Cialis Super Active
Cialis Super Active dosages: 20 mg
Cialis Super Active packs: 10 caps, 30 caps, 60 caps, 90 caps, 120 caps, 180 caps, 270 caps, 360 caps

Order 20 mg cialis super active otc
Although it is not fully understood what initiates and perpetuates the atherosclerotic process erectile dysfunction pump hcpcs purchase cialis super active in india, it is generally agreed that atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory process, that endothelial injury plays a critical role in initiating the process, and that circulating lipids are key to perpetuation and evolution of the lesion. Clearly, serum lipid abnormalities promote the development of atherosclerosis, but local factors are necessary for plaque development. All people have some degree of atherosclerosis, yet one individual may die of a myocardial infarct from an occluded coronary artery at the age of 35, whereas another individual may die at the age of 90 with only mild atherosclerosis. In addition, some populations in the world have very little atherosclerosis, but when individuals from these populations move to areas where atherosclerosis is more prevalent, their risk for developing atherosclerosis and its complications increases. The recognition of such environmental and individual variations has led to the identification of risk factors for atherosclerosis. Hyperlipidemia: Increased dietary intake and familial (genetically influenced) elevations of serum lipids are predisposing factors to atherosclerosis. Serum cholesterol values higher than 200 mg/dL are generally considered to confer an increased risk. Serum cholesterol levels represent the total of several forms of fats in the serum, some of which are more strongly associated with the development of atherosclerosis than are others. Lipoproteins, the major carriers of cholesterol in the serum, have been classified on the basis of their density and electrophoretic migration. Familial forms of hyperlipidemia confer a high risk for development of complications of atherosclerosis beginning at a relatively young age (30s and 40s, compared to 50s and 60s in the general population). Hypertension: the higher the blood pressure, the greater the risk for development of atherosclerosis. The reason is not known, but it may be related to trauma to the arterial intima, particularly at sites of turbulent blood flow, such as at bifurcations of arteries. In support of this hypothesis is the observation that when veins, which normally do not develop atherosclerosis, are transplanted to a position where they carry arterial blood-for example, when used as a coronary artery bypass graft-they can develop atherosclerotic lesions very rapidly. Cigarette smoking: the death rate from coronary atherosclerosis in smokers is more than double that of nonsmokers. The pathophysiologic links between diabetes and atherosclerosis are also not well understood, but appear to be related to the direct effect of increased glucose in the blood. However, epidemiologic studies have shown that excess blood glucose alone is not sufficient to drive the development of atherosclerosis: hyperlipidemia appears to be the necessary precondition for atherosclerotic plaque formation, even in diabetics. Obesity: People with obesity and/or high intake of calories, carbohydrates, and saturated lipids have a greater incidence of atherosclerosis. Hyperhomocysteinemia: Homocysteine is an amino acid involved in the conversion of methionine to cysteine.
Best 20 mg cialis super active
Patients must be followed after therapy with frequent cytologic examination of the urine erectile dysfunction 35 year old male discount cialis super active 20 mg line, which detects atypical urothelial cells that are sloughed into the urine. Five-year survival for early-stage urothelial carcinoma is close to 100%, but for muscle-invasive carcinoma, 5-year survival drops to 60%. It has the tendency to grow into the renal vein, and from there can rapidly grow into the inferior vena cava and even fill and occlude the right side of the heart. Renal cell carcinoma can grow in a variety of patterns, some of which have prognostic implications. The first line of treatment of renal cell carcinoma is surgical eradication, either by resection or, if the tumor is small, by ablating it with cryotherapy (cold) or high-frequency radio waves. Embolization of the arteries that supply it to deprive it of its oxygen supply may also be attempted if the tumor is so large that it is not amenable to surgical resection. Only about 500 cases of nephroblastoma are diagnosed in the United States annually, and the prognosis is excellent because the tumor tends to respond very well to chemotherapy. It counts among the top 10 cancers in the United States in terms of both incidence and mortality, and its incidence has been increasing steadily over the past 50 years. Risk factors for renal cell carcinoma are common to many other cancers: smoking, age, and male sex. Some pharmaceutical drugs, chronic kidney disease, dialysis, and family history are also predisposing factors. The renal tissue in this area is entirely destroyed, and the tumor is causing the capsule of the kidney to bulge outward. The cut surface of the neoplasm reveals soft, partially hemorrhagic and partially necrotic tissue. Overall, the 5-year survival is about 75%, but survival varies from more than 90% for small, localized tumors to 10% for tumors that have already metastasized. One, caused by toxic or ischemic insults, is called acute kidney injury, and the other, caused by smoldering diseases that slowly scar the kidneys, is chronic kidney failure. These two forms of kidney injury have different clinical presentations, different etiologies, different consequences and sequelae, and different treatments. When the renal tubular epithelial cells sustain a sudden, severe injury, they are liable to undergo necrosis. Whatever the reason for the injury, the dead renal tubular epithelial cells slough into the proximal or distal tubules, where they accumulate and block the flow of urine. Consequent water retention and electrolyte imbalances can be life threatening even before metabolic toxins rise to dangerous levels. Drugs that enhance the filtering capacity of nondamaged nephrons are given, and in severe cases, patients need dialysis to remove accumulating waste products.
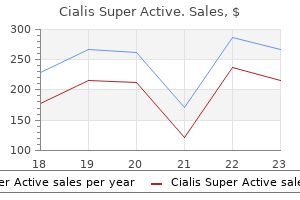
20 mg cialis super active purchase overnight delivery
They rarely develop beyond the first instar in humans and so symptoms are self-limiting erectile dysfunction effects on women purchase 20 mg cialis super active fast delivery, but symptoms are relieved by removing larvae under slit-lamp examination. Other causes of human ophthalmomyiasis include Rhinoestrus purpureum, Dermatobia hominis, Hypoderma spp. Larvae of Hypoderma, Cochlyomyia, and Dermatobia are more dangerous, as they may burrow into the eye, resulting in pain, nausea, and destruction. Hookworm larvae move day by day, producing an itchy or painful tortuous, serpiginous track. Migratory myiasis larvae (Gastrophilus and Hypoderma) also produce dark serpentine tracks, initially without making any aperture, but they are large enough to be visible, move more slowly, migrate less extensively, and can persist for much longer (months) than hookworm larvae (see Chapter 124). Human myiasis caused by the reindeer warble fly, Hypoderma tarandi, case series from Norway, 2011to2016. Anoutbreakofhumanexternal ophthalmomyiasis due to Oestrus ovis in southern Afghanistan. Warrell 138 Some blood-feeding invertebrates infest the skin and hair of human bodies and clothing for long periods. Tropical climate, poverty, and lack of personal hygiene increase the risk of acquiring and harboring ectoparasites from other humans, animals, or the environment. These infestations are irritating, distressing, embarrassing, and anti-social, but it is only during the past century that Westerners have rejected being flea-ridden and lousy. Biting and burrowing are painful, irritating, and may lead to hypersensitivity, secondary local infection, or systemic infectious diseases acquired from the arthropod vectors. Treatment Repeated application of insecticide lotion (pyrethroid, organophosphate, or carbamate) and combing. Body Lice (Pediculus humanus) Body lice infestation is promoted by poor hygiene (unwashed clothes and bodies) and crowding. Such conditions are common accompaniments of disasters, wars, forced immigration, and cold wet seasons. Lice and their eggs may be discovered on skin, body hair, or in clothing, especially in the seams. Flea bites cause small groups of intensely itchy bites, appearing as red macules with a central puncta, often in a line a few centimeters apart, especially on the trunk or buttocks. Fleas may not remain on the body after feeding, but retreat to bedding or crevices and cracks in the bed or room. Examination of underclothing or quickly turning back the sheets may reveal jumping fleas. Pubic (Crab) Lice (Pthirus pubis, Family Phthiridae) Pubic lice cause sexually transmitted infestation of the pubic hair, body hair, eyebrows, and eyelashes, where they provoke itching, scratching, secondary infection, and a curious bluish staining (maculae caeruliae).
Order cialis super active 20 mg line
Monogenetic (single-gene) defects encompass the classic genetic diseases in which a single abnormal gene is responsible for the disease and can be traced through family trees impotence smoking purchase cialis super active. Polygenetic (multiple-gene) or complex gene defects involve more than one abnormal gene and sometimes interaction with environmental factors for their expression. Inheritance patterns of multiple-or complex gene defects are not clear-cut, but there is some tendency for these diseases to occur in families. Chromosomal diseases are defined by microscopically visible structural changes in chromosomes. Chromosomal diseases often result in genetic abnormalities so severe as to preclude reproduction and transmission of the abnormality. Gordana Raca, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health. Genetic and chromosomal diseases may also not manifest until sometime after birth. Familial diseases are diseases in which several family members have the same genetically or chromosomally based disease. Many individuals with genetic diseases do not have a family history of the disease either because it is recessive. In the latter situation, the disease can be classified as both congenital and familial. The abnormality appears in a parent of each involved individual; half the children of a parent with the trait will inherit it. Frequency and Significance of Developmental Abnormalities Approximately 2% of newborns have congenital anomalies. The causes of these anomalies can roughly be estimated as follows: 65% unknown, 20% genetic, 5% chromosomal, and 10% environmental. The overall frequency of genetic diseases is difficult to establish because of the delayed onset of some types and the variable effects of environmental factors on their expression. Monogenetic Diseases Monogenetic diseases are classified according to whether the abnormal gene is located on an autosome or sex chromosome, and whether it is dominant or recessive. Thus, there are four possible modes of inheritance: autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, sex-linked recessive, and sex-linked dominant. Many of the thousands of types of genetic diseases are incompletely penetrant (not all persons with the affected genes will have the disease) and many are variably expressed (not all persons will have the disease to the same severity). Most genetic diseases are uncommon or rare; yet, when taken in aggregate, most families are influenced by some type of multifactorial genetic disease. Huntington disease, a devastating disease causing destruction of neurons in the brain, is an example of an autosomal dominant disease with complete penetrance. Because it is a dominant trait, the offspring of an affected individual have a 50% chance of inheriting the defective gene, and because it is completely penetrant, if they inherit the gene, they will develop manifestations. Unfortunately, manifestations of Huntington disease do not develop until the individual has reached middle age and has most likely already had children, so the gene has already been transmitted to the next generation.
Purchase line cialis super active
The remainder is processed either by (1) compression between glass slides erectile dysfunction how young cialis super active 20 mg order, followed by microscopic examination, and/or (2) digestion in 1% pepsin and 1% hydrochloric acid, 1. International Commission on Trichinellosis: Recommendations on the use of serological tests for the detection of Trichinella infection in animals and humans. Ryan Visceral toxocariasis usually occurs in young children, perhaps reflecting their propensity to ingest larger amounts of dirt (geophagia) or to place their hands in their mouth after contamination with environmental samples or fomites that contain infectious eggs. Clinical manifestations reflect a marked inflammatory response to numerous migrating larvae throughout tissues, especially the liver. Affected individuals may present with red eyes, strabismus, eye pain, photophobia, vision changes, or endophthalmitis. Affected individuals may also present with a field defect when the peripheral orbital area is involved, or significant visual loss if the area of the fovea is involved. Clinically inapparent infections may be incidentally noticed by the unilateral absence of a red reflex on photographic imaging in the affected eye. Adult Toxocara worms eventually reside in the intestine of dogs and cats, and unembryonated eggs are passed into the environment, where over a 2- to 4-week period, the eggs embryonate to contain an infectious larva that can be ingested directly by dogs and cats, or ingested by paratenic hosts such as rabbits that can then be ingested by dogs and cats. Humans represent a dead-end host in which they ingest infectious eggs and Toxocara larvae enter into tissues and cause an inflammatory response. Humans can also become infected by eating undercooked meat (such as rabbit) that contains infectious larvae. After ingestion of embryonated eggs, the egg shell is digested and the larva escapes. Larvae enter into the vascular system and can spread systemically, burrowing into tissues and causing focal hemorrhagic necrosis and secondary inflammation. Toxocariasis antibodies can remain elevated for years, so a fourfold change or a one-time positive result in the appropriate clinical setting is usually required for a presumptive diagnosis of active toxocariasis. Seroprevalence studies suggest a wide range of antibody positivity from 4% to almost 90%; however, a positive serologic test does not necessarily indicate active clinical disease. Children account for the vast majority of individuals diagnosed with active clinical disease. Differential Diagnosis Hepatic capillariasis can present in a similar manner to toxocariasis, with involvement of the liver, hepatomegaly and eosinophilia, and abnormal liver function tests. Treatment of ocular toxocariasis is usually based on limiting the inflammatory response to lessen the likelihood of vision loss and retinal detachment. The benefit of anti-helminthic therapy is controversial due to the theoretical fear of increasing the inflammatory response; however, albendazole has been safely administered with concomitant steroids. Ophthalmic interventions, including laser treatments, scleral buckling, and vitrectomies, may also be required. Incidental noting of a positive antibody in an asymptomatic individual does not warrant treatment. To limit exposure to Toxocara eggs, many playgrounds, daycares, and schools have either removed sandboxes or placed fences and night tarps to limit the likelihood that animals will use the sandboxes for defecation.

Stinking Balm (Pennyroyal). Cialis Super Active.
- How does Pennyroyal work?
- What is Pennyroyal?
- Reducing spasms, intestinal gas, pneumonia, stomach pains, weakness, fluid retention, killing germs, skin diseases, causing abortion (only in amounts that can be fatal to the woman), and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Pennyroyal.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96487
Purchase cialis super active 20 mg on-line
A thrombus converted to granulation tissue or scar tissue is called an organized thrombus erectile dysfunction and heart disease purchase 20 mg cialis super active with amex. There can be a favorable outcome with these "clot busters" if they are administered within approximately 3 hours after the onset of symptoms, or before there is permanent tissue damage. Hemostasis is needed to prevent bleeding, but unregulated coagulation is not otherwise desirable. Several inhibitors of the coagulation mechanism have been identified that protect against the potentially devastating consequences of unchecked coagulation. As already mentioned, the endothelium produces prostacyclin, which is a potent inhibitor of platelet function. Other molecules are activated at the same time as the factors in the coagulation cascade. Many of these antithrombotic molecules are genetically defective in many patients who present with problems relating to sporadic thromboses, such as myocardial infarcts, deep vein thromboses, and repeated pregnancy losses. Most Frequent and Serious Problems Trauma is the most common cause of hemorrhage: everyone experiences bleeding as a result of trauma. Minor traumatic hemorrhages, such as scraped knees or cut fingers, are controlled by the normal hemostatic mechanisms. However, injury to larger vessels may not result in hemostasis rapidly enough to prevent exsanguination. Access to medical facilities, where the lost blood volume can be replaced and excessive bleeding surgically Most Frequent and Serious Problems controlled, is of the essence in such injuries. For example, fatal hemorrhage may occur from a ruptured aortic aneurysm or from a bleeding peptic ulcer. In addition, trauma and surgical operations increase the likelihood of significant hemorrhage in patients with preexisting vascular disease. Spontaneous bleeding may be anticipated when the platelet count drops below 10,000 per microliter or when platelets are defective. As already mentioned in Chapter 9, typical causes of thrombocytopenia (decreased numbers of circulating platelets) include bone marrow failure and peripheral destruction of platelets. Bone marrow failure can be induced by many primary or secondary diseases, including leukemia or metastases to bone marrow. In these cases, megakaryocytes disappear and platelet numbers drop rapidly as circulating platelets are consumed. For example, if the spleen becomes enlarged, it can sequester platelets so that they are not available to circulate in the blood.
20 mg cialis super active order overnight delivery
These are rare and poorly understood autoimmune conditions that cause inflammation of arteries and/or capillaries with subsequent destruction of the arterial walls erectile dysfunction treatment karachi cheap cialis super active 20 mg mastercard, hemorrhage into surrounding tissue, and ischemic damage of the pulmonary parenchyma distal to the site of inflammation. Malignant cells form Neoplastic Diseases Cancer of the lung is the most common cause of cancer death in the United States. Its relation to smoking has already been discussed in the opening section of this chapter. Benign lung neoplasms are rare and even less rarely cause any functional disturbance. They may present as incidentally found lesions on radiography, and be removed out of concern that they harbor cancer. Most lung cancers arise from stem cells in the bronchial epithelium-hence the alternate term bronchogenic carcinoma. For the purposes of treatment and prognostication, cancers are initially classified as small cell and non-small cell carcinoma, of which nonsmall cell carcinoma is more common. This division is useful clinically because, in general, non-small-cell carcinomas are potentially curable by surgery while small cell carcinoma, though it responds initially to chemotherapy, is not curable surgically and has a worse prognosis. There are numerous histologic variants of non-smallcell carcinoma, some of which have a predilection for arising in certain areas of the lung. If not treated, carcinoma extensively invades adjacent tissues, such as the pleura, chest wall, and mediastinal structures. Some symptoms of the cancer can be related to direct extension of the tumor, such as hoarseness from involvement of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Others are related to obstructive symptoms, as the cancer grows into and occludes bronchi: dyspnea, pneumonia, and hemoptysis. Spread to lymph nodes of the hilar region is common, as is hematogenous spread to many organs. Metastasis to the brain and bone is notorious for producing clinical problems, and liver metastasis is pretty much universal in the terminal stages. The diagnosis may be suggested by X-ray but must be confirmed by cytology and/or lung biopsy. As with all cancers, it is preferable to detect the carcinoma while it is still small and confined to the lung, because surgical cure can be achieved. The malignant cells in invasive carcinoma destroy the surrounding parenchyma and cause fibrosis as they grow. By this calculation, a patient who smoked one pack a day for 30 years has the same risk as one who smoked two packs a day for 15 years (in both cases, the patients have a 30 pack year smoking history). Note that exposure to secondhand smoke does not figure in the screening algorithm.
Cheap cialis super active 20 mg visa
A medical relief team is sent to a rural area in China to help after an earthquake left thousands of people homeless erectile dysfunction doctor in los angeles 20 mg cialis super active buy otc. Which of the following diarrheal illnesses should the team take immediate precautions to prevent, by maintaining a clean water supply and sanitation Which of the following correctly describes the distribution of inflammation in ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease In Crohn disease, the inflammation is continuous, while it is patchy in ulcerative colitis. In Crohn disease, the inflammation is limited to the mucosa, while it extends through all layers of the bowel wall in ulcerative colitis. The inflammation always involves the rectum in Crohn disease, while it spares the rectum in ulcerative colitis. Name the hepatitis viruses and compare them in terms of their manifestations and the diseases or complications they cause. Recognize the difference between dose-dependent and idiosyncratic drug reactions, and give examples of each. Describe the patients who are vulnerable to developing fatty liver disease, and describe its complications. Describe the causes, lesions, and manifestations of acute and chronic pancreatitis. List the complications of cirrhosis and relate them to the underlying hepatic dysfunction. Be able to define and use in proper context all the terms in bold print in this chapter. Review the structure and function of the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas, and name some of the major functions of hepatocytes. Describe the most frequent diseases of the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas, and state which are likely to be fatal. List some of the more common symptoms and signs of injury to the liver, gallbladder, or pancreas, and relate these to the underlying abnormality. List some of the common laboratory tests that are used to detect diseases of the liver and pancreas. Describe the role of imaging techniques and liver biopsy in the detection and management of diseases of the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. Describe the etiology, lesions, and manifestations of cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. The excretory product of the liver is bile, which is transported from the liver via hepatic bile ducts. On its way to the duodenum, bile is stored in a reservoir called the gallbladder, which is connected to the bile ducts by the cystic duct and in turn drains to the papilla of Vater via the common bile duct. The excretory product of the pancreas is a fluid rich in enzymes that digest food they come in contact with in the duodenum.
Cole, 46 years: Bitot spots ("X1B") are corneal lesions that represent worsening keratinizing conjunctival metaplasia ("X1A"). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blot testing are suggested to detect the presence of antibodies against A.
Brontobb, 31 years: Falciparum malaria as a cause of fever in adult travellers returning to the United Kingdom: observational study of risk by geographical area. Although the precise cause of clubfoot is not known, there is evidence that a genetic factor is involved.
Fedor, 25 years: This discovery was followed over the next 30 years by a series of observations that demonstrated transmission of protozoa, helminths, viruses, and bacteria by ticks, flies, mosquitoes, fleas, and lice. In addition, the procedure is expensive and therefore not really affordable for people who are uninsured.
Fraser, 24 years: Portions of these cysts are frequently necrotic and mineralized, and the only remains of the metacestode are the hooks and calcareous corpuscles. However, these kits offer microscope-free assessments and can be run without electricity, making them valuable in the field.
9 of 10 - Review by Z. Rathgar
Votes: 161 votes
Total customer reviews: 161