral and/or spinal shock and is unable to integrate the systems control of posture and movement. They will have difficulty in maintaining and sustaining upright posture against the force of gravity and will be unable to create appropriate alignment and activity levels. The presence of hypotonia and weakness automatically gears the neuromuscular system to compensate for lack of postural stability which can lead to fixation. This prevents the recruitment of selective movement to attain functional skills (Edwards 2002). When considering posturing of an individual or body part, this is an active component on which selective movement is based. Factors that influence the recovery of postural control, and therefore function, include support, seating and appropriate alignment and realignment of the patient (Amos et al. The way the patient is handled, transferred and enabled to move within their environment optimises success at all stages of recovery. Therapeutic use of potential environmental constraints such as plinths, pillows, doorframes and walls can assist with spatial, visual and perceptual deficits. As movement performance improves, the environmental supports can gradually be adapted to create greater challenges. As the patient becomes increasingly independent, we need to consider the safety of the patient ensuring that the level of compensatory activity does not compromise their rehabilitation.
20 mg zyprexa otc
The aim of this book is to provide the therapist with an understanding and ability to apply the principles of the contemporary Bobath Concept and to promote and enable greater clinical effectiveness and to optimise the functional outcome for all patients in the area of neurorehabilitation treatment vaginitis cheap zyprexa american express. The primary objective is to improve the quality of life of all the patients we treat. Linzi Meadows is a Clinical Director of the Manchester Neurotherapy Centre and Neurological Teaching Centre and an Advanced Bobath Tutor. Jenny Williams is a Senior Physiotherapist at the Stroke and Head Injury Clinic in Warrington and a Bobath Tutor. Helen Lindfield is Principal Physiotherapist at the Wolfson Rehabilitation Centre, Wimbledon and a Bobath Tutor. Debbie Strang is a Team Lead Physiotherapist at Hairmyers Hospital, Glasgow and a Bobath Tutor. Lynne Fletcher is a Clinical Director of the Manchester Neurotherapy Centre and Neurological Teaching Centre and an Advanced Bobath Tutor. Catherine Cornall is a Physiotherapy Clinical Specialist at the National Rehabilitation Hospital, Dun Laoghaire, Ireland and a Bobath Tutor. Ann Holland is a Clinical Specialist (Physiotherapy) at the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery at Queens Square, London and a Bobath Tutor. Mary Lynch-Ellerington is a Fellow of the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy and a Senior Bobath Instructor. Janice Champion is a Specialist Clinician at Medway Maritime Hospital, Gillingham, Kent and a Bobath Tutor. Christine Barber is the Director of Therapy Services at the Bobath Centre for Children with Cerebral Palsy and Adults with Neurological Disability and a Bobath Tutor. For their contribution to Chapter 3 we thank Ann Holland and Liz Mackay, and for Chapter 7 we thank Lynne Fletcher. For data collection and analysis with Chapter 6 we thank Professor Jon Marsden and Dr Gita Ramdharry. We feel privileged to have had Professor Raymond Tallis write the foreword of this book. Our very special thanks are owed to the patients and their families who have kindly allowed their case histories and aspects of their clinical treatment to form such a major part of this book. The Bobath Concept: Developments and Current Theoretical Underpinning Sue Raine Introduction There are a number of neurological approaches used in the management of the patient following a neurological deficit. The Bobath Concept is one of the most commonly used of these approaches (Davidson & Walters 2000; Lennon 2003), and it offers therapists working in the field of neurological rehabilitation a framework for their clinical interventions (Raine 2006). This chapter will provide the reader with an overview of the Bobath Concept including the founders of the approach and its inception, the theoretical underpinning and its application into clinical practice. The founders and development of the Bobath Concept Karel Bobath was born in Berlin, Germany in 1906, and trained there as a medical doctor, graduating in 1936. Her early training was as a remedial gymnast, where she developed her understanding of normal movement, exercise and relaxation (Schleichkorn 1992).
Kamak, 49 years: Genetics Racial differences in incidence and familial aggregation suggest a common genetic susceptibility factor. When present, the pyramidalis muscle originates from the pubic crest and inserts into linea alba. For example, if you tell a friend that you have a scar "above the wrist" is it located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand By using precise anatomical terminology, including anatomical position, regional terms, directional terms, body planes, and body cavities, we can eliminate ambiguity and increase precision.
Cole, 58 years: Activities vary from requiring strength but little dexterity, such as carrying a heavy case or using a hammer, to those requiring selective grasp and dexterity, such as threading a needle. There is evidence from animal studies that the production of melatonin is regulated by the amount of light in the environment. Notable Muscle Facts Semitendinosus works with semimembranosus, popliteus, and gracilis in medially rotating the tibia (see popliteus).
Mitch, 51 years: Of course, proper cardiac care often involves other classifications of drugs such as anticoagulants, diuretics, pulmonary medications, and others. Gamma irradiation of at least 34 kGy is recommended to substantially reduce the infectivity titer of enveloped and non-enveloped viruses [220]. Exogenous stress (including school pressures, bullying or other forms of abuse, and even parental pressure) is a common accompanying feature, although often unrecognized by the parents.
Mason, 22 years: The rationale for the use of the treadmill is to drive spinal motor programmes through proprioceptive inputs and modulate central pattern-generated activity (Dietz 2003). Unicellular glands composed of columnar cells that secrete mucous are known as:a) Cilia b) Microvilli c) Goblet cell d) Endocrine glands e) Basal cell 2. Ligament extending from the crest of the head of the rib to the intervertebraldisc.
Kaffu, 46 years: With a nerve supply by a branch of the lumbar plexus, this muscle flexes laterally the trunk and fixes/depresses the lowest rib during forced expiration. On the weight-bearing side, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus contract to pull the ilium down, so that the other ilium rises, allowing the other limb to swing through when walking. Using the cross section of compact bone virtual microscope slide, identify osteons, concentric lamellae, interstitial lamellae, osteocytes, lacunae, and canaliculi.
Sancho, 60 years: Anaerobic respiration is ultimately limited by depletion of glucose and a build up of lactic acid within the muscle fibre. This ileal diverticulum is often within 2 feet of the ileocecal junction, but may be as far as 5 ½ feet from the ileocecal junction. Made up of horizontal, cribriform plate, median perpendicular plate, paired lateral masses; contains ethmoidal sinuses, crista galli, superior and middle conchae.
Silas, 59 years: Tibial tuberosity: Find the patella and move directly distal about an inch or an inch and a half. Feedback via spinoreticular neurons and inputs from other regions of the brain appear to be necessary to stabilise the locomotor rhythm (Mackay-Lyons 2002). Embedded within the cartilage matrix are chondrocytes, or cartilage cells, and the space they occupy are called lacunae (singular = lacuna).
Torn, 52 years: The venous return is done by bronchial veins, which drain into the azygos vein on the right side and hemiazygos vein on the left side. In addition to optimising functional reach with appropriate back support (May et al. Motor learning can be divided into three distinct phases (Halsband & Lange 2006): 1.
Agenak, 21 years: Aqueous humor is constantly being formed, drained, and replaced in the anterior cavity. These postural adjustments usually involve a backward and lateral displacement of the centre of pressure towards the swing limb prior to shifting towards the stance limb (Shumway-Cook & Woollacott 2007). Finally, criterion validity is when a new measure correlates with a gold standard measure of the target outcome.
Gnar, 56 years: If the Rh antigen is transfused to an Rh negative person, the production of anti-Rh factor (antibody) is stimulated. It continues along the esophagus as the posterior vagal trunk through the esophageal hiatus into the abdomen. This versatile muscle flexes the leg at the knee and flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates the leg at the hip allowing us complex movement patterns like sitting cross-legged.
Peratur, 55 years: Hypertonicity is a combination of disinhibition (neural changes), plastic reorganisation and mechanical changes (Raine 2007). It is noticeably higher in African American, Asian and Afro-Caribbean populations than in white populations. Another major inward current, carried by Ca2+ and conducted through "slow channels," contributes to the plateau phase (phase 2) of the action potential.
8 of 10 - Review by I. Kulak
Votes: 187 votes
Total customer reviews: 187