Coumadin
Coumadin dosages: 5 mg, 2 mg, 1 mg
Coumadin packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Order coumadin 5 mg visa
Lungs from donation after circulatory death donors: an alternative source to brain-dead donors? Novel approaches to expanding the lung donor pool: donation after cardiac death and ex vivo conditioning arrhythmia consultants greenville sc coumadin 2 mg buy without a prescription. Lung transplantation with donation after cardiac death donors: long-term follow-up in a single center. Liver transplantation from controlled non-heart-beating donors: an increased incidence of biliary complications. Non-HeartBeating Organ Transplantation: Medical and Ethical Issues in Procurement. Health Resources and Services Administration, Department of Health and Human Services. Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations, Health care at the crossroads. United Network for Organ Sharing: Critical Pathway for Donation after Cardiac Death. A position paper by the Ethics Committee, American College of Critical Care Medicine, Society of Critical Care Medicine. Victims of cardiac arrest occurring outside the hospital: a source of transplantable kidneys. Using livers from donation after cardiac death donors-a proposal to protect the true Achilles heel. Time is of the essence: the pressing need for comprehensive non-heart-beating cadaveric donation policies. Time to cardiac death after withdrawal of life-sustaining treatment in potential organ donors. Combined liver and pancreas procurement from a controlled non-heart-beating donor with aberrant hepatic arterial anatomy. Liver transplantation with grafts from controlled donors after cardiac death: a 20-year follow-up at a single center. Extracorporeal support for organ donation after cardiac death effectively expands the donor pool. Hypothermic machine perfusion in human liver transplantation: the first clinical series. Normothermic acellular ex vivo liver perfusion reduces liver and bile duct injury of pig livers retrieved after cardiac death.
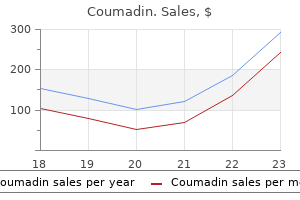
Quality 5 mg coumadin
Glomerular filtration rates using iothalamate are felt to be more accurate and are probably the gold standard today blood pressure medication protocol order generic coumadin on-line. Careful attention must be paid to volume status, which is frequently tenuous in patients with marked ascites on high-dose diuretic therapy. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs should be used only with close follow-up because the subsequent decrease in renal prostaglandin may precipitate acute renal failure. Radiographic imaging studies using intravenous contrast dye also must be approached with caution because of the known risk for renal injury. The use of acetylcysteine together with hydration is the treatment of choice to protect against radiographic contrast mediainduced nephropathy. The cause of renal vasoconstriction is unknown but may predominantly involve both increased vasoconstrictor and decreased vasodilator factors in its pathogenesis. The patients should be monitored in an intensive care unit setting because 12% have ischemic or cardiovascular complications that warrant rapid discontinuation or dose reduction. These manifestations are present in acute as well as chronic liver failure and are potentially reversible. These compounds gain access to the systemic circulation as a result of decreased hepatic function or portosystemic shunts. In fulminant liver failure, elevated arterial levels (>200 mg/dL of ammonia) have been associated with an increased risk for cerebral herniation. An electroencephalogram may be helpful in advanced stages to avoid erroneous diagnosis. Besides these, other causes of acute change in mental status such as intracranial bleeding, mass, drug toxicity, systemic infection, or aberrant electrolytes should be ruled out. Nutritional Management the increased catabolic rate of cirrhosis leads to a recommendation of 1 to 1. This should be done with the assistance of a specialty dietitian, because patients can inadvertently decrease their protein intake to a dangerous level. Zinc, a cofactor of urea cycle enzymes, may be deficient in cirrhotic patients, especially if associated with malnutrition. Zinc supplementation improves 36 Monitoring and Care 487 the activity of the urea cycle in experimental models of cirrhosis. However, patients with zinc deficiency should receive oral zinc supplements because there is enough evidence for treatment and minimal downside. Lactulose increases fecal nitrogen excretion by facilitation of the incorporation of ammonia into bacteria and by a cathartic effect. Lactulose administered orally reaches the cecum, where it is metabolized by the enteric bacteria, causing a fall in pH.
Syndromes
- Hearing loss (common in type I and type III)
- Learning disorders
- Alclometasone dipropionate (Delonal)
- Unsteady walk
- Thyroid gland
- Slow growth in the womb
- Neglecting to eat
- MRI of the spine
Coumadin 5 mg with amex
Dystonic reactions are most common in young men and in patients taking highpotency antipsychotics blood pressure cuff cvs purchase coumadin 5 mg without a prescription. The sudden onset of respiratory distress in a patient on neuroleptics may reflect laryngeal dyskinesia (laryngospasm). Extrapyramidal side effects including tremor, masked facies, and skeletal muscle rigidity may occur, especially in elderly patients. Patients with antipsychotic-induced akathisia often appear restless (inability to tolerate inactivity), which may be confused with the underlying psychotic disorder. Risperidone is an antipsychotic drug that has been associated with exaggerated systemic hypotension during a spinal anesthetic, perhaps reflecting risperidone-induced a blockade. A cardiac antidysrhythmic effect of chlorpromazine may reflect the potent local anesthetic activity of this drug. Indeed, tolerance to the hypotensive effect develops so that after several weeks of therapy, the blood pressure returns toward normal. Nevertheless, some element of orthostatic hypotension may persist for the duration of therapy. Risk factors for the development of this syndrome may include dehydration and intercurrent illness. The syndrome typically develops over 24 to 72 hours in young men and is characterized by (a) h yperthermia; (b) g eneralized hypertonicity of skeletal muscles; (c) i nstability of the autonomic nervous system manifesting as alterations in systemic blood pressure, tachycardia, and cardiac dysrhythmias; and (d) fluctuating levels of consciousness. Extrapyramidal Effects Tardive dyskinesia may occur in 20% of patients who receive antipsychotic drugs for greater than 1 y ear. Only clozapine has not been implicated as a cause of this potentially permanent side effect. Elderly patients and women of all ages seem to be more susceptible to the development of tardive dyskinesia. Manifestations of tardive dyskinesia include abnormal involuntary movements, which may affect the tongue, facial and neck muscles, upper and lower extremities, truncal musculature, and, occasionally, skeletal muscle groups involved in breathing and swallowing. Compensatory increases in the function of dopamine activity in the basal ganglia may be responsible for the development of tardive dyskinesia. Increased skeletal muscle tone may so decrease chest wall expansion that it becomes necessary to provide mechanical support of ventilation. Skeletal muscle rigidity may be severe enough to cause myonecrosis leading to increased creatine phosphokinase levels, myoglobinuria, and renal failure. The cause of neuroleptic malignant syndrome is not known and, as a result, treatment is empirical and includes supportive measures and the administration of the directacting muscle relaxant dantrolene and the dopamine agonists bromocriptine or amantadine.
Order line coumadin
Propranolol and esmolol are eff ctive for controlling the rate of ventricular response in patients with atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter heart attack what to do 5 mg coumadin sale. Multifocal atrial tachycardia may respond to esmolol or metoprolol but is best treated with amiodarone. Acebutolol, propranolol, and metoprolol are approved for prevention of sudden death following myocardial infarction. For example, in contrast to class I antiarrhythmic drugs, propranolol decreases sudden death as well as reinfarction rates in the first year after acute myocardial infarction. As a result, the rate of spontaneous phase 4 depolarization and sinoatrial node discharge is decreased. The rate of Propafenone Propafenone, like flecainide, is an eff ctive oral antiarrhythmic drug for suppression of ventricular and atrial tachyarrhythmias. Propafenone may be proarrhythmic, especially in patients with poor left ventricular function and sustained ventricular tachycardia. Absorption after oral administration is excellent, and peak plasma levels occur in about 3 h ours. In addition to b-adrenergic blockade, these drugs cause alterations in the electrical activity of myocardial cells. This cell membrane effect is probably responsible for some of the antidysrhythmic effects of badrenergic antagonists. Indeed, dextropropranolol, which lacks b-adrenergic antagonist activity, is an eff ctive cardiac antiarrhythmic. The usual oral dose of propranolol for chronic suppression of ventricular arrhythmias is 10 to 80 mg every 6 to 8 h ours. The total daily dose is determined by the physiologic effects of propranolol on the heart rate and systemic blood pressure. Effective b blockade is usually achieved in an otherwise normal person when the resting heart rate is 55 to 60 beats per minute. Administration at 1-minute intervals is intended to minimize the likelihood of excessive pharmacologic effects on the conduction of cardiac impulses. In patients with marginal systemic blood pressure or left ventricular dysfunction, the rate of administration may need to be slowed and the total dose limited to less than 3 mg. The principal metabolite of propranolol is 4-hydroxypropranolol, which possesses weak b-adrenergic antagonist activity. Th s active metabolite most likely contributes to the antiarrhythmic activity after the oral administration of propranolol.
Coumadin 2 mg purchase on-line
It is difficult for these clinical monitors to measure at a true static "no flow" point at end-inspiration and therefore measured compliance changes may be truly due to increased tissue elastance arterial bleeding cheap 5 mg coumadin fast delivery. It is important because, in the perioperative period, complications such as bronchospasm or secretions in an endotracheal tube or partial circuit obstruction will present primarily as increased resistance. Nonelastic resistance is a major component of the work of breathing and because it cannot be stored, it is lost and dissipated as heat. Nonelastic resistance also includes the resistance of lung and chest wall tissue to deformation and compression of intrathoracic gas. Elastic resistance is the recoil of the lung and chest wall, and because it is recovered during expiration, it does not contribute to the work of breathing. Airflow resistance in normal healthy individuals breathing spontaneously is approximately 1 cm H 2O/L per second. Fortunately, it is relatively simple to monitor changes in respiratory resistance in the operating room by following changes in dynamic compliance. Turbulent flow in the larger conducting airways aids clearing of secretions by coughing. This is due to hysteresis of the lung tissue and is present whether the curves are measured dynamically (during a continuous flow) or statically (during interrupted flow). This is primarily due to the combined nonelastic resistance of the airway and circuit. This gas flow resistance cannot easily be monitored during pressure control ventilation, which has only a plateau pressure. Small airway caliber can be decreased by contraction of smooth muscle in the airway wall or by compression (due to reversal of the normal transluminal pressure gradient in the collapsible distal airways). An increase in resistance to inspiration is detected by the muscle spindles in the diaphragm and leads to an increased force of contraction. However, the ensuing increased intrathoracic pressure may decrease venous return and cardiac output. Eventually, a major increase in airway resistance may lead to respiratory muscle fatigue and the Paco 2 will start to rise. An elevated Paco 2 in a patient with increased respiratory resistance who has a normal baseline Paco 2 is an ominous sign of impending respiratory failure. The Equal Pressure Point Expiratory respiratory resistance will normally be lower than inspiratory resistance because the lung is at a larger volume at all stages of expiration than inspiration. However, there are situations when expiratory resistance exceeds inspiratory resistance, these include the following: during a forced expiration (or cough) in a normal patient, during quiet breathing in some patients with severe emphysema (see the following text), and during forced expiration in some patients with an intrathoracic tracheal tumor or tracheobronchial compression from a mediastinal mass. As inspiration begins, (b) intrapleural and alveolar pressure falls by 3 cm H 2O and flow begins.
Coumadin 1 mg purchase online
For this reason, the myotomy may be combined with an antireflux procedure (fundoplication) arrhythmia mayo clinic 1 mg coumadin order overnight delivery. Endoscopic injection of botulinum toxin into the area of the lower esophageal sphincter blocks the excitatory (acetylcholine-releasing) neurons that contribute to lower esophageal sphincter tone. Strong emotional stimulation, such as occurs preoperatively, can increase interdigestive secretion of highly acidic gastric fluid to . The major secretions are hydrochloric acid, pepsinogen, intrinsic factor, and mucus. Mucous secretion protects the gastric mucosa from mechanical and chemical destruction. Substances that disrupt the mucosal barrier and cause gastric irritation include ethanol and drugs that inhibit prostaglandin synthesis (aspirin, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs). At this pH, the hydrogen ion concentration is approximately 3 m illion times that present in the arterial blood. Hydrochloric acid kills bacteria, aids protein digestion, provides the necessary pH for pepsin to start protein digestion, and stimulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice. Secretion of hydrochloric acid depends on stimulation of receptors in the membrane of parietal cells by histamine, acetylcholine (vagal stimulation), and gastrin. Blockade of receptors with specific antagonist drugs produces Stomach the stomach is a specialized organ of the digestive tract that stores and processes food for absorption. The ability to secrete hydrogen ions in the form of hydrochloric acid is a hallmark of gastric function. Gastric Secretions Total daily gastric secretion is approximately 2 L with a pH of 1. Blockade of muscarinic receptors is produced by atropine or the more specific anticholinergic pirenzepine. Pharmacologic manipulation of gastric fluid pH has special implications in the management of patients considered to be at risk for pulmonary aspiration during the perioperative period. Intrinsic factor, which is essential for absorption of vitamin B12 from the ileum, is secreted by parietal cells. For this reason, destruction of parietal cells, as is associated with chronic gastritis, produces achlorhydria and often pernicious anemia. Chief Cells Pepsinogens secreted by chief cells undergo cleavage to pepsins in the presence of hydrochloric acid. G Cells Gastrin is secreted by gastric antral cells (G c ells) into the circulation, which carries this hormone to responsive receptors in parietal cells to stimulate gastric hydrogen ion secretion. Gastrin also increases the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter and relaxes the pylorus. Clinical manifestations of delayed gastric emptying include anorexia, persistent fullness after meals, abdominal pain, and nausea and vomiting.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Epa (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)). Coumadin.
- Treating depression, when used with conventional antidepressants.
- Reducing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems in people with heart disease.
- For wound healing, when used with RNA and L-arginine following surgery.
- Reducing growths in the uterus.
- Treating symptoms of cystic fibrosis.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96955
Generic coumadin 5 mg buy online
Symptoms of zinc deficiency include disturbances in taste and smell, suboptimal growth in children, hepatosplenomegaly, alopecia, cutaneous rashes, glossitis, and stomatitis blood pressure monitor reviews buy coumadin from india. Chromium Chromium is important in a cofactor complex with insulin and thus is involved in normal glucose utilization. Deficiency has been accompanied by a diabetes-like syndrome, peripheral neuropathy, and encephalopathy. Deficiency of selenium has been associated with cardiomyopathy, suggesting the need to add this trace element to supplements administered during prolonged hyperalimentation. Manganese Manganese is concentrated in mitochondria, especially in the liver, pancreas, kidneys, and pituitary. Deficiency is unknown clinically, but supplementation is recommended during prolonged hyperalimentation. It is believed to be essential for the formation of connective tissues, hematopoiesis, and function of the central nervous system. It is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is present in bones, liver, and kidneys. Deficiency is rare, whereas excessive ingestion has been associated with a gout-like syndrome. Rapid saline infusion produces hyperchloremic acidosis in patients undergoing gynecologic surgery. Zinc Zinc is an enzymatic cofactor essential for cell growth and the synthesis of nucleic acid, carbohydrates, and proteins. Diets in which protein is obtained primarily from vegetable sources may not supply adequate zinc. Alternative magnesium sulphate regimens for women with pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. Intravenous magnesium for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Part 1: executive summary: 2010 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations. Correlation among ionized calcium, citrate, and total calcium levels during hepatic transplantation. Serum potassium level and risk of postoperative atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Hypophosphataemia: pathophysiology, effects, and management on the intensive care unit. Bariatric surgery versus nonsurgical treatment for obesity: a s ystematic review and metaanalysis of randomised controlled trials. The pharmacokinetics and tolerability of an intravenous infusion of the new hydroxyethyl starch 130/0. Assessment of volume responsiveness during mechanical ventilation: recent advances. Predicting volume responsiveness by using the end-expiratory occlusion in mechanically ventilated intensive care unit patients.

Coumadin 2 mg overnight delivery
To meet the demand for organs and to address cultural reasons for the lack of a deceased donor organ supply blood pressure elevated 1 mg coumadin buy amex, living donor procedures are increasing. The number of living donors providing right or left lobes of their livers for adult or pediatric patients may complicate the logistics of the procedures because two anesthesia teams need to be available at the same time. This scenario requires significant preparation and resources by the perioperative team. There may be alterations in physiological and pharmacological responses, a severe coagulopathy, encephalopathy, cardiomyopathy, respiratory failure, massive abdominal ascites and pleural effusions, renal dysfunction, and severely deranged serum electrolyte levels, together with an emergent situation. The patient may have been admitted from home, having been evaluated months before the time the donor organ becomes available. The clinical status may have changed significantly from the time of initial evaluation until admission to hospital for the liver transplantation. Consequently, a careful preoperative assessment is necessary in the often short time available before transplantation. Significant portopulmonary hypertension (see Chapter 39) may have developed in the months spent waiting for the availability of an organ. The pathophysiological processes of end-stage liver disease may affect all major organ systems, and therefore the anesthetic management must include measures for the optimal protection of all these organs, as well as the liver. Occasionally a patient may present with a hepatocellular carcinoma and still have good synthetic liver function. The metabolic function of the liver includes the processing of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and other substances, including drugs. The end pathway for most carbohydrates is the conversion of glucose to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate, carbon dioxide, and water. The liver also plays a critical role in protein metabolism, including amino acid deamination and formation of urea and plasma proteins. Combining two molecules of ammonia with carbon dioxide forms urea, and this can readily pass out of the liver and be excreted by the kidneys. Failure of this process will cause an accumulation of ammonia in the body and resultant ill effects. The plasma proteins produced by the liver include albumin and many of the coagulation factors. The hepatocytes also secrete bile salts, cholesterol, and conjugated bilirubin that are excreted into the intestinal lumen and are essential for the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. Liver Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a serious and progressive pathological disease that eventually results in hepatic failure. It usually is the result of chronic viral disease or chronic alcoholic disease, although now because of the epidemic of morbid obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is becoming more prevalent. Pathophysiology of Liver Disease A good understanding of the pathophysiology of endstage liver disease is required to be able to develop an optimal care plan for the patient undergoing transplantation Table 46-2). The pathological condition of the liver will depend on the diagnosis and indication for liver transplantation. Genetic causes may affect more than just one major organ; an example is amyloidosis, with which significant cardiac amyloidosis may also occur.

Cheap coumadin 1 mg otc
This may be remedied by either downsizing the liver by resection of a lobe or creating a silo on the abdominal wall so that a temporary closure can be made prehypertension and viagra discount coumadin 2 mg with visa. The most common complication after transplantation in the pediatric patient is hepatic artery thrombosis. If the operation has been uneventful and the graft is functioning well, routine monitoring of vital signs, fluid balance, coagulation, and liver function is all that is required. Patients are ventilated until they fully recover from anesthesia and are then extubated. The hepatic artery is studied by Doppler ultrasonography to ensure that it has remained patent. If no flow is detected, the patient undergoes emergent reexploration, and the hepatic artery is reconstructed. This early intervention can salvage the graft and prevent the need for retransplantation. The introduction of calcineurin inhibitors for immunosuppression, although improving the survival of liver grafts, has increased the incidence of kidney dysfunction. Sepsis and retransplantation are major risk factors for the development of adult respiratory distress syndrome. Postoperative hemorrhage may be the result of surgical bleeding or a coagulopathy. Early intervention is warranted so that large blood clots or collections do not accumulate and result in ongoing coagulopathy or as a nidus for infection or fibrinolysis. Hypertension is seen in more than 50% of posttransplantation patients and requires treatment. The risk for a cerebrovascular accident is increased in the early postoperative period because some degree of bleeding tendency exists. Living Donor Liver Transplantation Living donor liver donation is the major source of organs for recipients in Asia. The anesthetic management of the donor has a focus on minimizing risk to the donor and providing an optimal graft for the recipient. A low central venous pressure of less than 5 cm H2O will reduce blood loss but must be carefully balanced with maintaining good hemodynamics. Good postoperative analgesia may be obtained by using multimodal anesthesia or epidural techniques. Pearls and Pitfalls · · · · · · · · · · Treat the patient, not the laboratory data. Liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, and hepatic neoplasms. Designated liver transplant anesthesia team reduces blood transfusion, need for mechanical ventilation, and duration of intensive care. Mechanics of the excessive sedative response of cirrhosis to benzodiazepines: model experiments with triazolam.
2 mg coumadin order otc
Outcome of post liver transplant ischemic and nonischemic biliary stenoses treated with percutaneous interventions: the bologna experience blood pressure jumps from high to low coumadin 1 mg low price. Hilar biliary strictures after liver transplantation: cholangiography and percutaneous treatment. Fully covered metallic stents in biliary stenosis after orthotopic liver transplantation. Managing the post liver transplantation anastomotic biliary stricture: multiple plastic versus metal stents: a systematic review. Hemobilia complicating transhepatic catheter drainage in liver transplant recipients: management with selective embolization. For practical purposes the score is capped at 40, a point at which patients have virtual 100% mortality in 3 months. As with all cirrhotic patients, assessment of subclinical portosystemic encephalopathy, ascites, and peripheral edema are mandatory. If patients have been prescribed -blockers, blood pressure and pulse measurements should be performed with the goal of adjusting medications optimally. Vento et al16 reported that fulminant hepatitis is associated with hepatitis A superinfection in chronic hepatitis C patients and recommended that these patients should be immunized for hepatitis A. Recent publications show that hepatitis A and B vaccination rates in adult patients with chronic liver diseases remain low. The response rate to these vaccines is also decreased among patients with decompensated cirrhosis. In addition to hepatitis A and B vaccination, these patients should also receive influenza vaccine yearly and pneumococcal vaccination (0. The introduction of interferon- release assays may improve the detection of latent tuberculosis in patients with more advanced liver disease. A comprehensive ear, nose, and throat evaluation should be done in alcoholics with history of tobacco use because of their increased nasopharyngeal cancer incidence. The viral suppression was also associated with a 23% drop in alanine aminotransferase levels. This is a promising study that will have to be expanded to be able to reach more definitive conclusions. Entecavir and tenofovir are the preferred drugs in this setting because of high intrinsic barriers to resistance. Screening of first-degree relatives with iron studies and hemochromatosis mutation analysis is recommended for early diagnosis and prevention of complications. Calcium (1000 to 1500 mg/day) and vitamin D (1000 International Units/day) supplementation should be considered for postmenopausal women and anyone with osteopenia, and vitamin D levels should be checked annually. Bisphosphonate therapy is recommended for patients with osteoporosis; patients with advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis should first have upper endoscopy to exclude esophageal varices.
Vibald, 53 years: Effect of mean arterial pressure, haemoglobin and blood transfusion during cardiopulmonary bypass on postoperative acute kidney injury.
Finley, 41 years: Death from traumatic injury is the third leading cause of death overall in the United States and the primary cause of death in individuals younger than the age of 45 years.
Marlo, 45 years: Efficacy, dose-response, and adverse effects of droperidol for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting.
Hauke, 34 years: Determination of the plasma concentration of aminoglycosides is an essential guide to the safe administration of these antimicrobials in the setting of renal dysfunction.
Julio, 31 years: Cerebellar symptoms correlate with phenytoin blood levels of greater than 18 mg/mL.
Mufassa, 65 years: Like lomitapide, mipomersen frequently causes elevations in liver enzymes as well as steatosis.
Boss, 64 years: However, a more severe and even life-threatening syndrome develops 650 Part V � Blood and Hemostasis in 0.
Amul, 33 years: Accuracy and utility of 3-dimensional computed tomography in evaluating donors for adult living related liver transplantation.
Aldo, 38 years: It is my preference to clamp the thoracic rather than supraceliac aorta during superrapid procurement.
Dimitar, 59 years: Common causes of loss of vasomotor tone and subsequent neurogenic shock are traumatic transection of the spinal cord and acute blockade of the peripheral sympathetic nervous system by spinal or epidural anesthesia.
Bandaro, 44 years: Interpositional donor iliac artery or vein should be used for the venous reconstruction.
Musan, 42 years: At higher heparin concentrations used during cardiac surgery the activated clotting time is used.
8 of 10 - Review by T. Ningal
Votes: 28 votes
Total customer reviews: 28